Polynomials (Exercise 2.1) RD Sharma Solutions | Advance Learner Course: Mathematics (Maths) Class 9 PDF Download
Question: 1
Find the zeros of each of the following quadratic polynomials and verify the relationship between the zeroes and their coefficients:
(i) f(x) = x2 – 2x – 8
(ii) g(s) = 4s2 – 4s + 1
(iii) 6x2 – 3 – 7x
(iv) h(t) = t2 – 15
(v) p(x) = x2 + 2√2 x – 6
(vi) q(x) = √3 x2 + 10x + 7√3
(vii) f(x) = x2 - (√3 + 1)x + √3
(viii) g(x) = a(x2 + 1) – x(a2 + 1)
Solution:
(i) f(x) = x2 – 2x – 8
We have,
f(x) = x2 – 2x – 8
= x2 – 4x + 2x – 8
= x (x – 4) + 2(x – 4)
= (x + 2)(x – 4)
Zeroes of the polynomials are – 2 and 4.
Now,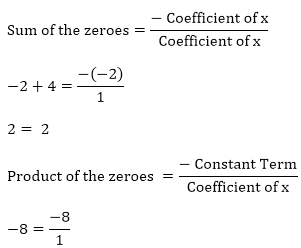
Hence, the relationship is verified.
(ii) g(s) = 4s2 – 4s + 1
We have,
g(s) = 4s2 – 4s + 1
= 4s2 – 2s – 2s + 1
= 2s(2s – 1)− 1(2s – 1)
= (2s – 1)(2s – 1)
Zeroes of the polynomials are 1/2 and 1/2.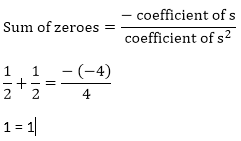
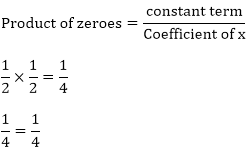
Hence, the relationship is verified.
(iii) 6s2 − 3 − 7x
= 6s2 − 7x − 3 = (3x + 11) (2x – 3)
Zeros of the polynomials are 3/2 and (-1)/3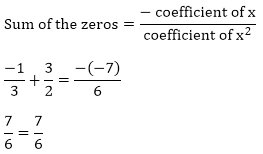
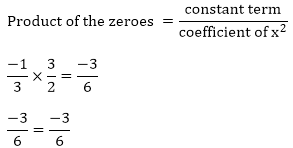
Hence, the relationship is verified.
(iv) h(t) = t2 – 15
We have,
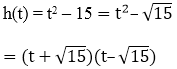
Zeroes of the polynomials are - √15 and √15
Sum of the zeroes = 0 - √15 + √15 = 0
0 = 0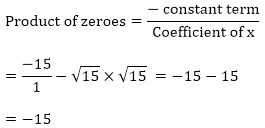
Hence, the relationship verified.
(v) p(x) = x2 + 2√2 x – 6
We have,
p(x) = x2 + 2√2 - 6
= x2 + 3√2x + 3√2x - 6
= x(x + 3√2) - √2(x + 3√2)
= (x + 3√2)(x - √2)
Zeroes of the polynomials are 3√2 and –3√2 Sum of the zeroes
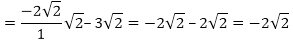
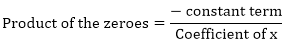
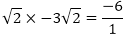
- 6 = – 6
Hence, the relationship is verified.
(vi) q(x) = √3 x2 + 10x + 7√3
q(x) = √3x2 + 10x + 7√3
= √3x2 + 7x + 3x + 7√3
= √3x(x+√3)7(x+√3)
= (x + √3)(7 + √3x)
Zeros of the polynomials are -√3 and -7/√3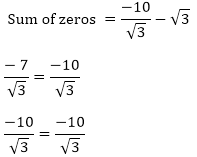
Product of the polynomials are - √3, 7/√3
7 = 7
Hence, the relationship is verified.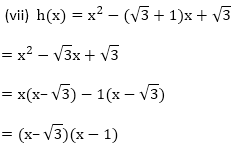
Zeros of the polynomials are 1 and √3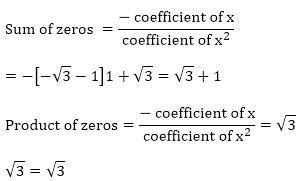
Hence, the relationship is verified
(viii) g(x) = a[(x2 + 1)– x(a2 + 1)]2
= ax2 + a − a2x − x
= ax2 − [(a2x + 1)] + a
= ax2 − a2x – x + a
= ax(x − a) − 1(x – a) = (x – a)(ax – 1)
Zeros of the polynomials are 1/a and 1 Sum of the zeros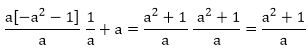
Product of zeros = a/a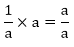
Hence, the relationship is verified.
