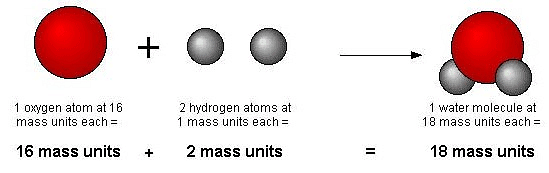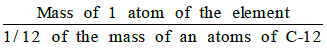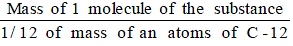Class 9 Exam > Class 9 Notes > Science Class 9 > Basic Concepts: Atoms and Molecules
Basic Concepts: Atoms and Molecules | Science Class 9 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Dalton's Atomic Theory |

|
| Atoms |

|
| Molecules |

|
| Gram Molecular Mass and Formula Mass |

|
Introduction
- The structure of matter has been a subject of speculation from very early times.
- According to Greek philosopher Democritus, if we go on dividing matter into smaller parts, a stage would be reached when particles obtained cannot be divided further. He called these particles 'atoms' meaning indivisible.
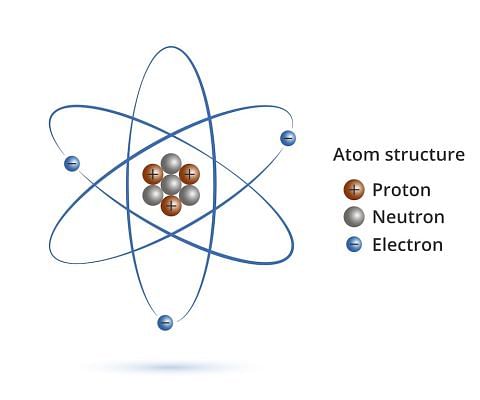 Structure of an Atom
Structure of an Atom
- All matter is made up of small particles called atoms. Different kinds of atoms and molecules have different properties due to which different kinds of matter also show different properties.
Dalton's Atomic Theory
- On the basis of laws of chemical combination, John Dalton proposed the atomic theory in 1808.
 Dalton's Atomic Theory
Dalton's Atomic Theory
Postulates of Dalton's Atomic Theory
- All matter is made up of very tiny particles called atoms.
- Atoms are indivisible particles, which cannot be created or destroyed in a chemical reaction.
- Atoms of a given element are identical in mass size and chemical properties.
- Atoms of different elements have different mass, size, and chemical properties.
- Atoms combine in the ratio of small whole numbers to form compounds.
- The relative number and kinds of atoms are constant in a given compound. Dalton's atomic theory was based on the laws of chemical combination.
- Atoms of the same element can combine in more than one ratio to form more than one compound.
Example: Hydrogen and oxygen combine to give water and hydrogen peroxide. In water, two atoms of hydrogen combine with one atom of oxygen while in hydrogen peroxide, two atoms of hydrogen combine with two atoms of oxygen.
Note:
The postulates of Dalton's atomic theory that "atoms can neither be created nor destroyed", was the result of law of conservation of mass and the postulates of Dalton's atomic theory that "the elements consist of atom having fixed mass", and that the number and kind of atom in a given compound is fixed came from the law of constant proportions.
Drawbacks of Dalton's Atomic Theory
Some of the drawbacks of Dalton's atomic theory of matter are given below:
- According to Dalton's atomic theory, atoms were thought to be indivisible. But it is now known that atoms can be further divided into smaller particles called electrons, protons, and neutrons.
- Dalton's atomic theory said that all the atoms of an element have exactly the same mass. But it is now known that atoms of the same element can have slightly different masses, as in the case of isotopes.
- Dalton's atomic theory said that atoms of different elements have different masses. But it is now known that even atoms of different elements can have the same mass as in the case of isobars.
Atoms
- All the matter is made up of atoms. An atom is the smallest particle of an element that can take part in a chemical reaction.
- Atoms of most of the elements are very reactive and do not exist in the free state (as a single atom). They exist in combination with the atoms of the same elements or another element.
- Atoms are very small in size. The size of an atom is indicated by its radius which is called atomic radius (radius of an atom).
- Atomic radius is measured in nanometer (nm).
(1 meter = 109 nanometers or 1 nm = 10-9 m). - Hydrogen atoms are the smallest atom of all, having an atomic radius of 0.037 nm. Atoms are so small that we cannot see them under the most powerful optical microscope.
Question for Basic Concepts: Atoms and MoleculesTry yourself:Which of the following statements is not true about an atom?
View Solution
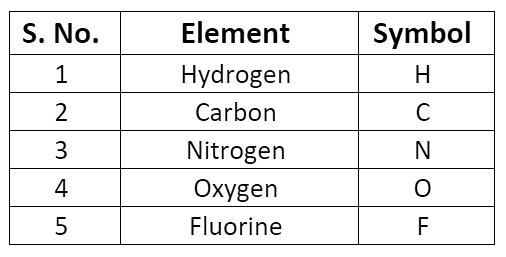
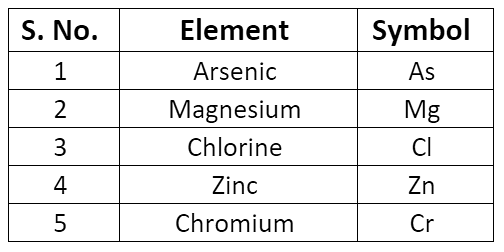
Symbols of Elements
- The symbol may be defined as the abbreviation used for the name of an element.
- The symbol of an element is generally either the first letter or the first two letters or the first and the third letters of the name of the element.
Example: The symbols of the following elements are the first letter of the name of that element.
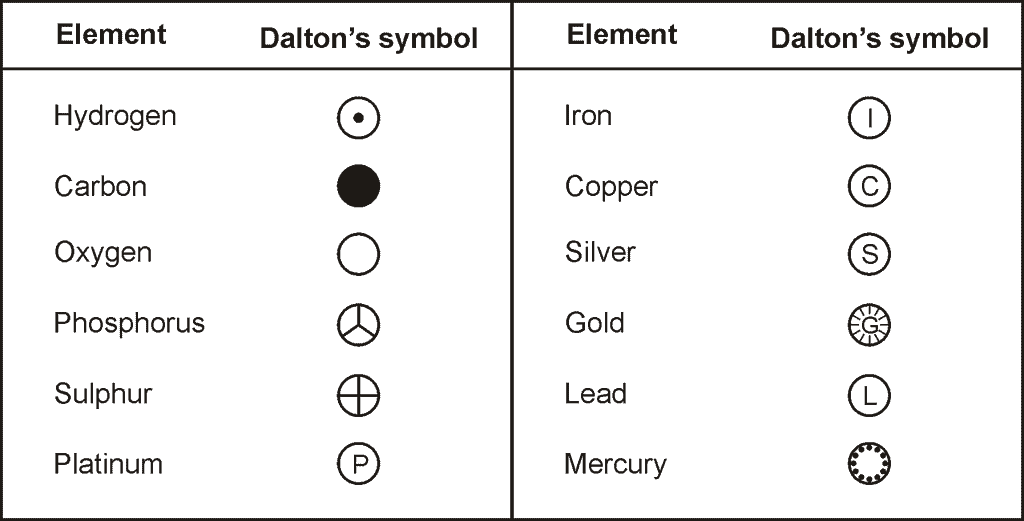
- Some symbols derived from the first letter of the names of the element.
- Some symbols derived from the first and the second letter of the names of the elements.

