NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 10 - Ex 10.1,10.2 and 10.3 Practical Geometry- 1
Exercise 10.1
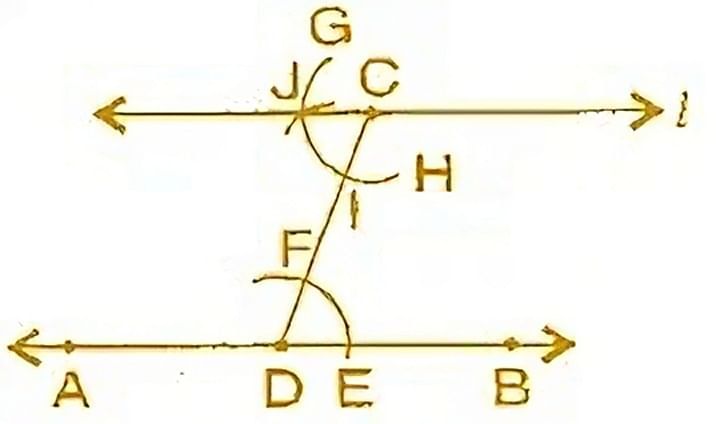
Q.1. Draw a line, say AB, take a point C outside it. Through C, draw a line parallel to AB using ruler and compasses only.
To construct: A line, parallel to given line by using ruler and compasses.
Steps of construction:
(a) Draw a line-segment AB and take a point C outside AB.
(b) Take any point D on AB and join C to D.
(c) With D as centre and take convenient radius, draw an arc cutting AB at E and CD at F.
(d) With C as centre and same radius as in step 3, draw an arc GH cutting CD at I.
(e) With the same arc EF, draw the equal arc cutting GH at J.
(f) Join JC to draw a line l. This the required line .
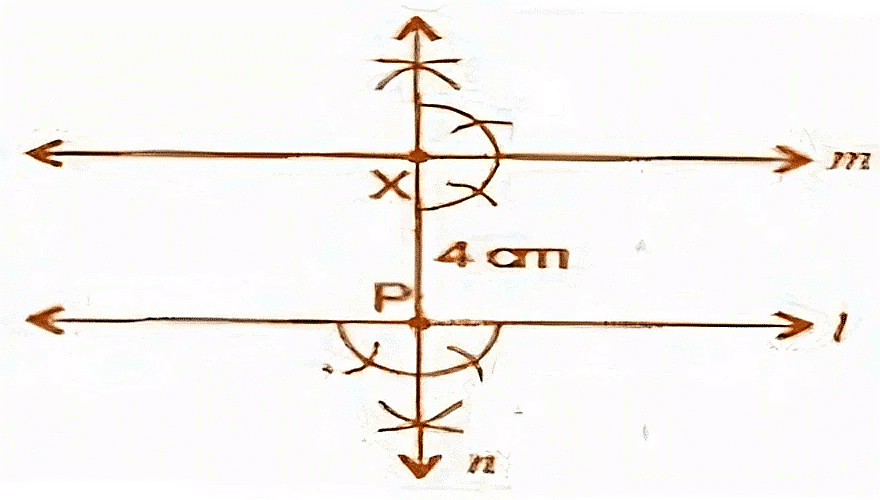
Q.2. Draw a line l. Draw a perpendicular to l at any point on l. On this perpendicular choose a point X, 4 cm away from l. Through X, draw a line m parallel to l.
To construct: A line parallel to given line when perpendicular line is also given.
Steps of construction:
(a) Draw a line l and take a point P on it.
(b) At point P, draw a perpendicular line n.
(c) Take PX = 4 cm on line n.
(d) At point X, again draw a perpendicular line m.
It is the required construction.
Q.3. Let l be a line and P be a point not on l. Through P, draw a line m parallel to l. Now join P to any point Q on l. Choose any other point R on m. Through R, draw a line parallel to PQ. Let this meet l at S. What shape do the two sets of parallel lines enclose?
To construct: A pair of parallel lines intersecting other part of parallel lines.
Steps of construction:
(a) Draw a line l and take a point P outside of l .
(b) Take point Q on line l and join PQ.
(c) Make equal angle at point P such that ∠Q = ∠P.
(d) Extend line at P to get line m.
(e) Similarly, take a point R online m, at point R, draw angles such that ∠P = ∠R.
