Linear Equations in One Variable Class 8 Notes Maths Chapter 2
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Linear Equation in One Variable |

|
| Solving equation having variables on both sides |

|
| Reducing Equations to Simpler Form |

|
Introduction
In earlier classes, you’ve worked with algebraic expressions like 5x and 2x−3, and equations like 5x=25 and 2x−3=9. Remember, expressions don’t have an equals sign, while equations do. Some expressions have more than one variable, like 2xy+5, but when forming linear equations, we stick to one variable and ensure the variable’s highest power is 1. For example, 2x+1 is linear, but x2 +1 isn’t. In this chapter, we’ll focus on linear equations in one variable, building on what you’ve already learned.
Linear Equation in One Variable
A linear equation in one variable is a special type of equation that has the following features:
- as the name suggests, It has only one variable, usually denoted by x, y, or z.
- now what does linear means ? it means that The variable has a power of 1, which means it is not raised to any other exponent like 2, 3, etc.
- example x-7 = 3 is a linear equation but x2 - 7 = 3 is not a linear equation, because here x is raised to the power of two.

Left Hand Side(LHS)=3x + 4
Right Hand Side(RHS)=10
For x= 2,
Let us take LHS and RHS
LHS= 3(2) + 4 = 6 + 4 = 10
RHS = 10
Now since, LHS = RHS
x = 2 is the solution of the equation.

Constant
A constant is a value or number that never changes in an expression and it’s constantly the same.
Variable
A variable is a letter representing some unknown value. Its value is not fixed, it can take any value. On the other hand, the value of a constant is fixed.
For example, in the expression 3x+4, 3 and 4 are the constants and x is a variable.
Coefficient
A coefficient is any number or numerical value being multiplied to a variable.Terms
A multiplication of constants and variables, is called an algebraic term.
For example, 10x, 5y, 3z, x etc. are all algebraic terms
Algebraic Expressions
When we write one or more algebraic terms together, separated by plus or minus signs, is called an algebraic expression.
For example, 10x + 5y, 4y - 9 + 3z, 2x + 7 - 5, etc. are all algebraic expressions.
Algebraic Equation
Now, what if we want to compare two algebraic expressions using an equal sign? For example, what if we want to say that the amount of money you need to buy x chocolates is equal to the amount of money that is 20 rupees you have in your pocket? Then we can write an equation like this:
10x = 20.
Here, 10x is the algebraic expression on the left side of the equal sign, and 20 is the algebraic expression on the right side of the equal sign. This as a whole is called an equation.
Methods for solving linear equation:- 3 common methods
 Method 1 Method 2
Method 1 Method 2
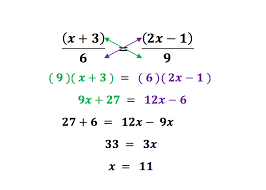 Method 3
Method 3
Note:- Names of the following methods are : Method 1:- Balancing method, Method 2:- Transposing method, Method 3:- Cross multiplication method
Solving equation having variables on both sides
We have seen equations such as 2x-3 = 7, 4y = 2 or 4+3y = 7 that have linear expressions on the one side and numbers on the other side but this might not be the case always.
Both sides could have expressions with variables.
Let us look at some of the examples.
Example: Solve 2x – 4 = x + 2
We have 2x – 4 = x + 2
we get
2x = x + 2 + 4
2x = x + 6
2x – x = x + 6 – x (subtracting x from both sides)
x = 6 is the required answer.
Example : Solve 5x + 7/2 = 3/2x -14, then x= ?
Reducing Equations to Simpler Form
For example: Solve 
Multiplying both sides by 6, we get
2 (6x + 1) + 6 = x – 3
12x + 2 + 6 = x –3
12x + 8 = x – 3
12x – x + 8 = – 3
11x + 8 = – 3
11x = –3 – 8
11x = –11
x = – 1
Example: Solve 5x – 2 (2x – 7) = 2 (3x – 1) + 9/2
LHS = 5x – 4x + 14 = x + 14
RHS = 6x – 2+
Now,
x + 14= 6x +
14 -= 6x –x
So, x = 2.3
Example: Solve
Here, the given equation is not in linear forms.
On cross multiplying, we get
10(x+1) = 3(2x + 3)So it gets converted into the linear form.
Now, 10x + 10 = 6x + 9
Transposing 10 and 6x to the other side, we get
10x – 6x = 9 – 10
4x = -1
Dividing both sides by 4, we get
Example:
Solve the equation:
Solution:
Combine like terms:
Isolate
Divide both sides by 14 to solve for
Final Answer:
|
79 videos|408 docs|31 tests
|
FAQs on Linear Equations in One Variable Class 8 Notes Maths Chapter 2
| 1. How do you solve linear equations in one variable? |  |
| 2. What is the process for solving equations with variables on both sides? |  |
| 3. How can you reduce equations to a simpler form? |  |
| 4. What are the common mistakes to avoid when solving linear equations in one variable? |  |
| 5. How do you know if a linear equation in one variable has a solution or is inconsistent? |  |






 = 6x –x
= 6x –x





