Question: 2
If α and β are the zeroes of the quadratic polynomial f(x) = x2 – 5x + 4, find the value of 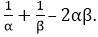
Solution:
We have,
α and β are the roots of the quadratic polynomial.
f(x) = x2 – 5x + 4
Sum of the roots = α + β = 5
Product of the roots = αβ = 4
So,
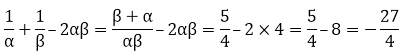
Question: 3
If α and β are the zeroes of the quadratic polynomial f(x) = x2 – 5x + 4, find the value of 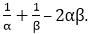
Solution:
Since, α and β are the zeroes of the quadratic polynomial.
p(y) = x2 – 5x + 4
Sum of the zeroes = α + β = 5
Product of the roots = αβ = 4
So,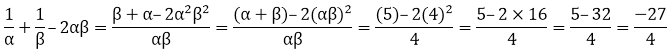
Question: 4
If α and β are the zeroes of the quadratic polynomial p (y) = 5y2 – 7y + 1, find the value of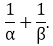
Solution:
Since, α and β are the zeroes of the quadratic polynomial.
p(y) = 5y2 – 7y + 1
Sum of the zeroes = α + β = 7
Product of the roots = αβ = 1
So,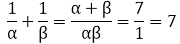
Question: 5
If α and β are the zeroes of the quadratic polynomial f(x) = x2 – x – 4, find the value of 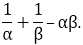
Solution:
Since, α and β are the zeroes of the quadratic polynomial.
We have,
f(x) = x2 – x – 4
Sum of zeroes = α + β = 1
Product of the zeroes = αβ = - 4
So,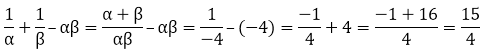
Question: 6
If α and β are the zeroes of the quadratic polynomial f(x) = x2 + x – 2, find the value of 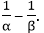
Solution:
Since, α and β are the zeroes of the quadratic polynomial.
We have,
f(x) = x2 + x – 2
Sum of zeroes = α + β = 1
Product of the zeroes = αβ = – 2
So,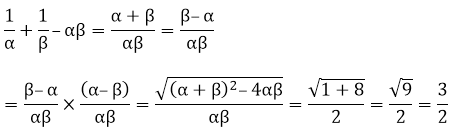
Question: 7
If one of the zero of the quadratic polynomial f(x) = 4x2 – 8kx – 9 is negative of the other, then find the value of k.
Solution:
Let, the two zeroes of the polynomial f(x) = 4x2 – 8kx – 9 be α and − α.
Product of the zeroes = α × − α = – 9
Sum of the zeroes = α + (− α) = – 8k = 0
Since, α – α = 0
⇒ 8k = 0 ⇒ k = 0
Question: 8
If the sum of the zeroes of the quadratic polynomial f(t) = kt2 + 2t + 3k is equal to their product, then find the value of k.
Solution:
Let the two zeroes of the polynomial f(t) = kt2 + 2t + 3k be α and β.
Sum of the zeroes = α + β = 2
Product of the zeroes = α × β = 3k
Now,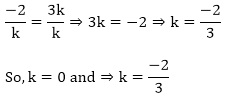
Question: 9
If α and β are the zeroes of the quadratic polynomial p(x) = 4x2 – 5x – 1, find the value of α2β + αβ2.
Solution:
Since, α and β are the zeroes of the quadratic polynomial p(x) = 4x2 – 5x – 1
So, Sum of the zeroes α + β = 5/4
Product of the zeroes α × β = – ¼
Now,
α2β + αβ2 = αβ (α + β)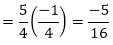
Question: 10
If α and β are the zeroes of the quadratic polynomial
f(t) = t2 – 4t + 3, find the value of α4β3 + α3β4.
