Gibberellins | Science for ACT PDF Download
GIBBERELLINS
First of all Japanese farmers observed peculiar symptoms in rice seedlings & called the bakanae disease (foolish seedling disease)
Rice plants become thin, tall & pale due to infection of Gibberella (Ascomycetes) or Fusarium (Deuteromycetes) confirmed by Kurosawa & Swada.
Yabuta and Sumiki 1938 were the first to extract a crystalline substance from the Gibberella fungus , which they named as Gibberellin.
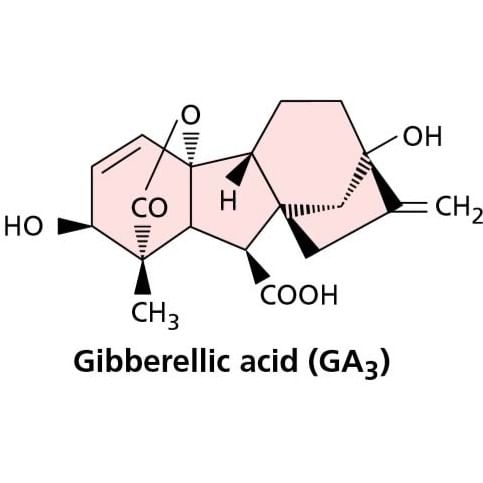
Gibberellin, is an acidic & possess a gibbon ring structure, are able to overcome genetic dwarfism in plants.
100 type of Gibberellins (GA1, GA2 GA3 ............ GA100) are known. GA3 [C19H26O6] is representative of all gibberellins.

GA found in all groups of plants (algae, to angiosperms, but as a flowering hormone acts only in angiosperms.
Biosynthesis of gibberellin takes place by mevalonic acid pathway (Kaurene→GA)
Physiological effects and applications
(1) Stem/internode elongation :- GA induces internode elongation, leaf expansion & used in sugarcane cultivation.
Gibberellins induce stem elongation in rosette plants (Cabbage) this phenomenon known as bolting effect. (Elimination of rosette habit in some plants by gibberellins action is bolting)
(2) Elongation of genetic dwarf plants :- When gibberellin are applied to dwarf maize, Pisum & Vicia faba, then they become tall. The rosett plant of sugar beet indicate an extreme dwarfism, this habit can be eliminate by GA.
(3) Flowering in LDP, in short light duration :- (Shortening of life cycle)
(4) Parthenocarpy :- Like auxin, exogenous use of GA also induces the formation of seedless fruits.
(5) Substitution of cold treatment or vernalisation :- The biennials plants form their vegetative body in the Ist year. Then they pass through a winter season & produce flower & fruits in IInd year. GA induces flower in first year.
(6) Breaking of dormancy :- GA breaks the dormancy of seeds, buds and tubers
(7) Seed germination :- Gibberellin induce the synthesis of hydrolysis enzymes like a-amylase, lipases, & proteases
(8) Sex expression :- GA induces maleness in Cucumis, Cannabis.
(9) Germination of photoblastic seeds :- Gibberellin treated light sensitive seeds can germinates in dark. Ex. Lettuce, Tobacco.
(10) Fruit & flower enlarger :- Size of grape fruits & bunch & Geranium flowers increased by GA
Pomalin ⇒ GA (GA4 + GA7) + CK (6 - Benzyladenine) - acts as an apple enlarger
(11) In fermentation :- More growth of yeast cells by GA.
(12) Increase height of Sugarcane plant :- (More sugar contents by IAA )
Bio–assay :–
(1) a-amylase activity test in Barley endosperm
(2) Dwarf Pea & Maize test
|
486 videos|517 docs|337 tests
|
FAQs on Gibberellins - Science for ACT
| 1. What are gibberellins and what is their role in plant growth and development? |  |
| 2. How do gibberellins affect seed germination? |  |
| 3. Can gibberellins be used to increase crop yield? |  |
| 4. Are gibberellins only found in plants? |  |
| 5. Can excessive use of gibberellins have negative effects on plants? |  |

|
Explore Courses for ACT exam
|

|