Forest and Wildlife Class 4 Notes SST
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Natural Vegetation? |

|
| Importance of Forests |

|
| Types of Natural Vegetation in India |

|
| Types of Forests in India |

|
| Wild Animals in India |

|
| Conservation of Forests |

|
What is Natural Vegetation?
Vegetation growing naturally in a region due to land formation, climate, and other environmental factors is called natural vegetation.  Forests are a type of natural vegetation but are studied differently due to their organized economic usefulness to humans.
Forests are a type of natural vegetation but are studied differently due to their organized economic usefulness to humans.
Importance of Forests
Forests are a valuable gift from nature, and ideally, one-third of a country's area should be under forests. However, currently, only about one-fourth of India's total area is covered by forests.
 Forest
Forest
- Ecological Importance: Forests are crucial for maintaining soil, water, humidity levels, and preventing floods and dust storms.
- Economic Importance: They provide resources like timber, grazing lands, and support local economies.
- Survival Dependence: Our survival depends on forests as they are essential for clean air, water, and biodiversity.
Types of Natural Vegetation in India
India has different physical features and different climates; therefore it has different natural vegetation across the country.
Tropical Evergreen Vegetation
- It is found in the regions where rainfall is very high, above 300cm annually.
- The dry season is short. Trees do not shed their leaves.
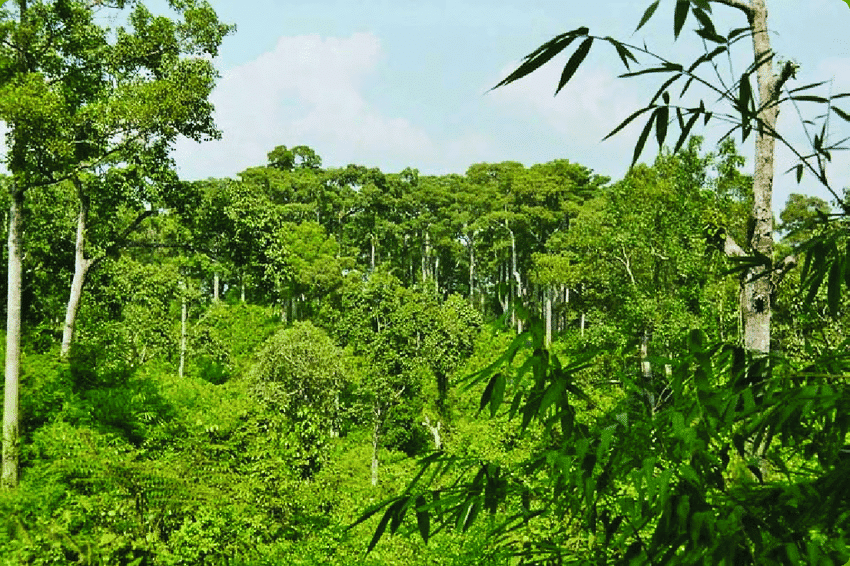

- Trees grow very tall, up to 60m and above. Forests are very dense, and every type of plant life grows.
- Grass is almost absent.
- This vegetation is found in the Western Ghats of Kerala, Karnataka and the North Eastern Hills.
- Mahogany, chincona, bamboo and palms are some of the plants found in this vegetation.
Tropical Semi-evergreen Vegetation
- It is found in the region where rainfall is 250cm to 300cm annually.
- The dry season is a little longer. Vegetation is evergreen and deciduous.
- Deciduous vegetation is that in which trees shed leaves once a year.
- The vegetation is less dense than the evergreen.
- This vegetation is found in the Meghalaya plateau, Sahyadris and Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
- Rosewood and ebony are two economically important products.
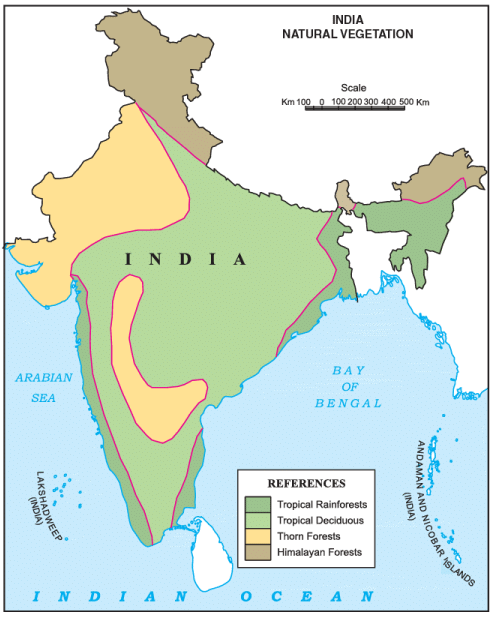 India – Natural Vegetation
India – Natural Vegetation
Tropical Deciduous Vegetation
- It is found in the region where rainfall is 100 to 200cm annually.
- The dry season is three to four months. Vegetation shed leaves once a year in the dry season.
- This is the most widespread vegetal cover in India.
- This vegetation is found in Sahyadris, the Himalayan foothills in the Siwaliks. Teak, sal, sandalwood, shisha, cane and bamboo are important trees in these forests.

