Adjectives | English Grammar for Class 6 PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What are Adjectives? |

|
| Types of Adjectives |

|
| Nouns Used as Adjectives |

|
| Verbs Used as Adjectives |

|
| Comparison of Adjectives |

|
What are Adjectives?
- An adjective is a word that adds more detail to a noun or pronoun.
- For example, in the sentence, "The rose is a beautiful flower," the word "beautiful" adds information about the rose, describing its appearance.
Similarly, in "Geeta is an intelligent girl," the word "intelligent" tells us about Geeta's smartness, and in "Monkeys have long tails," "long" describes the tails of the monkeys. - These descriptive words are called adjectives because they give us more information about the nouns in the sentences.

Types of Adjectives
1. Adjectives of Quality
Words that describe the qualities of a noun or pronoun are called adjectives of quality.
Examples:
- The milk is cold.
- Vinay is thin.
- Golu is fat.
- The cake looks delicious.
2. Adjectives of Quantity
Words that indicate the quantity of a noun are called adjectives of quantity. These adjectives show "how much."
Examples:
- There was little food left on the plate.
- How many books do you want?
- I need some money.
- There was no milk in the jar.
3. Adjectives of Number or Numeral Adjectives
These adjectives indicate the number of people or things, showing "how many."
Examples:
- I have ten candies.
- Several passengers boarded the bus.
- I have many classmates.
Difference between Adjectives of Quantity and Adjectives of Number:
Nouns can be either countable or uncountable.
- Adjectives of quantity are used with uncountable nouns, like water, milk, and sugar.
Examples: much water, little sugar, sufficient milk - Adjectives of number are used with countable nouns, like books and chairs.
Examples: many bottles - Some adjectives, such as "some," "sufficient," and "few," can be used with both countable and uncountable nouns.
Examples: some rice, some children
4. Demonstrative Adjectives
These adjectives are used to point out specific people or things. Common demonstrative adjectives include "this," "that," "these," "those," and "such."
Examples:
- You should not believe such people.
- This truck is heavy.
Remember
A demonstrative pronoun stands alone while a demonstrative adjective is followed by a noun.
Examples:
That is a gift for you. (Demonstrative pronoun)
That book is good. (Demonstrative adjective + noun)
5. Interrogative Adjectives
These adjectives are used with nouns to ask questions. The common interrogative adjectives are "which," "what," and "whose."
Examples:
- Which fruit do you like most?
- Whose car is this?
- Which class are you in?
- Which book do you want to buy?
Remember
Interrogative adjectives differ from interrogative pronouns in the manner that the former is followed by nouns in sentences.
6. Possessive Adjectives
Possessive adjectives show ownership or possession, indicating to whom something belongs.
Examples:
- The team's success was due to their hard work and dedication.
- Her brother's drawing won first place in the art contest.
Nouns Used as Adjectives
Nouns can be used as adjectives while keeping their original form. In this case, the noun describes another noun.
Examples:
- Rohan gave Meera a silk scarf.
(Here, silk acts as an adjective, describing the scarf, which is a noun.) - Rohan gave Meera a scarf made of fine silk.
(Here, silk is used as a noun.)
Verbs Used as Adjectives
The present and past participles of verbs can function as adjectives.
Examples:
- Last night, Grandma told us an engaging story.
- Throw away all your worn-out shoes.
- The injured athlete was taken to the hospital.
Comparison of Adjectives
Comparing adjectives helps us describe how things differ from each other. When we want to say that something is more, less, or the same as something else, we use comparative forms. The three forms of comparison are positive, comparative, and superlative.
1. Positive Degree
The positive degree describes a noun or action without any comparison.
Example:
- The black puppy is cute and playful.
2. Comparative Degree
The comparative degree is used when comparing two things or actions. To form the comparative, we often add "er" to short adjectives or "more" before longer adjectives.
Examples:
- I found that the black puppy was cuter and more playful than the kitten.
- I am smarter than my cousin.
3. Superlative Degree
The superlative degree is used when comparing more than two things or actions, showing that something has the highest or most extreme quality. To form the superlative, we often add "est" to short adjectives or "most" before longer adjectives.
Examples:
- Later, I realized that the rabbit was the cutest and most playful of all the animals in the shop.
- The parrot was the most colorful and most interesting bird in the aviary.
Formation of Comparative & Superlative Degrees of Adjectives
Adjectives usually form their comparative and superlative degrees:
1) By addition of '-er' and '-est' to the positive degree
2) By addition of '-r' and '-st' to the positive degree ending in 'e'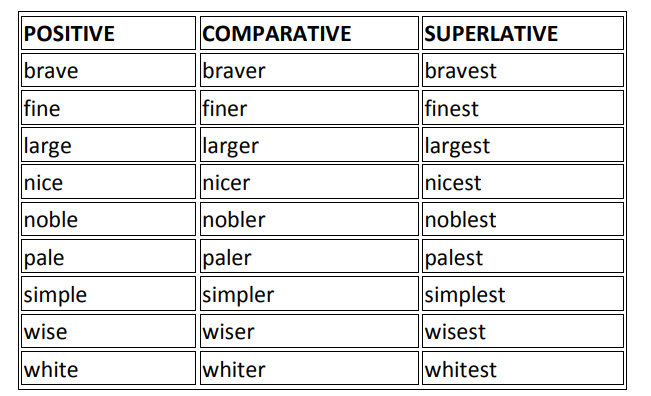
3) When the positive ends in 'y' and has a consonant before it, we change 'y' into 'i' and then add 'er' and
'est'.
4) When the positive degree ends in a consonant with a vowel before it, we double the consonant & then
add '-er' and '-est'
5) By addition of '-er' and '-est' to the positive degree when it ends in '-y'
6) By placing 'more' and 'most' before the positive form
7) Some adjectives do not follow any of the rules explained earlier. They are compared irregularly. Here are
the different forms of such adjectives.
|
47 videos|188 docs|46 tests
|
FAQs on Adjectives - English Grammar for Class 6
| 1. What is the definition of adjectives? |  |
| 2. How do adjectives help in improving the quality of a sentence? |  |
| 3. Can adjectives be used to compare different nouns or pronouns? |  |
| 4. What are some common examples of adjectives? |  |
| 5. How can adjectives be identified in a sentence? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 6 exam
|

|


















