Class 9 Geography Chapter 2 Notes - Physical Features of India
India's Physical Features
India's varied landscape includes mountains, plateaus, deserts, plains, and islands. The Peninsular Plateau is one of the oldest landforms on Earth, while the Himalayas and Northern Plains are more recent. The Himalayas are the highest and one of the most rugged mountain ranges in the world. They are relatively young in geological terms and consist of folded mountains that stretch along the northern border of India. These mountains run from the Indus to the Brahmaputra in a west-east direction, creating an unstable zone with high peaks, deep valleys, and fast-flowing rivers. The Northern Plains are made up of alluvial deposits, while the Peninsular Plateau features igneous and metamorphic rocks, gentle hills, and wide valleys.
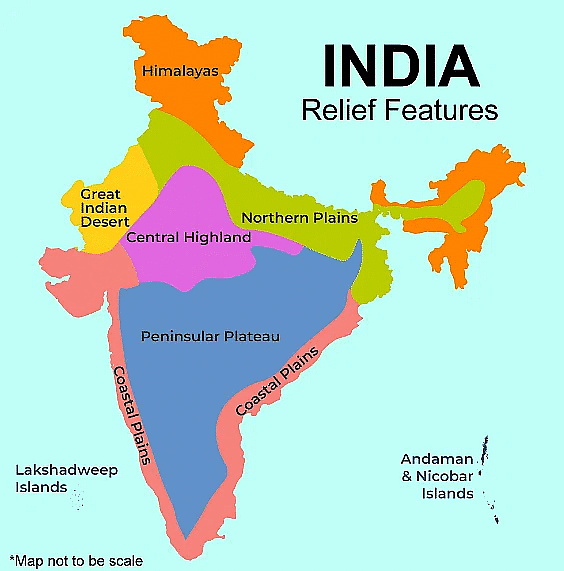
Major Physiographic Divisions
India's major physiographic divisions include different types of landforms such as mountains, plateaus, plains, deserts, and coastal regions.
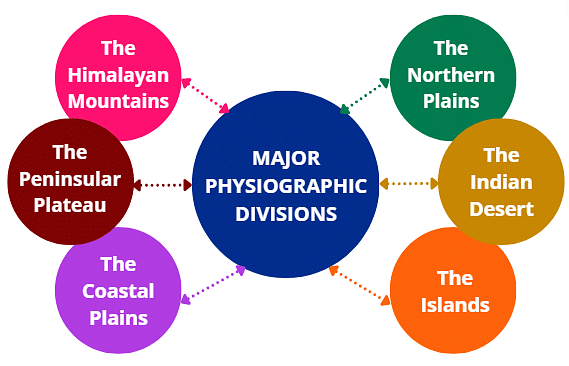
The physical features of India can be grouped into the following divisions:
- The Himalayan Mountains
- The Northern Plains
- The Peninsular Plateau
- The Indian Desert
- The Coastal Plains
- The Islands
1. The Himalayan Mountains
The Himalayas consist of three parallel ranges: the Great or Inner Himalayas (Himadri), the Lesser Himalayas, and the Outer Himalayas. The Great Himalayas are the longest and contain the highest peaks, averaging around 6,000 metres. This mountain range features a youthful landscape with considerable geological activity.
The Northern Plains are made from alluvial deposits, while the Peninsular Plateau has igneous and metamorphic rocks, along with gently rising hills and broad valleys.
The Himalayas are young fold mountains found in northern India. They stretch from the Indus River in the west to the Brahmaputra River in the east, forming an arc that is about 2,400 km long. The width of the range varies; it is about 400 km in Kashmir and narrows to around 150 km in Arunachal Pradesh. The eastern part has more noticeable height differences compared to the western part.
 Himalayas on map
Himalayas on mapThree Parallel Ranges
The Himalayas consist of three main parallel ranges:
- The northern-most range is known as the Great Himalayas or Inner Himalayas, also called the Himadri. It is the longest range and has the highest peaks, with an average height of 6,000 metres.
- The Lesser Himalayas (Himachal) are made up of compressed and altered rocks.
- The Shiwaliks are the outermost range, formed by sediments carried by rivers.
