Industry Class 4 Notes SST
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Utilizing Nature's Resource |

|
| The Role of Industries |

|
| Factors Influencing Industrial Development |

|
| Classification of Industries |

|
| Based on Raw Material Sources |

|
| Based on Size |

|
Introduction
Manufacturing is how we create the things we use every day, from clothes to cars. It’s like a giant workshop where raw materials are turned into products that make our lives easier and more comfortable. Understanding manufacturing helps us see how the things around us are made and the role of industries in our world.
What is Manufacturing?
Manufacturing is the process of turning one type of resource into another useful item or resource.

The materials used in manufacturing can be either natural or already processed for a specific industry's needs. These materials are known as inputs. For instance, wood pulp is an input for the paper industry, where paper becomes the output.
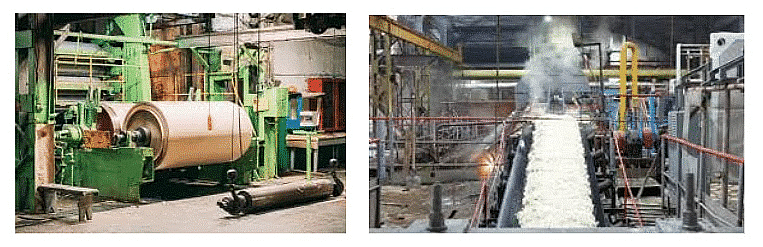 Pulp Industry(left) and Sugar Industry(right)
Pulp Industry(left) and Sugar Industry(right)Utilizing Nature's Resource
- Nature offers us a variety of resources that are essential for meeting our needs. For instance, we have crops like wheat, materials like cotton, leaves for tea, wood logs, and deposits of iron ore.
- However, these resources are in their raw form and cannot be directly utilized for our purposes.
- Before they become usable, they need to undergo a transformation process, where they are converted into finished products that we commonly use in our daily lives.
- For instance, wheat is turned into bread, cotton into cloth, tea leaves into tea, wood logs into furniture, and iron ore into utensils or machinery parts.
The Role of Industries
- Industries play a crucial role in this transformation process. They serve as the hubs where raw materials are processed and transformed into finished goods.
- This process involves the use of various machines and technologies to efficiently convert raw materials into products that are suitable for consumption or further use.
- To establish and operate an industry effectively, several factors come into play, including access to raw materials, availability of machinery, a stable power supply, sufficient human labor, financial resources, and a reliable transportation network.
Factors Influencing Industrial Development
The growth of a country's economy heavily relies on its industries. For industrial development to thrive, several key factors must be in place
Technical Skills
- Technical skills are the abilities needed to operate machinery, develop products, conduct research, and manage industrial processes effectively.
- This includes knowledge in areas like engineering, manufacturing, design, and technology.
- Quality education and training programs are essential for building and maintaining a skilled workforce.
- Investment in research and development (R&D) drives innovation and improves technical skills, which in turn supports industrial growth.
Resources
- Resources include natural resources like raw materials, energy sources, and human resources like skilled and unskilled workers.
- Access to these resources is crucial for industrial development.
- Efficient management of resources ensures sustainability and long-term success for industries.
Infrastructure
- Infrastructure supports industrial development by facilitating the movement of goods, services, and people.
- This includes energy, transportation, and communication networks.
- Adequate infrastructure in education and healthcare contributes to a healthy and skilled workforce, boosting productivity and innovation.
Entrepreneurship
- Entrepreneurship drives industrial development by seizing opportunities, mobilizing resources, and taking risks to establish and grow businesses.
- Entrepreneurs innovate, invest, and create jobs, fostering economic growth.
- Supportive regulations, access to financing, and a favorable business environment encourage entrepreneurship.
- Traits like continuous learning and adaptability are crucial for success in dynamic markets.
Classification of Industries
Industries can be grouped in various ways, known as classification.
Some common classifications include:Based on Raw Material Sources:
- Mineral-based Industries: Utilizing minerals like iron ore, chemicals, etc.
- Agro-based Industries: Using agricultural products like sugarcane, fruits, etc.
Based on Size:
- Large-scale Industries: Such as iron and steel, requiring significant manpower, machinery, and capital, operating round the clock.
- Small-scale Industries: Like pencil and pen manufacturing, employing fewer people, lighter machinery, and lesser capital, often with flexible working hours.
- Rural and Cottage Industries: Including handicrafts and handlooms, typically home-based and family-owned, with irregular working hours and workers attending to other responsibilities.
Based on Raw Material Sources