- Some symbols derived from the first and the third letter of the names of the elements.
- There are certain symbols that seem to here no relationship to their names. The symbol of these elements is derived from their Latin names.
Atomic Mass
- The atomic mass of an element may be defined as the average relative mass of an atom of the element as compared with the mass of an atom of carbon (C-12 isotope) taken as 12 a.m.u.
- Atomic mass =

How do Atoms exist?
- The atoms of only a few elements called noble gases (such as helium, neon, argon, krypton, etc.) which are chemically unreactive and exist in the free state (as a single atom).
- Generally, atoms of the elements are chemically very reactive and do not exist in the free state (as a single atom).
Molecules
- A molecule is the smallest particle of an element or compound that has an independent existence. A molecule contains one or more than one atom.
- The molecules of elements contain atoms of only one kind.
- The number of atoms in a molecule of an element is known as the atomicity of the element.
Example: The atomicity of the noble gases is 1; that of hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen, etc. is 2 each; and that of ozone is 3.
Thus, noble gases, hydrogen, and ozone are respectively monoatomic, diatomic, and triatomic molecules.
Molecules of Elements
- The molecules of an element contain two similar atoms chemically bonded together, Example: Ozone gas has 3 oxygen atoms combined together, so ozone exists in the form of O3.
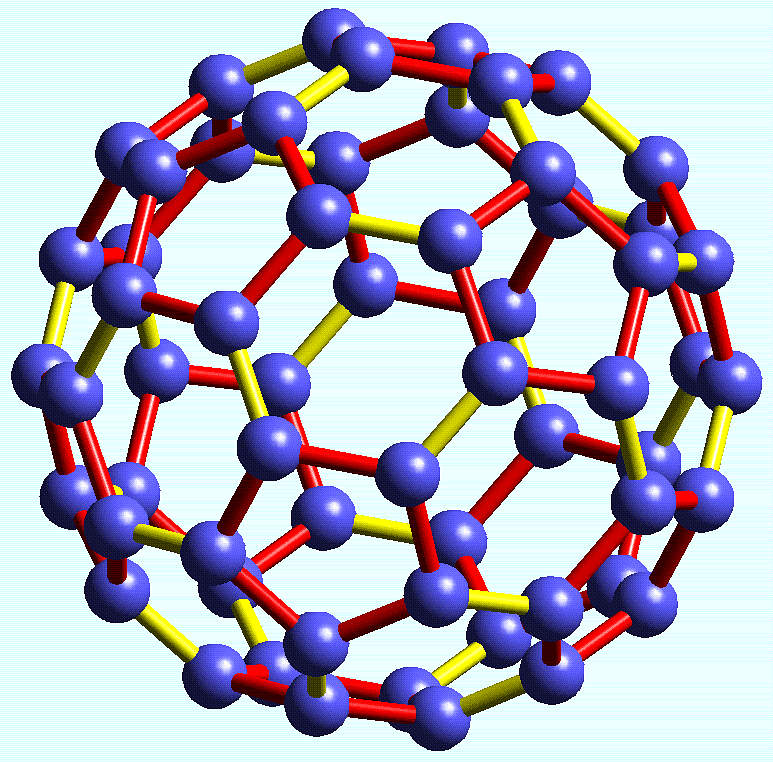
- A recently discovered form of carbon called Buckminsterfullerene, that has the molecular formula C60.
 Buckminsterfullerene
Buckminsterfullerene
Molecules of Compounds
- The molecules of a compound contain two or more different types of atoms chemically bonded together.
Example: The molecule of Sulphur dioxide (SO2) contains one atom of Sulphur chemically bonded with two atoms of oxygen.
Gram Molecular Mass and Formula Mass
- The molecular mass of a substance (an element or a compound) may be defined as the average relative mass of a molecule of the substance as compared with the mass of an atom of carbon (C-12 isotope) taken as 12 a.m.u.
- Molecular Mass =

