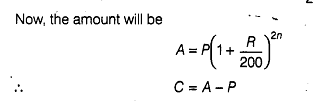NCERT Exemplar Solutions: Comparing Quantities | Mathematics (Maths) Class 8 PDF Download
Multiple Choice Questions
Q1: Suppose for the principal P, rate R% and time T, the simple interest is S and compound interest is C. Consider the possibilities.
(i) C > S
(ii) C = S
(iii) C < S
Then:
(a) only (i) is correct.
(b) either (i) or (ii) is correct.
(c) either (ii) or (iii) is correct.
(d) only (iii) is correct.
Answer: (a)
Solution: Let Principal, P = Rs. 100, Rate = 10% and Time = 1 year
Simple interest (SI)= (P×R×T)/100 = (100×10×1)/100 = Rs.10
Since, Amount = P(1+R/100)T=100(1+10/100)1= 100(11/10) = Rs. 110
Compound interest (CI) = Amount – Principal = 110 -100 = 10
So, CI>SI
Q2: Suppose a certain sum doubles in 2 years at r % rate of simple interest per annum or at R% rate of interest per annum compounded annually. We have
(a) r < R
(b) R < r
(c) R = r
(d) can’t be decided
Answer: (b)
Solution: If the total amount received in 2yr is same for both simple interest and compound interest on same principal, then the rate of simple interest is greater than the rate of compound interest.i.e. R < r.
Q3: The compound interest on Rs 50,000 at 4% per annum for 2 years compounded annually is
(a) Rs 4,000
(b) Rs 4,080
(c) Rs 4,280
(d) Rs 4,050
Answer: (b)
Solution: P = Rs.50000, R = 4%, T = 2 years
A = P(1+R/100)T = 50000(1+4/100)2 = 50000(1+1/25)2
A = 50000(26/25)2 = 54080
Compound interest = A – P = 54080 – 50000 = Rs. 4080
Q4: If marked price of an article is Rs 1,200 and the discount is 12% then the selling price of the article is
(a) Rs 1,056
(b) Rs 1,344
(c) Rs 1,212
(d) Rs 1,188
Answer: (a)
Solution: Marked price = Rs.1200
Discount = 12%
Since, Discount = Discount% on Marked price
Discount price = 12% of 1200 = 12/100 × 1200 = 12 × 12 = 144
Selling price = Marked price-discount price = 1200 – 144 = Rs. 1056
Q5: If 90% of x is 315 km, then the value of x is
(a) 325 km
(b) 350 km
(c) 350 m
(d) 325 m
Answer: (b)
Solution: 90% of x is 315 km
90/100 × x = 315
X = 315 × 100/90 = 315 × 10/9 = 350
Q6: To gain 25% after allowing a discount of 10%, the shopkeeper must mark the price of the article which costs him Rs 360 as
(a) Rs 500
(b) Rs 450
(c) Rs 460
(d) Rs 486
Answer: (a)
Solution: Say, marked price = x
Cost price = Rs.360
As per the question;
x – [x×(10/100)] – [(25×360)/100] = 360
x – x/10 – 90 = 360
9x/10 = 360 + 90
9x = 4500
x = 500
Q7: If a % is the discount per cent on a marked price x, then discount is
(a) (x/a) × 100
(b) (a/x) × 100
(c) x × (a/100)
(d) 100/(x × a)
Answer: (c)
Solution: (Discount = Discount% on Marked Price)
Q8: Ashima took a loan of Rs 1,00,000 at 12% p.a. compounded half-yearly. She paid Rs.1,12,360. If (1.06)2 is equal to 1.1236, then the period for which she took the loan is:
(a) 2 years
(b) 1 year
(c) 6 months
(d) 1(1/2) years
Answer: (b)
Solution: P = Rs.100000, R = 12% per annum compounded half-yearly.
Amount = Rs.112360
Since we know,
A = P (1+R/100)T
112360 = 100000(1+12/100)T
112360/100000 = (1+12/100)T
(1.1236)1 = (1.12)T
If we compare the base terms, 1.1236 is approximately equal to 1.12
Hence, T = 1 year.