Between the Lesser Himalayas and Shiwaliks are the valleys known as Duns, which are fertile areas.
The Himalayas are divided into various regions based on river valleys, including Punjab, Kashmir, Himachal, Kumaon, Nepal, and Assam Himalayas. There are also regional names within these broad categories.
Eastern Extension (Purvachal Hills)
- The Brahmaputra River marks the eastern boundary.
- Beyond the Dthang gorge, the range curves south, forming the Purvachal hills, which include the Patkai, Naga, Mizo, and Manipur hills. These hills, found in the north-eastern states, are primarily composed of sedimentary rocks known as strong sandstones. They are covered in dense forests and mainly run as parallel ranges with valleys.
2. The Northern Plain
The Northern Plain has been shaped by the interaction of three major river systems: the Indus, the Ganga, and the Brahmaputra, along with their tributaries. This area consists of alluvial soil, which has formed from the accumulation of alluvium over millions of years in a vast basin at the base of the Himalayas. It covers about 7 lakh sq. km, stretching around 2400 km long and between 240 to 320 km wide. This region is heavily populated and very productive for agriculture due to its rich soil, sufficient water supply, and favourable climate.
The largest section of the Northern Plain is made up of older alluvium known as Bhangar, which is located above the river floodplains and has a terrace-like appearance. The soil here contains calcareous deposits, called Kankar. The newer deposits found in the floodplains are referred to as Khadar. These deposits are refreshed almost every year, making them very fertile and ideal for intensive farming.  Divisions of Northern Plains
Divisions of Northern Plains
Sections of the Northern Plain
The Northern Plains can be divided into three main sections:
- Punjab Plains: This is the western part of the Northern Plain, created by the Indus and its tributaries. A significant portion of this plain is in Pakistan. The Indus and its tributaries—the Jhelum, Chenab, Ravi, Beas, and Satluj—originate in the Himalayas. This area is marked by the presence of doabs.
- Ganga Plain: This section lies between the Ghaggar and Teesta rivers, covering parts of North India including Haryana, Delhi, U.P., Bihar, parts of Jharkhand, and West Bengal.
- Brahmaputra Plain: Located to the east of the Ganga Plain, especially in Assam.
The Northern Plains do not have a completely flat landscape; they show various relief features. Based on these features, the plains can be categorised into four distinct regions according to river deposits and landforms:
- Bhabar Belt: A narrow strip where rivers deposit pebbles, located at the foothills of the Himalayas. Here, all streams vanish.
- Terai Region: To the south of the Bhabar is the Terai, a wet and marshy area that was once a dense forest teeming with wildlife. It has largely been cleared for farming, and Dudhwa National Park is found here.
- Bhangar: This is the region of older alluvium, which includes calcareous deposits known as Kankar.
- Khadar: The fertile floodplains of rivers, which are refreshed nearly every year, making them very suitable for agriculture.
In summary, the Northern Plain is an important geographical area in India, known for its extensive alluvial deposits, agricultural productivity, and varied landforms.
3. The Peninsular Plateau
The Peninsular Plateau is a flat area made up of old crystalline, igneous, and metamorphic rocks. It was created when the Gondwana land broke apart, making it one of the oldest landmasses. The plateau features wide, shallow valleys and rounded hills. It can be divided into two main parts: the Central Highlands and the Deccan Plateau. 
The Central Highlands
- Location and Boundaries: The Central Highlands are situated north of the Narmada River and include the Malwa Plateau. They are bordered by the Vindhyan Range to the north, the Satpura Range to the south, and the Aravalli Range to the northwest. The Aravalli Hills are badly eroded, appearing as broken hills stretching from Gujarat to Delhi in a southwest-northeast direction.
- Slope and River Flow: The slope of the Central Highlands goes from southwest to northeast, as shown by the rivers flowing in that direction. The highlands are broader in the west and become narrower towards the east.
- Extensions of the Central Highlands: The Bundelkhand and Baghelkhand areas are the eastern extensions of this region. The Chotanagpur Plateau, located further east, is drained by the Damodar River.