Dry Tropical Deciduous Vegetation
- It is found in the region where rainfall is 70 to 100cm annually.
- The dry season is three to four months. Vegetation shed leaves once a year in the dry season.
- This vegetation is found in parts of Uttar Pradesh, parts of Madhya Pradesh, parts of Gujarat, Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka and Tamil Nadu.
- Characteristics of this vegetation are long stretches of grassland between groups of trees. Teak is the dominant tree of this type of vegetation.
 Barren hill slopes cause landslides
Barren hill slopes cause landslides
Dry Tropical Thorny Vegetation
- It is found in the region where rainfall is less than 70 cm annually.
- The dry season is three to four months. Vegetation shed leaves once a year in the dry season.
- This vegetation is found in parts of the north and northwestern parts of India.
- Characteristics of this vegetation are vast, poor and coarse grassland with widely spaced trees and bushes.
- Acacia and cacti are dominant trees of this type of vegetation.
 Pine forests
Pine forests
Tidal Vegetation
- It is found in the delta region. It is found in deltas of the Ganga, Mahanadi, Godavari and Krishna.
- These are flooded by the tidal waves. Mangroves are representative of this type of vegetation.
- Sundari is the typical tree of this vegetation. The name Sunderban is derived from it.
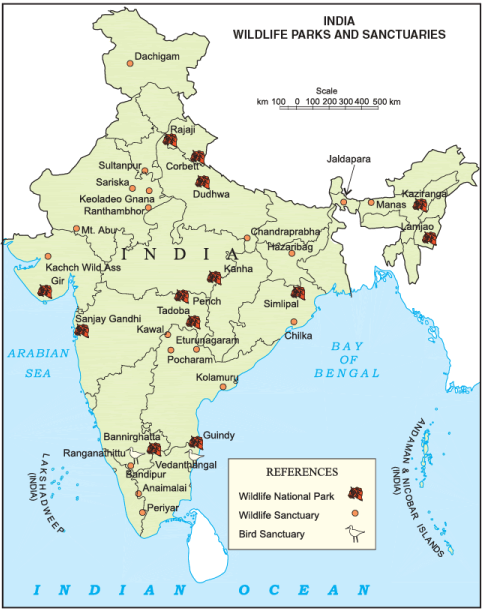 India – Wildlife Parks and Sanctuaries
India – Wildlife Parks and Sanctuaries
The Mountain Vegetation
India has broadly two types of mountains. These are:
(a) Mountains of Peninsular Plateau
These include Nilgiri, Annamalai, Mahabaleshwar in Western Ghats, Satpura and Maikal hills. Mostly these are covered with grass and part of these are with mosses and ferns. Magnolia and elm are common trees. Eucalyptus has been brought in later.
(b) The Mountain Vegetation of The Himalayan Ranges
It provides a very wide variety. In brief, the vegetation changes with altitude and location. There is no vegetation near the snowline. Tree composition changes with altitude and there is a wide variety. Altitudes determine the character of vegetation in many ways. Deodar, silver fir, spruce, oak, birch, pine and rhododendron are common trees at various altitudes and climatic conditions available on mountains.
Types of Forests in India
1. Evergreen Forests
- Found in Western Ghats, north-east India, Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
- Trees: ebony, mahogany, rosewood.
- Features: Trees do not shed leaves, remain green throughout the year.
2. Deciduous Forests
- Found in foothills of the Himalayas, southern plateaus.
- Trees: teak, sal, sandalwood.
- Features: Trees shed leaves in the dry season.
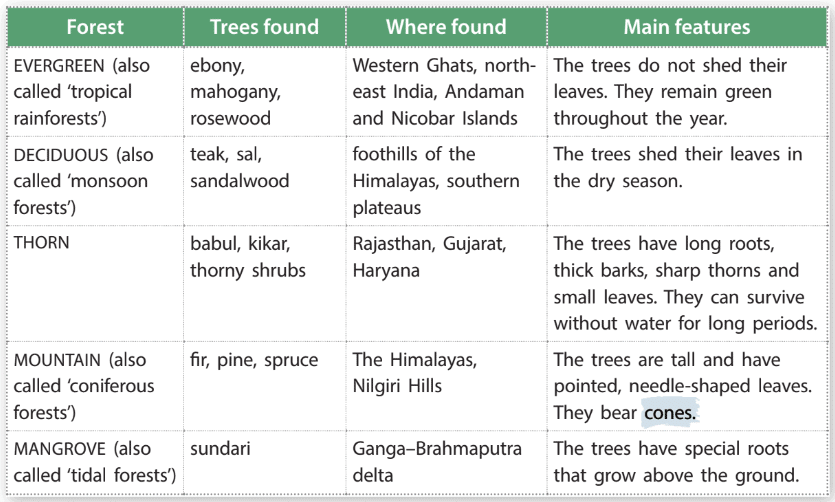
3. Thorn Forests
- Found in Rajasthan, Gujarat, Haryana.
- Trees: babul, kikar, thorny shrubs.
- Features: Long roots, thick barks, sharp thorns, small leaves, can survive without water for long periods.
4. Mountain Forests
- Found in the Himalayas, Nilgiri Hills.
- Trees: fir, pine, spruce.
- Features: Tall trees with pointed, needle-shaped leaves, bear cones.
5. Mangrove Forests
- Found in Ganga–Brahmaputra delta.
- Trees: sundari.
- Features: Special roots that grow above the ground.
Wild Animals in India
