Class 8 Civics Chapter 1 Important Question Answers - The Indian Constitution
Q1. What is democracy?
Ans: Democracy is a system of government in which the people hold the power to make decisions regarding their governance.
- Citizens participate in elections to choose their leaders.
- Leaders are responsible for making decisions on behalf of the people.
- Examples of democratic nations include India.
Q2. Define the term constitution. Why do we need a constitution?
Ans: Constitution refers to a set of fundamental principles or laws that govern a country or organisation. It defines:
- The structure of the government.
- The powers of various branches.
- The rights and duties of citizens.

We need a constitution for several important reasons:
- It establishes the ideals that shape the society we aspire to live in.
- It clarifies the fundamental nature of our community, accommodating diverse beliefs.
- It provides a common set of rules and principles that all citizens can agree upon.
- It outlines the type of government and the shared values that should be upheld.
- It includes safeguards against the misuse of power by political leaders.
Q3. Differentiate between a monarchy and a democracy?
Ans:
A monarchy is a form of government led by a king, queen, or emperor, with power typically passed down through family lines. For instance:
- Saudi Arabia is a monarchy where the king holds considerable control over the government.
In contrast, a democracy is governed by the people, who exercise power primarily through voting for their leaders. An example is:
- India, where citizens elect their government officials.
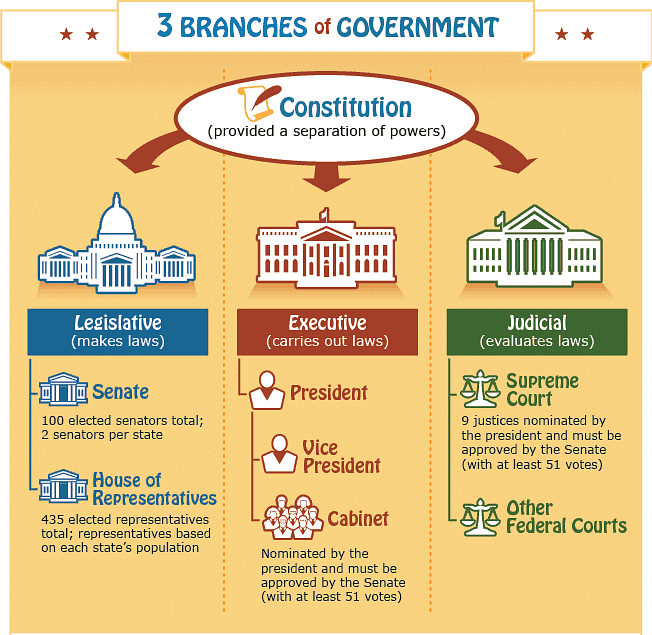
Q4. Explain the functions of organs of government.
Ans: According to the constitution, there are three organs of the state:
- Legislature: This includes our elected representatives who create laws and procedures.
- Executive: A smaller group responsible for implementing laws and managing government operations.
- Judiciary: This consists of the court system that interprets laws and resolves disputes.
Q5. What do you mean by the tyranny of the majority?
Ans: The tyranny of the majority refers to a situation where the majority in a democracy imposes its will on the minority in a way that is unfair or oppressive. This can occur when the majority uses its power to:
- Make decisions that overlook the rights of minority groups.
- Pass laws that negatively impact minority interests.
For example, if a dominant religion enacts laws that limit the practices of a minority religion, this illustrates the tyranny of the majority.
Q6. Describe in detail the various features of the Indian constitution.
Ans:
(a) Federalism
- India has multiple levels of government, each with its own authority derived from the constitution.
- Both the central and state governments create laws and policies that govern all citizens.
(b) Parliamentary Form of Government
- The government is made up of representatives elected by the people.
- The constitution guarantees universal adult suffrage, allowing all citizens to vote.
- Any citizen can contest elections, regardless of social background.
(c) Separation of Powers
- The constitution establishes three branches of government:
- Legislature: Elected representatives.
- Executive: A smaller group responsible for implementing laws.
- Judiciary: The system of courts that interprets laws.
(d) Fundamental Rights
- Considered the ‘conscience’ of the constitution, these rights protect citizens from misuse of state power.
- They were established to safeguard against arbitrary actions of the government.
(e) Secularism
- In a secular state, the government does not endorse any specific religion.
Q7. What will happen if there is no restriction to the powers of elected representatives?
Ans: If there were no restrictions on the powers of elected representatives, the following consequences could arise:
- They might misuse their authority for personal gain.
- There could be a rise in corruption and unethical behaviour.
- Representatives might prioritise the interests of a single group over the common good.
- Support for one religion could lead to discrimination against others.
These scenarios illustrate the importance of checks and balances in governance.
Q8. Explain how the constitution of India gets made?
Ans: The long experience of authoritarian rule under colonialism convinced Indians that a free India should be a democracy. This democracy would ensure that everyone is treated equally and can participate in government.
The Constitution was not created by a single individual but by a group of around 300 members of the Constituent Assembly. They faced a significant challenge in uniting a country made up of various communities with:
- Different languages
- Diverse religions
- Distinct cultures
During the drafting of the Constitution, India was also experiencing considerable turmoil, which added to the complexity of their task.
Q9. What is the importance of the constitution?
Ans: The constitution is crucial for several reasons:
- It establishes guidelines for decision-making in society.
- It provides rules that prevent the misuse of power by political leaders.
- It contains measures to guard against tyranny.
- It protects citizens from negative impacts on the core principles upheld by the nation.
Q10. What did Dr Ambedkar state about scheduled caste?
Ans: Dr Ambedkar highlighted that, despite the existence of laws for Scheduled Castes, there remained a sense of fear. This was due to the fact that the enforcement of these laws was managed by caste Hindu officers. Therefore, he encouraged Scheduled Castes to actively participate in the government and civil services.
|
65 videos|424 docs|46 tests
|
FAQs on Class 8 Civics Chapter 1 Important Question Answers - The Indian Constitution
| 1. भारतीय संविधान क्या है और इसकी मुख्य विशेषताएँ क्या हैं ? |  |
| 2. भारतीय संविधान का निर्माण कब और कैसे हुआ ? |  |
| 3. मौलिक अधिकार क्या हैं और उनमें कौन-कौन से अधिकार शामिल हैं ? |  |
| 4. भारतीय संविधान में संशोधन कैसे किया जा सकता है ? |  |
| 5. भारतीय संविधान की प्रमुख जिम्मेदारियाँ क्या हैं ? |  |



