The Deccan Plateau
- Location and Boundaries: The Deccan Plateau is found south of the Narmada River, bordered by the Satpura Range in the north. The plateau has a gentle slope towards the east and is higher in the west.
- Northeastern Extensions: The Meghalaya, Karbi-Anglong Plateau, and North Cachar Hills are the northeastern extensions of the Deccan Plateau. The prominent hill ranges in this area are the Garo, Khasi, and Jaintia Hills.
- Western and Eastern Edges: The Western Ghats and Eastern Ghats form the western and eastern borders of the Deccan Plateau, respectively. The Eastern Ghats are not continuous.
- Deccan Trap: A notable feature of the Deccan Plateau is the black soil area known as the Deccan Trap, which is of volcanic origin. The rocks here are igneous and have eroded over time, leading to the formation of black soil.
4. The Indian Desert
The Indian desert is found at the western edge of the Aravalli Hills. It is a sandy plain with many sand dunes. This area gets very little rainfall, under 150 mm a year, and has a dry climate with sparse vegetation.
Key Features of the Indian Desert
- The desert has a dry climate with little vegetation. Streams form during the rainy season but quickly vanish into the sand because they lack enough water to reach the sea.
- Luni is the only major river in this area.
- Barchans (crescent-shaped dunes) are widespread, while longitudinal dunes are more common near the Indo-Pakistan border.
5. The Coastal Plains
The Peninsular plateau is bordered by narrow coastal areas along the Arabian Sea to the west and the Bay of Bengal to the east. The western coast, located between the Western Ghats and the Arabian Sea, is a narrow plain divided into three parts:
- The northern section is known as the Konkan (Mumbai - Goa).
- The central area is referred to as the Kannad Plain.
- The southern part is called the Malabar coast.
Eastern Coastal Plains
- The plains along the Bay of Bengal are wide and flat. The northern area is called the Northern Circar, while the southern section is known as the Coromandel Coast.
- Large rivers like the Mahanadi, Godavari, Krishna, and Kaveri have created extensive deltas along this coast.
- The eastern coastal plains are also important for fishing and port activities, which show their economic significance.
- Lake Chilika, the largest saltwater lake in India, is a notable feature along the eastern coast, located in Odisha, south of the Mahanadi delta.
6. The Islands
India has a large mainland and two groups of islands. The Lakshadweep Islands group, previously called Laccadive, Minicoy, and Amindive, is situated near the Malabar coast of Kerala. This group consists of small coral islands that cover a total area of 32 sq km. Kavaratti Island is the administrative centre of Lakshadweep. The Andaman and Nicobar Islands are larger and more spread out, found in the Bay of Bengal, with the Andaman Islands located in the north and the Nicobar Islands in the south.
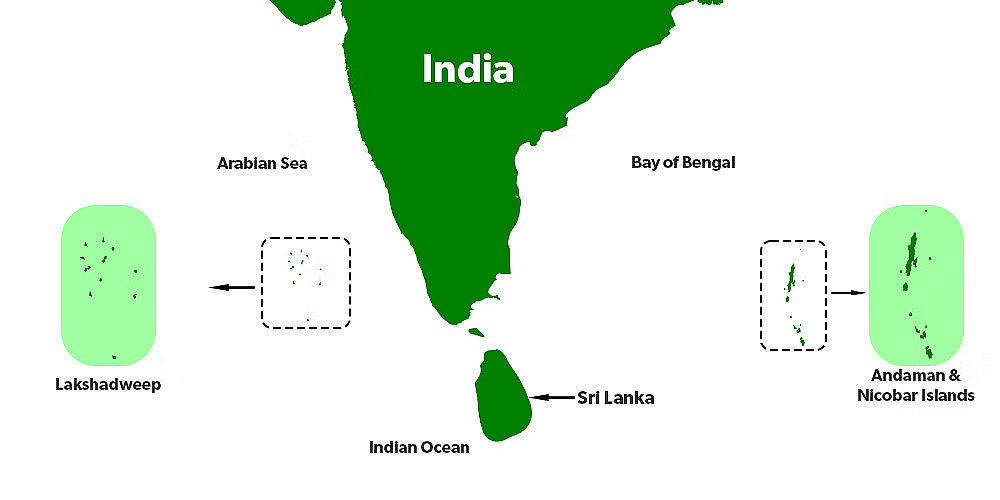
Ecological and Strategic Importance
- This island group has a great diversity of flora and fauna. Pitti Island, which is uninhabited, has a bird sanctuary, highlighting the ecological importance of the Lakshadweep Islands.