India is home to a diverse range of wild animals. In the past, excessive hunting led to the extinction of many species. To address this issue, hunting is now banned in the country. Additionally, the government has established national parks and wildlife sanctuaries across India to protect wildlife and preserve forests. 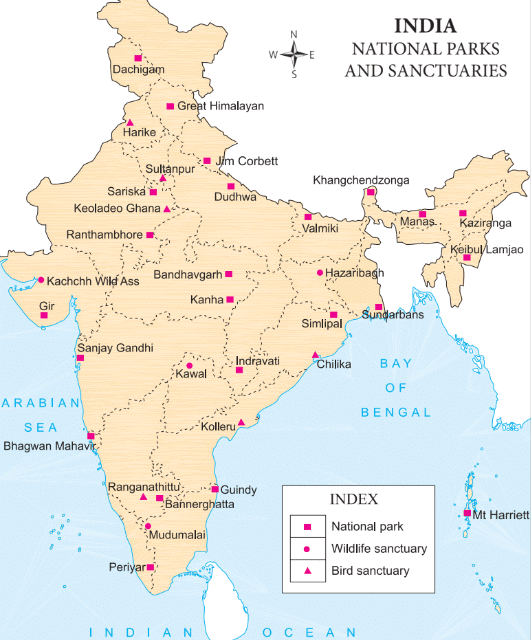 National Parks and Sanctuaries in India
National Parks and Sanctuaries in India
National Parks: These are areas designated for preserving wildlife, forests, and the natural beauty of a region.
Wildlife Sanctuaries: These are areas specifically reserved for endangered animals.
Prominent National Parks and Sanctuaries
- Kaziranga and Manas National Parks (Assam): Protect elephants and the greater one-horned rhinoceroses.
- Gir National Park (Gujarat): Home to Asiatic lions.
- Sundarbans (West Bengal): Known for Bengal tigers, which are also protected in Jim Corbett and Ranthambhore National Parks.
- Great Himalayan National Park: Habitat for snow leopards.
- Rann of Kachchh (Gujarat): Home to the Indian wild asses.
- Bird Sanctuaries: Birds are protected in Sultanpur and Ranganathittu bird sanctuaries.
Notable Facts
Jim Corbett National Park: Established in 1936 (originally called Hailey National Park), it is India’s oldest national park, aimed at protecting Bengal tigers.
India's efforts to conserve wildlife reflect its commitment to preserving biodiversity and the natural heritage of the country.
Conservation of Forests
Conservation of forests means taking care of forests so they stay healthy and we can keep using them without harming nature. Imagine forests like a big garden full of trees, animals, and plants.
Importance of Forest Conservation
- Forests are crucial ecologically, maintaining soil, water, humidity levels, and controlling flooding and dust storms.
- Economically, forests provide resources like timber, grazing lands, and support local economies.
- Wildlife protection is essential, with laws protecting animals like tigers, rhinos, and peacocks in sanctuaries.
Here's how we do it:
- Planting Trees: Just like how we plant flowers in a garden, we also plant new trees in areas where there aren't many trees. This helps make the forest green and full of life.
 Planting Trees
Planting Trees
- Taking Care of Trees: Trees need water and nutrients to grow big and strong. We make sure they have enough of these things so they can keep growing happily.

- Being Kind to Animals: Forests are homes for many animals like tigers, elephants, and birds. We create special places called national parks and wildlife sanctuaries where these animals can live safely without being disturbed.

- Keeping the Forest Clean: We don't litter or throw garbage in the forest. Just like how we keep our rooms tidy, we keep the forest clean so it stays healthy for all the plants and animals.

- Using Trees Wisely: When we need wood or other things from trees, we only take what we need and make sure to plant new trees to replace the ones we used. This is called sustainable use, which means using things in a way that doesn't harm nature.
|
50 videos|246 docs|46 tests
|
FAQs on Forest and Wildlife Class 4 Notes SST
| 1. What is natural vegetation and how is it formed? |  |
| 2. Why are forests important for the environment and human life? |  |
| 3. What are the main types of natural vegetation found in India? |  |
| 4. Can you explain the different types of forests in India? |  |
| 5. What are some effective methods for forest conservation in India? |  |