Solution:
Since, α and β are the zeroes of the quadratic polynomial f(t) = t2 – 4t + 3
So, Sum of the zeroes = α + β = 4
Product of the zeroes = α × β = 3
Now,
α4β3 + α3β4 = α3β3(α + β)
= (3)3(4) = 108
Question: 11
If α and β are the zeroes of the quadratic polynomial
f(x) = 6x2 + x – 2, find the value of
Solution:
Since, α and β are the zeroes of the quadratic polynomial f(x) = 6x2 + x – 2.
Sum of the zeroes = α + β = -⅙
Product of the zeroes =α × β = -⅓
Now,
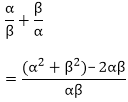
By substitution the values of the sum of zeroes and products of the zeroes, we will get
= - 25/12
Question: 12
If α and β are the zeroes of the quadratic polynomial f(x) = 6x2 + x – 2, find the value of 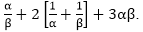
Solution:
Since, α and β are the zeroes of the quadratic polynomial f(x) = 6x2 + x – 2.
Sum of the zeroes = α + β = 6/3
Product of the zeroes = α × β = 4/3
Now,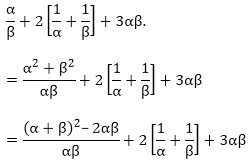
By substituting the values of sum and product of the zeroes, we will get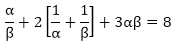
Question: 13
If the squared difference of the zeroes of the quadratic polynomial
f(x) = x2 + px + 45 is equal to 144, find the value of p.
Solution:
Let the two zeroes of the polynomial be αand β.
We have,
f(x) = x2 + px + 45
Now,
Sum of the zeroes = α + β = – p
Product of the zeroes = α × β = 45
So,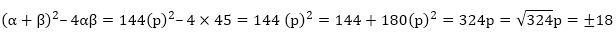
Thus, in the given equation, p will be either 18 or -18.
Question: 14
If α and β are the zeroes of the quadratic polynomial
f(x) = x2 – px + q, prove that 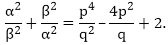
Solution:
Since, α and β are the roots of the quadratic polynomial given in the question.
f(x) = x2 – px + q
Now,
Sum of the zeroes = p = α + β
Product of the zeroes = q = α × β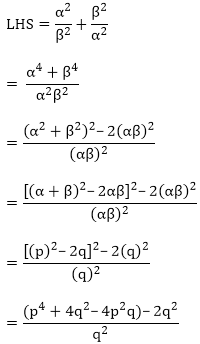
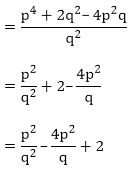
LHS = RHS
Hence, proved.
Question: 15
If α and β are the zeroes of the quadratic polynomial f(x) = x2 – p(x + 1) – c, show that (α + 1)(β + 1) = 1 – c.
Solution:
Since, α and β are the zeroes of the quadratic polynomial
f(x) = x2 – p(x + 1)– c
Now,
Sum of the zeroes = α + β = p
Product of the zeroes = α × β = (- p – c)
So,
(α + 1)(β + 1)
= αβ + α + β + 1
= αβ + (α + β) + 1
= (− p – c) + p + 1
= 1 – c = RHS
So, LHS = RHS
Hence, proved.
Question: 16
If α and β are the zeroes of the quadratic polynomial such that α + β = 24 and α – β = 8, find a quadratic polynomial having α and β as its zeroes.