- Both island groups are strategically important due to their location and resources.
Summary
India is a large country with a variety of landscapes. Depending on where you live, you might be used to flat plains or hilly areas with mountains and valleys. In fact, India encompasses almost all the major physical features found on Earth, including mountains, plains, deserts, plateaus, and islands.
The geography of India shows significant physical diversity. The Peninsular Plateau is one of the oldest landforms on the planet and is considered very stable.
Major Physiographic Divisions
The physical features of India can be divided into the following main categories:
- The Himalayan Mountains: The Himalayas are young mountains formed by folding and stretch along the northern border of India. They run east to west from the Indus to the Brahmaputra rivers and are among the tallest and most rugged mountains in the world. This region is geologically active and features high peaks, deep valleys, and fast-flowing rivers.
- The Northern Plains: These plains are made up of alluvial deposits and are the newest landforms in India, providing rich soil that is perfect for farming.
- The Peninsular Plateau: This plateau consists of igneous and metamorphic rocks, characterised by gently rising hills and broad valleys.
- The Indian Desert: This region consists of arid landscapes with sparse vegetation.
- The Coastal Plains: These are low-lying areas alongside the coast, featuring beaches and estuaries.
- The Islands: India has several islands, which are scattered across the seas.
Difficult Words
Fold Mountains: These are mountains that are formed primarily through the effects of folding on layers within the upper part of the Earth's crust. The Himalayas are an example of young fold mountains formed from the collision of tectonic plates.
Alluvial Deposits: Sediments deposited by rivers or floodwaters. In the context of the Northern Plains of India, these deposits create fertile land ideal for agriculture.
Igneous and Metamorphic Rocks: Igneous rocks are formed from the solidification of molten magma. Metamorphic rocks have been transformed by heat, pressure, or other natural processes from another type of rock.
Tableland: A plateau or a flat-topped area that is elevated significantly above the surrounding area.
Gondwana Land: A supercontinent that existed from the Late Paleozoic into the Mesozoic era. It later broke up to form continents including Africa, South America, Australia, and India.
Bhabar and Terai: Bhabar refers to a narrow belt of land at the foothills of the Himalayas along the Ganges River, characterized by pebbles and porous soil. Terai is the marshy land just south of the Bhabar belt, known for its rich biodiversity and fertile soil.
Deccan Trap: A large igneous province located on the Deccan Plateau of west-central India and one of the largest volcanic features on Earth. It consists of multiple layers of solidified flood basalt that are more than 2,000 meters thick over an area of 500,000 square kilometers.
Aravalli Range: One of the oldest mountain ranges in India, running northeast to southwest across Rajasthan in western India.
Duns: Valleys lying between the Lesser Himalayas and the Shiwaliks, filled with alluvial deposits.
Kankar: Calcareous or calcite nodules found in the alluvial or sedimentary soils in the dryer parts of India.
Deccan Plateau: A large plateau in India, making up most of the southern part of the country. It is made up of ancient crystalline, igneous, and metamorphic rocks.
Coromandel Coast: The southeastern coast of India along the Bay of Bengal, from Cape Comorin (Kanyakumari) in the south to False Divi Point in the north in Andhra Pradesh.
Coral Islands: Islands formed from coral detritus and associated organic material. They typically occur in tropical and subtropical areas, such as the Lakshadweep Islands off the southwest coast of India.
|
53 videos|437 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on Class 9 Geography Chapter 2 Notes - Physical Features of India
| 1. What are the major physiographic divisions of India? |  |
| 2. How do the Himalayan Mountains influence the climate of India? |  |
| 3. What are the characteristics of the Northern Plain of India? |  |
| 4. What are the major features of the Peninsular Plateau? |  |
| 5. What are the main geographical features of the Coastal Plains of India? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|


