Q9: For calculation of interest compounded half yearly, keeping the principal same, which one of the following is true.
(a) Double the given annual rate and half the given number of years.
(b) Double the given annual rate as well as the given number of years.
(c) Half the given annual rate as well as the given number of years.
(d) Half the given annual rate and double the given number of years.
Answer: (d)
Solution: If interest is compounded half-yearly, then R=R2 and T=2T=2n
So, half the given annual rate and double the given number of years. Hence, option (d) is correct.
Q10: Shyama purchases a scooter costing Rs 36,450 and the rate of sales tax is 9%, then the total amount paid by her is:
(a) Rs 36,490.50
(b) Rs 39,730.50
(c) Rs 36,454.50
(d) Rs 33,169.50
Answer: (b)
Solution: Scooter cost Rs.36450 at the rate of sales tax = 9%.
Total cost of scooter paid by Shyama = 9% of 36450 + 36450 = (9/100 × 36450) + 36450
= 3280.5 + 36450
= 39730.5
Q11: The marked price of an article is Rs 80 and it is sold at Rs 76, then the discount rate is:
(a) 5%
(b) 95%
(c) 10%
(d) appx. 11%
Answer: (a)
Solution: Marked price = Rs. 80
Sold price = Rs.76
We know that,
Selling price = Marked price – Discount
Discount = Marked price – Selling price
Discount = Rs.80-Rs.76 = Rs.4
Discount % = 4/80 x 100 = 5%
Q12: A bought a tape recorder for Rs 8,000 and sold it to B. B in turn sold it to C, each earning a profit of 20%. Which of the following is true:
(a) A and B earn the same profit.
(b) A earns more profit than B.
(c) A earns less profit than B.
(d) Cannot be decided.
Answer: (c)
Solution: Cost price of tape recorder bought by A = Rs.8000
Cost price of tape recorder for B =20% profit on cost price for A
= 20/100 x 8000 + 8000
= 20 x 80 + 8000
= 1600 + 8000
= Rs.9600
Cost price of tape recorder sold to C = 20% profit on cost price for B
= 20/100 x 9600 + 9600
=1929 + 9600
= Rs.11520
Here, profit for A= Rs.1600 Profit for B = Rs.1920
So, A earns less profit than B.
Q13: Latika bought a teapot for Rs 120 and a set of cups for Rs 400. She sold teapot at a profit of 5% and cups at a loss of 5%. The amount received by her is:
(a) Rs 494
(b) Rs 546
(c) Rs 506
(d) Rs 534
Answer: (c)
Solution: Price of teapot = Rs. 120
Price of set of cups = Rs. 400
Latika sold teapot at a profit of 5%
Selling price of teapot = 5/100 x 120 + 120
= 120/20 +120
= 6 + 120 = Rs.126
Also, cups were sold at a loss of 5%.
Now, selling price of cups = 400 –5/100 x 400
= 400 – 20
= Rs. 380
Therefore, total amount received = Rs. 126 + Rs. 380 = Rs. 506
Q14: A jacket was sold for Rs 1,120 after allowing a discount of 20%. The marked price of the jacket is:
(a) Rs 1440
(b) Rs 1400
(c) Rs 960
(d) Rs 866.66
Answer: (b)
Solution: Let marked price = x
Discount = 20%
Selling price = 1120
Hence, 1120 = x – x× 20/100
1120 = x – x/5
1120 = 4x/5
x = (1120×5)/4 = 1400
Q15: A sum is taken for two years at 16% p.a. If interest is compounded after every three months, the number of times for which interest is charged in 2 years is:
(a) 8
(b) 4
(c) 6
(d) 9
Answer: (a)
Solution: Rate of interest is compounded after every three months. Thus, the time period for amount in a year will be 4 times.
If amount is taken for 2 year, then 4×2 = 8 times charged in 2 year.
Q16: The original price of a washing machine which was bought for Rs 13,500 inclusive of 8% VAT is:
(a) Rs 12,420
(b) Rs 14,580
(c) Rs 12,500
(d) Rs 13,492
Answer: (a)
Solution: The original price of the washing machine = Rs.13500
VAT = 8%.