Solution:
We have,
α + β = 24 …… E-1
α – β = 8 …. E-2
By solving the above two equations accordingly, we will get
2α = 32 α = 16
Substitute the value of α, in any of the equation. Let we substitute it in E-2, we will get
β = 16 – 8 β = 8
Now,
Sum of the zeroes of the new polynomial = α + β = 16 + 8 = 24
Product of the zeroes = αβ = 16 × 8 = 128
Then, the quadratic polynomial is-K
x2– (sum of the zeroes)x + (product of the zeroes) = x2 – 24x + 128
Hence, the required quadratic polynomial is f(x) = x2 + 24x + 128
Question: 17
If α and β are the zeroes of the quadratic polynomial
f(x) = x2 – 1, find a quadratic polynomial whose zeroes are 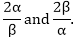
Solution:
We have,
f(x) = x2 – 1
Sum of the zeroes = α + β = 0
Product of the zeroes = αβ = – 1
From the question,
Sum of the zeroes of the new polynomial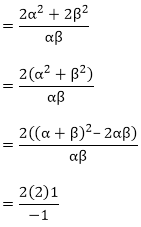
{By substituting the value of the sum and products of the zeroes}
As given in the question,
Product of the zeroes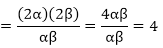
Hence, the quadratic polynomial is
x2 – (sum of the zeroes)x + (product of the zeroes)
= kx2 – (−4)x + 4x2 –(−4)x + 4
Hence, the required quadratic polynomial is f(x) = x2 + 4x + 4
Question: 18
If α and β are the zeroes of the quadratic polynomial f(x) = x2 – 3x – 2, find a quadratic polynomial whose zeroes are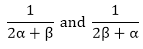
Solution:
We have,
f(x) = x2 – 3x – 2
Sum of the zeroes = α + β = 3
Product of the zeroes = αβ = – 2
From the question,
Sum of the zeroes of the new polynomial 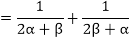
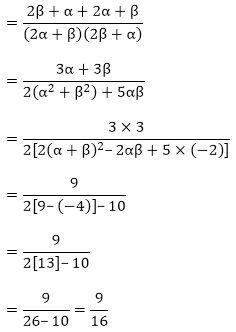
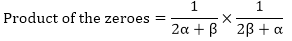
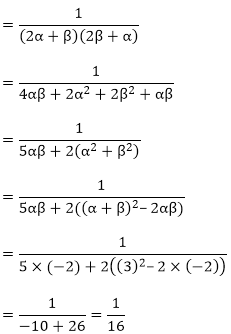
So, the quadratic polynomial is,
x2- (sum of the zeroes)x + (product of the zeroes)
x2 - (sum of the zeroes)x + (product of the zeroes)
Hence, the required quadratic polynomial is k 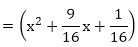
Hence, the required quadratic polynomial is k 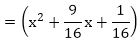
Question: 19
If α and β are the zeroes of the quadratic polynomial f(x) = x2 + px + q, form a polynomial whose zeroes are (α + β)2 and (α – β)2.
Solution:
We have,
f(x) = x2 + px + q
Sum of the zeroes = α + β = -p
Product of the zeroes = αβ = q
From the question,
Sum of the zeroes of new polynomial = (α + β)2 + (α – β)2
= (α + β)2 + α2 + β2 – 2αβ
= (α + β)2 + (α + β)2 – 2αβ – 2αβ
= (- p)2 + (- p)2 – 2 × q – 2 × q
= p2 + p2 – 4q
= p2 – 4q
Product of the zeroes of new polynomial = (α + β)2 (α – β)2
= (- p)2((- p)2 - 4q)
= p2 (p2–4q)
So, the quadratic polynomial is,
x2 – (sum of the zeroes)x + (product of the zeroes)
= x2 – (2p2 – 4q)x + p2(p2 – 4q)
Hence, the required quadratic polynomial is f(x) = k(x2 – (2p2 –4q) x + p2(p2 - 4q)).
