Worksheet Solutions: World Wars | General Knowledge Encyclopedia - Class 8 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Section A: Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs) |

|
| Section B: Short Questions |

|
| Section C: Fill in the Blanks |

|
| Section D: True or False |

|
| Section E: Match the Column |

|
Section A: Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
Q1: Which of the following was the immediate cause of World War I?
(a) The assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand
(b) The sinking of the Titanic
(c) The signing of the Treaty of Versailles
(d) The discovery of nuclear weapons
Ans: (a)
Explanation: The immediate cause of World War I was the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria-Hungary in Sarajevo on June 28, 1914.
Q2: In which year did World War I begin?
(a) 1914
(b) 1916
(c) 1918
(d) 1920
Ans: (a)
Explanation: World War I began in the year 1914 and lasted until 1918.
Q3: Which countries were part of the Allied Powers during World War I?
(a) Germany, Austria-Hungary, and the Ottoman Empire
(b) France, Russia, and Italy
(c) United States, United Kingdom, and Japan
(d) China, India, and Australia
Ans: (c)
Explanation: The Allied Powers in World War I included countries like the United States, United Kingdom, Japan, and other nations fighting against the Central Powers.
Q4: Who was the leader of Germany during World War II?
(a) Winston Churchill
(b) Adolf Hitler
(c) Franklin D. Roosevelt
(d) Joseph Stalin
Ans: (b)
Explanation: Adolf Hitler was the leader of Germany during World War II and the architect of the Holocaust.
Q5: When did World War II end in Europe?
(a) 1943
(b) 1945
(c) 1947
(d) 1949
Ans: (b)
Explanation: World War II ended in Europe on May 8, 1945, with the unconditional surrender of Germany.
Section B: Short Questions
Q1: What were the main causes of World War I?
Ans: The main causes of World War I were militarism, alliances, imperialism, and nationalism. The assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria-Hungary acted as the trigger.
Q2: Explain the significance of the Battle of Stalingrad in World War II.
Ans: The Battle of Stalingrad, fought between the Soviet Union and Nazi Germany, was a turning point in World War II. The Soviet victory in this battle halted the German advance and marked the beginning of their retreat.
Q3: Why did the United States enter World War II?
Ans: The United States entered World War II after the attack on Pearl Harbor by the Japanese on December 7, 1941.
Q4: Describe the impact of World War I on the global economy.
Ans: World War I had a profound impact on the global economy as it caused widespread destruction, loss of lives, and disruptions in trade and production.
Q5: How did the Treaty of Versailles contribute to World War II?
Ans: The Treaty of Versailles, signed in 1919, imposed harsh conditions on Germany, leading to economic hardships and resentment that contributed to the rise of Adolf Hitler and the outbreak of World War II.
Section C: Fill in the Blanks
Q1: World War I began in the year ______.
Ans: 1914
Explanation: World War I started on July 28, 1914, after the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria.
Q2: The leader of Nazi Germany during World War II was ____________.
Ans: Adolf Hitler
Explanation: Adolf Hitler was the dictator of Germany and the leader of the Nazi Party during World War II.
Q3: The treaty that ended World War I was called the _____________.
Ans: Treaty of Versailles
Explanation: The Treaty of Versailles was signed on June 28, 1919, and officially ended World War I.
Q4: The event that triggered the United States to enter World War II was the ____________.
Ans: Attack on Pearl Harbor
Explanation: The Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor on December 7, 1941, led to the United States' entry into World War II.
Q5: The two main sides in World War I were the _____________ and the ____________.
Ans: Allies, Central Powers
Explanation: The Allies (including countries like France, Britain, and Russia) fought against the Central Powers (including Germany, Austria-Hungary, and the Ottoman Empire) in World War I.
Section D: True or False
Q1: World War I began after the assassination of a British monarch.
Ans: False
Explanation: World War I began after the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria, not a British monarch.
Q2: The Treaty of Versailles imposed harsh penalties on Germany, contributing to World War II.
Ans: True
Explanation: The Treaty of Versailles imposed heavy reparations and restrictions on Germany, which contributed to the rise of Adolf Hitler and eventually World War II.
Q3: The Battle of Britain was fought on land between British and German forces.
Ans: False
Explanation: The Battle of Britain was an air battle fought between the Royal Air Force (RAF) of Britain and the German Luftwaffe during World War II.
Q4: The United States remained neutral throughout both World Wars.
Ans: False
Explanation: The United States remained neutral at the beginning of both World Wars but later entered the conflicts, aiding the Allies in World War I and fighting against the Axis powers in World War II.
Q5: The use of tanks was a significant factor in World War I.
Ans: True
Explanation: Tanks were first introduced in World War I and played a crucial role in overcoming trench warfare and revolutionizing land battles.
Section E: Match the Column
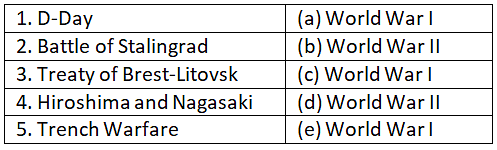
Ans:
|
18 videos|100 docs|13 tests
|

