(f) Extended line at R which intersects at S online l. Draw line RS.
Thus, we get parallelogram PQRS.
Exercise 10.2
Q.1. Construct ΔXYZ in which XY = 4.5 cm, YZ = 5 cm and ZX = 6 cm.
To construct: ΔXYZ, where XY = 4.5 cm, YZ = 5 cm and ZX = 6 cm.
Steps of construction:
(a) Draw a line segment YZ = 5 cm.
(b) Taking Z as centre and radius 6 cm, draw an arc.
(c) Similarly, taking Y as centre and radius 4.5 cm, draw another arc which intersects first arc at point X.
(d) Join XY and XZ. It is the required ΔXYZ.
Q.2. Construct an equilateral triangle of side 5.5 cm.
To construct: A ΔABC where AB = BC = CA = 5.5 cm
Steps of construction:
(a) Draw a line segment BC = 5.5 cm
(b) Taking points B and C as centers and radius 5.5 cm, draw arcs which intersect at point A.
(c) Join AB and AC. It is the required ΔABC.
Q.3. Draw ΔPQR with PQ = 4 cm, QR = 3.5 cm and PR = 4 cm. What type of triangle is this?
To construct: ΔPQR, in which PQ = 4 cm, QR = 3.5 cm and PR = 4 cm.
Steps of construction:
(a) Draw a line segment QR = 3.5 cm.
(b) Taking Q as centre and radius 4 cm, draw an arc.
(c) Similarly, taking R as centre and radius 4 cm, draw an another arc which intersects first arc at P.
(d) Join PQ and PR. It is the required isosceles ΔPQR.
Q.4. Construct ΔABC such that AB = 2.5 cm, BC = 6 cm and AC = 6.5 cm. Measure ∠B.
To construct: ΔABC in which AB = 2.5 cm, BC = 6 cm and AC = 6.5 cm.
Steps of construction:
(a) Draw a line segment BC = 6 cm.
(b) Taking B as centre and radius 2.5 cm, draw an arc.
(c) Similarly, taking C as centre and radius 6.5 cm, draw another arc which intersects first arc at point A.
(d) Join AB and AC.
(e) Measure angle B with the help of protractor. It is the required ΔABC whereB = 80o
Exercise 10.3
Q.1: Construct ΔDEF such that DE = 5 cm, DF = 3 cm and ∠EDF = 90o .
To construct: ΔDEF where DE = 5 cm, DF = 3 cm and m ∠EDF = 90 .
Steps of construction:
(a) Draw a line segment DF = 3 cm.
(b) At point D, draw an angle of 90o with the help of compass i.e., ∠XDF = 90o .
(c) Taking D as centre, draw an arc of radius 5 cm, which cuts DX at the point E.
(d) Join EF. It is the required right angled triangle DEF.
Q.2: Construct an isosceles triangle in which the lengths of each of its equal sides is 6.5 cm and the angle between them is 110o.
To construct: An isosceles triangle PQR where PQ = RQ = 6.5 cm and ∠Q = 110o
Steps of construction:
(a) Draw a line segment QR = 6.5 cm.
(b) At point Q, draw an angle of 110o with the help of protractor, i.e., ∠YQR = 110o
(c) Taking Q as centre, draw an arc with radius 6.5 cm, which cuts QY at point P.
(d) Join PR
It is the required isosceles triangle PQR.
Q.3. Construct ΔABC with BC = 7.5 cm, AC = 5 cm and m ∠C = 60o .
To construct: ΔABC where BC = 7.5 cm, AC = 5 cm and m ∠C = 60o .
Steps of construction:
(a) Draw a line segment BC = 7.5 cm.
(b) At point C, draw an angle of 60 with the help of protractor, i.e., ∠XCB =60o
(c) Taking C as centre and radius 5 cm, draw an arc, which cuts XC at the point A.
(d) Join AB It is the required triangle ABC.
|
276 docs|155 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Maths Chapter 10 - Ex 10.1,10.2 and 10.3 Practical Geometry- 1
| 1. What is Practical Geometry? |  |
| 2. What are the basic tools required for Practical Geometry? |  |
| 3. What are the applications of Practical Geometry in real life? |  |
| 4. What are the different types of geometrical constructions? |  |
| 5. Why is Practical Geometry important for students? |  |