(i) Agro-based Industries
Agro-based industries utilize agricultural products as their primary raw materials. These industries often involve processing, refining, or transforming agricultural produce into value-added products.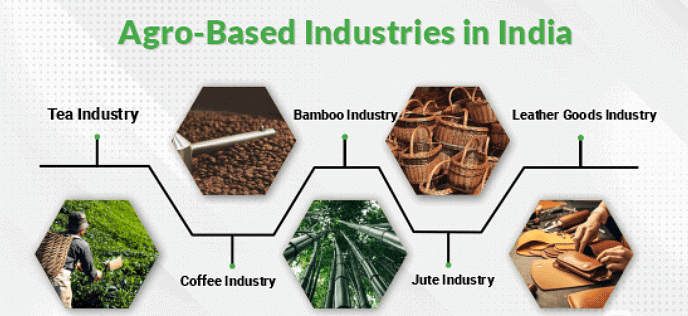
- Examples include sugar mills that process sugarcane into sugar, fruit processing units that turn fruits into juices, and dairy processing plants that convert milk into various dairy products like cheese, butter, and yogurt.
- These industries play a crucial role in the economy by adding value to agricultural produce, generating employment opportunities in rural areas, and contributing to economic development.
- Additionally, they help in reducing post-harvest losses by processing perishable agricultural goods into durable products.
(ii) Mineral-based Industries
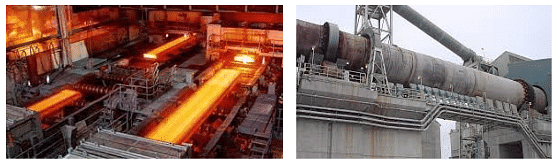 Iron and Steel Industry(left) and Cement Industry(right)
Iron and Steel Industry(left) and Cement Industry(right)
- The iron and steel industry, for instance, utilizes iron ore as its primary raw material to produce steel through processes like smelting and refining.
- Similarly, the chemical industry utilizes minerals like sulfur, phosphates, and limestone to produce a wide range of chemicals used in various sectors such as agriculture, pharmaceuticals, and manufacturing.
- These industries are vital for industrialization and infrastructure development. They provide essential materials for construction, manufacturing, and other economic activities, thereby contributing significantly to economic growth and development.
Based on Size
(i) Large-scale Industries
Large-scale industries are characterized by their extensive use of capital, advanced machinery, and significant manpower.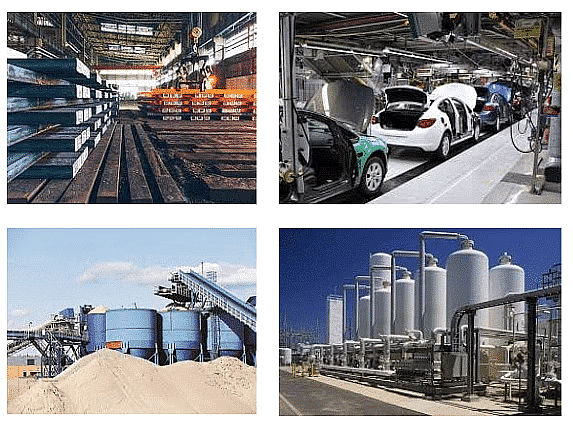 Various types of Large Scale Industries
Various types of Large Scale Industries- These industries typically operate on a large scale, requiring substantial investments in infrastructure and technology.
- Examples include the iron and steel industry, automobile manufacturing, and petrochemical industry.
- Large-scale industries often have a significant impact on the economy, generating substantial employment opportunities, driving technological innovation, and contributing significantly to GDP growth.
- They require substantial coordination and management due to their complex operations and large workforce.
(ii) Small-scale Industries
Small-scale industries, on the other hand, are characterized by their relatively smaller size, lighter machinery, and lesser capital investment. Soap and Candle Industry
Soap and Candle Industry
- These industries typically operate on a smaller scale, catering to local or niche markets. Examples include small-scale manufacturing units producing items like pencils, pens, soap, and candles.
- Small-scale industries play a crucial role in employment generation, particularly in rural and semi-urban areas.
- They provide opportunities for entrepreneurship and local economic development. These industries are often more flexible and adaptable to changing market conditions compared to large-scale industries.
(iii) Rural and Cottage Industries
Rural and cottage industries are typically small-scale enterprises operated in rural areas or within households. Examples include handloom weaving, pottery, basket making, and artisanal food production.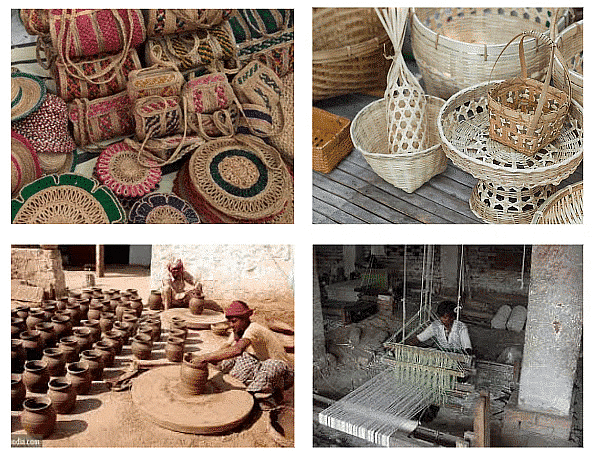 Various types of Cottage Industries
Various types of Cottage Industries- These industries often involve traditional crafts and skills passed down through generations.
- Rural and cottage industries contribute to rural livelihoods by providing employment opportunities to local communities, preserving traditional craftsmanship, and promoting cultural heritage.
- Workers in these industries often have flexible working hours, allowing them to balance work with other responsibilities such as household chores and agriculture.
- Manufacturing transforms raw materials into everyday products.
- Industries are essential for processing materials into usable goods.
- Key factors for industrial success include resources, skills, infrastructure, and entrepreneurship.
- Industries are classified by raw materials and size (e.g., agro-based, mineral-based, large-scale, small-scale).
Conclusionn
Manufacturing is crucial for creating the products we use daily, driving economic growth through various industries that process raw materials into finished goods.
|
50 videos|246 docs|46 tests
|
FAQs on Industry Class 4 Notes SST
| 1. What are the key characteristics of Industry Class 4? |  |
| 2. How is Industry Class 4 different from other industry classes? |  |
| 3. What are some examples of businesses that fall under Industry Class 4? |  |
| 4. What are the major challenges faced by Industry Class 4 businesses? |  |
| 5. How can Industry Class 4 businesses improve their efficiency and productivity? |  |