Question: 20
If α and β are the zeroes of the quadratic polynomial f(x) = x2 – 2x + 3, find a polynomial whose roots are:
(i) α + 2,β + 2
(ii) 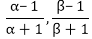
Solution:
We have,
f(x) = x2 – 2x + 3
Sum of the zeroes = α + β = 2
Product of the zeroes = αβ = 3
(i) Sum of the zeroes of new polynomial = (α + 2) + (β + 2)
= α + β + 4
= 2 + 4 = 6
Product of the zeroes of new polynomial = (α + 1)(β + 1)
= αβ + 2α + 2β + 4
= αβ + 2(α + β) + 4 = 3 + 2(2) + 4 = 11
So, quadratic polynomial is:
x2 – (sum of the zeroes)x + (product of the zeroes)
= x2 – 6x +11
Hence, the required quadratic polynomial is f(x) = k(x2 – 6x + 11)
f(x) = k(x2 – 6x + 11)
(ii) Sum of the zeroes of new polynomial 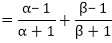
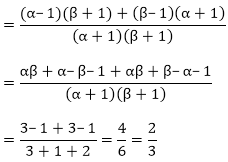
Product of the zeroes of new polynomial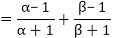
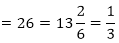
So, the quadratic polynomial is,
x2 – (sum of the zeroes)x + (product of the zeroes)
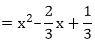
Thus, the required quadratic polynomial is f(x) = k(x2 – 23x + 13)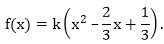
Question: 21
If α and β are the zeroes of the quadratic polynomial f(x) = ax2 + bx + c, then evaluate:
(i) α – β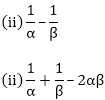
(iv) α2β + αβ2
(v) α4 + β4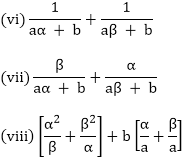
Solution:
f(x) = ax2 + bx + c
Here,
Sum of the zeroes of polynomial = α + β = -b/a
Product of zeroes of polynomial = αβ = c/a
Since, α + β are the roots (or) zeroes of the given polynomial, so
(i) α – β
The two zeroes of the polynomials are -
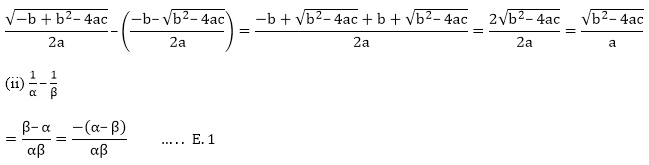
From the previous question, we know that,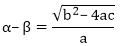
Also,
αβ = c/a
Putting the values in E.1, we will get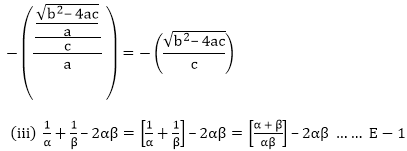
Since,
Sum of the zeroes of polynomial = α + β = – b/a
Product of zeroes of polynomial = αβ = c/a
After substituting it in E-1, we will get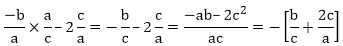
(iv) α2β + αβ2
= αβ(α + β) …….. E- 1.
Since,
Sum of the zeroes of polynomial = α + β = – b/ a
Product of zeroes of polynomial = αβ = c/a
After substituting it in E-1, we will get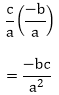
(v) α4 + β4
= (α2 + β2)2 – 2α2β2
= ((α + β)2 – 2αβ)2 – (2αβ)2 ……. E- 1
Since,
Sum of the zeroes of polynomial = α + β = – b/a
Product of zeroes of polynomial = αβ = c/a
After substituting it in E-1, we will get
Since,
Sum of the zeroes of polynomial = α + β = – b/a
Product of zeroes of polynomial = αβ = c/a
After substituting it, we will get
Since,
Sum of the zeroes of polynomial = α + β = – b/a
Product of zeroes of polynomial = αβ = c/a
After substituting it, we will get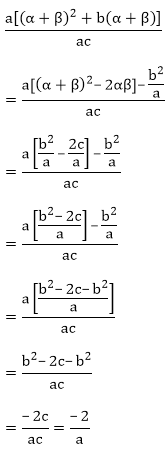
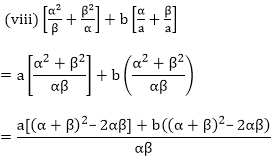
Since,
Sum of the zeroes of polynomial= α + β = – b/a
Product of zeroes of polynomial= αβ = c/a
After substituting it, we will get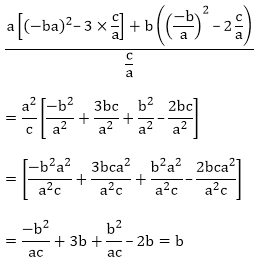
|
13 videos|79 docs|29 tests
|
FAQs on Polynomials (Exercise 2.1) RD Sharma Solutions - Advance Learner Course: Mathematics (Maths) Class 9
| 1. What are polynomials? |  |
| 2. How do you determine the degree of a polynomial? |  |
| 3. Can a polynomial have more than one variable? |  |
| 4. What are the different types of polynomials based on the number of terms? |  |
| 5. How can polynomials be used to solve real-life problems? |  |

















