Class 8 Civics Chapter 4 Notes - Understanding Laws
Law and Social Justice
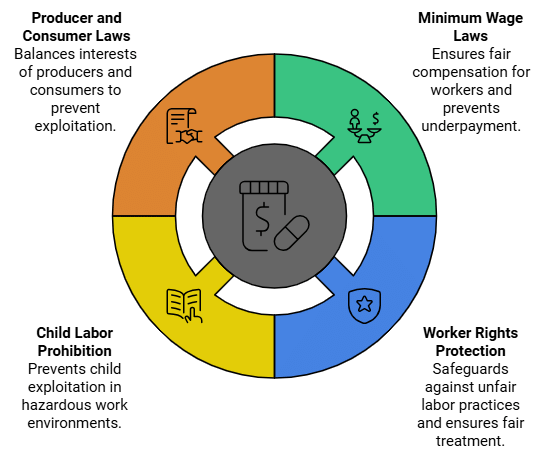
- Markets everywhere tend to be exploitative of people – whether as workers, consumers, or producers. To protect people from such exploitation, the government makes certain laws. These laws try to ensure that unfair practices are kept at a minimum in the markets.

- Private companies, contractors, businesspersons normally want to make as much profit as they can. In the drive for profits, they might deny workers their rights and not pay them wages.
Example: In the eyes of the law, it is illegal or wrong to deny workers their wages. - Similarly, to ensure that workers are not underpaid, or are paid fairly, there is a law on minimum wages.
- A worker has to be paid not less than the minimum wage by the employer. The minimum wages are revised upwards every few years.
- As with the law on minimum wages, which is meant to protect workers, there are also laws that protect the interests of producers and consumers in the market. These help ensure that the relations between these three parties – the worker, consumer, and producer – are governed in a manner that is not exploitative.
- Through making, enforcing, and upholding these laws, the government can control the activities of individuals or private companies so as to ensure social justice.
- Many of these laws have their basis in the Fundamental Rights guaranteed by the Indian Constitution.
Example: The Right against Exploitation says that no one can be forced to work for low wages or under bondage. Similarly, the Constitution lays down “no child below the age of 14 shall be employed to work in any factory or mines or any other hazardous employment.”
➢ Worker’s Worth
- One reason why foreign companies come to India is for cheap labour. Wages that the companies pay to workers are far higher than what they have to pay to workers in poorer countries like India.
- For lower pay, companies can get long hours of work. Additional expenses such as for housing facilities for workers are also fewer. Thus, companies can save costs and earn higher profits.
- One part of the answer lies in what is perceived as the worth of an Indian worker. One worker can easily replace another. Since there is so much unemployment, there are many workers who are willing to work in unsafe conditions in return for a wage.
- Making use of the workers’ vulnerability, employers ignore safety in workplaces. Thus, even so, many years after the Bhopal gas tragedy, there are regular reports of accidents in construction sites, mines, or factories due to the callous attitude of the employers.
➢ Enforcement of Safety Laws
- As lawmakers and enforcers, the government is supposed to ensure that safety laws are implemented.
- It is also the duty of the government to ensure that the Right to Life guaranteed under Article 21 of the Constitution is not violated.
- With more industries being set up both by local and foreign businesses in India, there is a great need for stronger laws protecting workers’ rights and better enforcement of these laws.
New Laws to Protect the Environment
- In 1984, there were very few laws protecting the environment in India, and there was hardly any enforcement of these laws.
- The environment was treated as a ‘free’ entity and any industry could pollute the air and water without any restrictions. Whether it was our rivers, air, groundwater - the environment is being polluted and the health of people disregarded.
 Air Pollution by Industry in Delhi
Air Pollution by Industry in Delhi - The Bhopal disaster brought the issue of the environment to the forefront. Several thousands of persons who were not associated with the factory in any way were greatly affected because of the poisonous gases leaked from the plant.
- This made people realize that the existing laws, though weak, only covered the individual worker and not persons who might be injured due to industrial accidents.
- In response to this pressure from environmental activists and others, in the years following the Bhopal gas tragedy, the Indian government introduced new laws on the environment.
- Henceforth, the polluter was to be held accountable for the damage done to the environment. The environment is something that people over generations will share, and it could not be destroyed merely for industrial development.
Conclusion
- Laws are necessary for many situations, whether this be the market, office, or factory so as to protect people from unfair practices.
- Private companies, contractors, business persons, in order to make higher profits, resort to unfair practices such as paying workers low wages, employing children for work, ignoring the conditions of work, ignoring the damage to the environment (and hence to the people in the neighbourhood), etc.
- A major role of the government, therefore, is to control the activities of private companies by making, enforcing, and upholding laws so as to prevent unfair practices and ensure social justice.
- This means that the government has to make ‘appropriate laws’ and also has to enforce the laws. Laws that are weak and poorly enforced can cause serious harm, as the Bhopal gas tragedy showed.
Do Laws Apply to All:
(i) All persons in independent Indian are equal before the law.
(ii) The law cannot discriminate between persons on the basis of their religion, caste or gender.
(iii) All laws apply equally to all citizens of the country and no one can be above the law.
(iv) Any crime or violation of law has a specific punishment.
(v) In ancient India, there were innumerable and overlapping local laws which did not apply equally to all.
(vi) The punishment for the same crime varied depending upon their caste background with lower castes being more harshly penalized.
(vii) The British colonialists introduced the rule of law in India. The colonial rule was arbitrary.
(viii) The British law of the Sedition Act of 1870 set a perfect example of the arbitrariness.
(ix) Under this Act, a person protesting or ciriticising the British government could be arrested without due trial.
(x) Indian nationalists began protesting and criticizing the arbitrary use of authority by the British.
(xi) They began fighting for greater equality and wanted to change the idea of law from a set of rules that they were forced to obey, to law as including ideas of justice.
(xii) By the end of 19th century, the Indian legal profession began emerging and demanded respect in colonial courts.
(xiii) Indian judges began to play a greater role in making decisions.
(xiv) With the adoption of the constitution, laws for the country began to the made by the representatives.
How Do New Laws Come About:
(i) The Parliament has an important role in making laws.
(ii) An important role of Parliament is to be sensitive to the problems faced by people.
(iii) The issue of domestic violence was brough to the attention of the Parliament and the process adopted for this issue to become law.
(iv) The Protection of Women from Domestic Violence Act 2005was implemented to protect women from being abused and injured by male.
(v) The role of citizens is crucial in helping Parliament frame different concerns that people migh have into laws.
Unpopular and Controversial Laws:
(i) Sometimes the Parliament passes laws that turn out to be very popular.
(ii) Sometimes a law can be constitutionally valid and legal, but it can continue to be popular and unacceptable to people because they feel that the intention behind it is unfair and harmful.
(iii) People might criticize this law, hold public meetings, write about it in newspaper, report to TV news channels etc.
(iv) In a democracy, citizens can express their unwillingness to accept repressive laws framed by the Parliament.
(v) When a large member of people begin to feel that a wrong law has been passed, then there is pressure on the Parliament to change this.
(vi) If the law favours one group and disregards the other, it will be controversial and lead to conflict.
(vii) The court has the power to modify or cancel laws if it finds that they don’t adhere to the Constitution.
(viii) In India, people have the right to protest against unjust laws.
FAQs on Class 8 Civics Chapter 4 Notes - Understanding Laws
| 1. What is the importance of laws in society? |  |
| 2. How do laws reflect social justice? |  |
| 3. What are some examples of laws that promote social justice? |  |
| 4. How can individuals contribute to social justice through laws? |  |
| 5. What role do courts play in upholding laws and social justice? |  |