- The molecular mass of a compound can be obtained by adding atomic masses of all the atoms present in the molecule of the compound.
Example: Molecular mass of CO2 = (12 × 1) + (16 × 2) = 44 u
Question for Basic Concepts: Atoms and MoleculesTry yourself:Molecular mass is defined as the:
View Solution
Gram Molecular Mass
- Gram molecular mass of a substance is defined as that much quantity of the substance whose mass expressed in grams is numerically equal to its molecular mass.
Example: The molecular mass of CO2 is 44 u, its gram molecular mass is 44 g. - Gram molecule mass of a substance is also known as the gram-molecular mass of the substance.
Formula Mass
- The formula mass of an ionic compound is obtained by adding atomic masses of all the atoms in a formula unit of the compound.
Example:
Formula mass of potassium chloride (KCl) = Atomic mass of potassium + Atomic mass of chlorine
= 39 + 35.5 = 74.5
The document Basic Concepts: Atoms and Molecules | Science Class 9 is a part of the Class 9 Course Science Class 9.
All you need of Class 9 at this link: Class 9
|
87 videos|369 docs|67 tests
|
FAQs on Basic Concepts: Atoms and Molecules - Science Class 9
| 1. What is Dalton's Atomic Theory? |  |
Ans. Dalton's Atomic Theory was a scientific theory that proposed that all matter is made up of tiny, indivisible particles called atoms. It also stated that atoms of the same element are identical in size, mass, and other properties, while atoms of different elements have different properties. Additionally, the theory suggested that chemical reactions involve the rearrangement of atoms to form new compounds.
| 2. What are atoms? |  |
Ans. Atoms are the basic building blocks of matter. They are the smallest unit of an element that retains the chemical properties of that element. Atoms consist of a nucleus made up of positively charged protons and neutral neutrons, with negatively charged electrons orbiting around the nucleus. The number of protons in an atom's nucleus determines its atomic number and therefore its identity as a particular element.
| 3. What are molecules? |  |
Ans. Molecules are groups of two or more atoms that are chemically bonded together. They can be made up of atoms from the same or different elements. For example, a molecule of water (H2O) consists of two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom chemically bonded together. Molecules can exist as individual units or can be part of larger structures such as polymers or crystals.
| 4. What is Gram Molecular Mass and Formula Mass? |  |
Ans. Gram Molecular Mass (GMM) and Formula Mass are both methods of calculating the mass of a substance. GMM is the mass of one mole of a molecular substance, while Formula Mass is the mass of one mole of an ionic compound. To calculate GMM, you add up the atomic masses of all the atoms in a molecule and multiply by the number of moles. For Formula Mass, you add up the atomic masses of all the ions in a formula unit and multiply by the number of moles.
| 5. What is the difference between an atom and a molecule? |  |
Ans. The main difference between an atom and a molecule is that an atom is a single particle that cannot be broken down further, while a molecule is a group of two or more atoms chemically bonded together. Atoms are the basic building blocks of matter, while molecules are the building blocks of compounds. Additionally, atoms of the same element are identical, while molecules of the same compound can have different arrangements of the same atoms.

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches