Class 8 Science Question Answers - Materials : Metals and Non-metals (Old Syllabus)
Q19: Explain how metals and non-metals react with water.
Ans:
- Reaction with water:-
Metals react with water to form metal hydroxides and hydrogen.
Eg. Sodium reacts with water to form sodium hydroxide and hydrogen.
2 Na + 2 H2O ----> 2 Na OH + H2
Magnesium reacts with water to form magnesium hydroxide and hydrogen.
Mg + H2O ----> Mg(OH)2+ H2 - Reaction with water:
Non-metals do not react with water
Q20: What do you mean by displacement reaction?
Ans: In a displacement reaction a more reactive metal can replace a less reactive metal, but a less reactive metal cannot replace a more reactive metal.
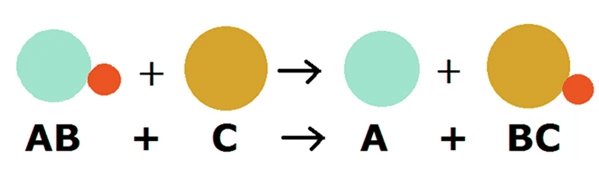
For e.g. Iron replaces copper from copper sulphate solution to form iron sulphate and copper
Fe + CuSO4 →FeSO4+ Cu
Q21: Write down the physical properties of metals.
Ans: Physical properties of metals:
- Metals are solid except mercury.
- Metals are hard.
- Metals are malleable that is can be beaten into thin sheets.
- Metals are ductile that is can be drawn into wires.
- Metals produce ringing sounds are called sonorous.
- Metals are lustrous.
- Metals are good conductors of heat and electricity.
Q22: Write down the physical properties of non-metals.
Ans: Physical properties of non-metals:
- Non- metals are solid, liquid or gas.
- Non- metals which is solid are brittle (diamond is the hardest).
- Non- metals are soft and dull in appearance.
- Non- metals are not malleable, and break down into powdery mass on tapping with a hammer.
- They are not sonorous.
- They are poor conductors of heat and electricity.
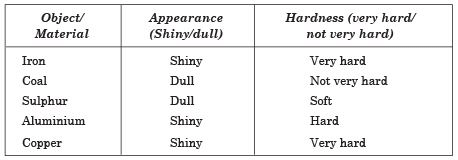
Q. 23. Complete the following table on the basis of appearance and hardness of the materials:

Ans.
Q.24. Have you ever seen a blacksmith beating an iron piece? Do you find a change in the shape of these pieces on beating? Would you expect a similar change in wood log on beating?
Ans. Yes, we have seen blacksmith beating the iron pieces. We have seen the changes in the shape on beating. It increases in size and it does not break.
If a wood log is beaten, it does not change its shape but it breaks into pieces.
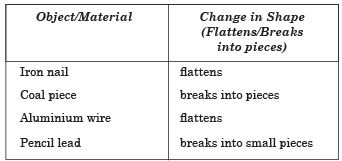
Q. 25. What happens when some materials are beaten? Explain with the help of an activity and write your observations in a table.
Ans. Take a small iron nail, coal piece, aluminium wire and a pencil lead. Beat these materials with a hammer one by one. Record your observation in the following table:
Q.26. What is malleability? Name two most malleable metals.
Ans. We see that the shape of iron and aluminium and other metals changes on beating. This property of metals due to which they can be beaten into thin sheets is called malleability. Silver and gold are the most malleable metals.
Q. 27. Explain that metals are good conductors of electricity with the help of an activity.
Ans. Prepare an electric circuit as shown in the figure. This circuit is used to test whether electricity can pass through a material or not. Repeat this activity with different materials shown in the table.

Observe and group these materials into good conductors and poor conductors:
Electrical Conductivity of Materials
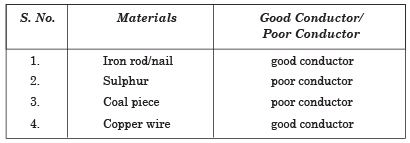 We see that iron nail and copper wire are made of metals and are good conductors. So we can say that metals are good conductors.
We see that iron nail and copper wire are made of metals and are good conductors. So we can say that metals are good conductors.
Q. 28. What happens when a magnesium ribbon is heated in presence of air?
Ans. When a magnesium ribbon is heated in presence of air on a burner flame, after some time it starts burning with a white flame and white powder is formed which is called magnesium oxide.
Mg (Magnesium) + O2 (Oxygen) → MgO (Magnesium Oxide)
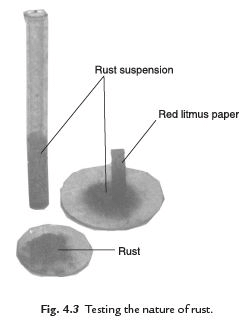
Q. 29. Explain an activity to test the nature of rust.
Ans. Collect some amount of rust after a reaction between iron, oxygen and water. Dissolve it in a very little amount of water. Shake well the mixture of rust and water. Test the solution with the red and blue litmus papers. We observe that the red litmus paper turns into blue. It shows that the nature of rust is basic.
Q. 30. Explain the reaction of sodium and water with the help of an activity.
Ans. Take a beaker, fill it half with water. Cut a small piece of sodium metal. Dry it using filter paper and wrap it in a small piece of cotton. Put the piece of sodium, wrapped in cotton into the beaker. We observe that the beaker becomes hot. We test the solution with red and blue litmus papers. It turns red litmus into blue. This activity indicates that sodium is highly reactive and it reacts vigorously with water. A lot of heat is generated in the reaction to form basic solution of sodium hydroxide.

Q. 31. Explain displacement reaction with the help of an activity.
Ans. Take five beakers of 100 mL and label them A, B, C, D and E. Take about 50 mL of water in each beaker. Dissolve in beakers A and B, a tea spoon of copper sulphate (CuSO4) in beakers C, D and E zinc sulphate (ZnSO4), iron sulphate (FeSO4) and zinc sulphate (ZnSO4), respectively. Put zinc granule (Zn), iron nail (Fe), copper turnings (Cu); copper turnings (Cu) and iron nail (Fe) in the beakers respectively. Observe the changes. We see that in beakers A and B colour is changed while in C, D, E, there is no change of colour. Beakers A and B show the displacement reaction.

Beaker A: Copper sulphate (CuSO4) + Zinc granule (Zn)
Beaker B: Copper sulphate (CuSO4) + Iron nail (Fe)
Beaker C: Zinc sulphate (ZnSO4) Copper turning (Cu)
Beaker D: Iron sulphate (FeSO4) + Copper turning (Cu)
Beaker E: Zinc sulphate (ZnSO4) + Iron nail (Fe)
Reactions:
A: CuSO4 + Zn → ZnSO4 + Cu
B: CuSO4 + Fe → FeSO4 + Cu
C: ZnSO4 + Cu → No change
D: FeSO4 + Cu → No change
E: ZnSO4 + Fe → No change
In these reactions, we have seen that only more reactive metal displaces the less reactive metal but the less reactive metal does not do so.
|
137 videos|271 docs|60 tests
|
FAQs on Class 8 Science Question Answers - Materials : Metals and Non-metals (Old Syllabus)
| 1. What are the properties of metals and non-metals? |  |
| 2. What are some examples of metals and non-metals? |  |
| 3. How are metals and non-metals used in everyday life? |  |
| 4. What is the difference between metals and non-metals in terms of their chemical properties? |  |
| 5. Do metals and non-metals have any common properties? |  |
