The original price of the washing machine including of 8% VAT
= 13500-13500 x 8/100
= 13500-135 x 8
= 13500-1080
= Rs.12420
Q17: Avinash bought an electric iron for Rs 900 and sold it at a gain of 10%. He sold another electric iron at 5% loss which was bought Rs 1200. On the transaction he has a:
(a) Profit of Rs 75
(b) Loss of Rs 75
(c) Profit of Rs 30
(d) Loss of Rs 30
Answer: (c)
Solution: Price of electric iron = Rs. 900
Sold at 10% profit
Now, selling price of the electric iron = (10/1000) x 900 + 900 = 90+ 900 = Rs.990
Another electric iron sold at 5% loss.
Cost price of another electric iron = Rs.1200
Thus, selling price of the electric iron = 1200 – 1200 x (5/100) = 1200 – 60 = Rs.1140
Total cost paid by Avinash for purchasing electric irons = Rs.900 + Rs.1200 = Rs.2100
Total received amount = Rs.990 + Rs.1140 = Rs. 2130
Therefore, his profit = Rs.2130- Rs.2100 = Rs.30
Q18: A TV set was bought for Rs 26,250 including 5% VAT. The original price of the TV set is
(a) Rs 27,562.50
(b) Rs 25,000
(c) Rs 24,937.50
(d) Rs 26,245
Answer: (c)
Solution: Cost price of TV set = Rs. 26250.
VAT including = 5%
Original price = Cost price of article including VAT = 26250 – (5/100) x 26250
= 26250-1312.5
= 24,937.50
Therefore, original price of TV set is = Rs. 24,937.50
Q19: 40% of [100 – 20% of 300] is equal to:
(a) 20
(b) 16
(c) 140
(d) 64
Answer: (b)
Solution: 40% of [100 – 20% of 300]
= 40% × [100 – (20/100×300)]
= 40% × [100 – 60]
= 40/100 × 40
= 16
Q20: Radhika bought a car for Rs 2,50,000. Next year its price decreased by 10% and further next year it decreased by 12%. In the two years overall decrease per cent in the price of the car is
(a) 3.2%
(b) 22%
(c) 20.8%
(d) 8%
Answer: (c)
Solution: Radhika bought a car for Rs. 250000.
Cost price = Rs.250000
Its price decreased next year for 10%.
Thus, new price = 250000 – (10/100) × 250000
= 250000 – 25000 = 225000
Again, the price of car decreased by 12% next year. So the price will be:
=225000 – 225000 × (12/100)
= 225000 – 27000
= 198000
So, the overall decrease in percentage of car price = (250000-198000)/250000 × 100
= (52000/250000) × 100 = 520/25 = 20.8%
Fill in the blanks
Q21: ________ is a reduction on the marked price of the article
Answer: Discount
Q22: Increase of a number from 150 to 162 is equal to increase of ____ per cent.
Answer: 8%
Solution: Increase of a number from 150 to 162 = 162-150 = 12
Percentage of increased number = 12/150 × 100 = 120/15 = 8%
Q23: 15% increase in price of an article, which is Rs.1,620, is the increase of ____.
Answer: Rs.212
Solution: Let x is the price of the article.Thus, as per given question;
1620 = x + x × (15/100)
1620 = 115x/100
115x = 1620 × 100
x = (1620×100)/115
x = 1408
Hence, increase in price = 1620 – 1408 = 212.
Q24: Discount = _______-_______.
Answer: Discount = Marked Price – Selling Price.
Q25: Discount = Discount % of ______.
Answer: Discount = Discount % of Marked Price.
Q26: _____ is charged on the sale of an item by the government and is added to the bill amount.
Answer: Sales tax
Q27: Amount when interest is compounded annually is given by the formula ______.
Answer: A = P(1+R/100)T [P = Principal, R = Rate, T = time]
Q28: Sales tax = tax % of _______.
Answer: Bill amount
Q29: The time period after which the interest is added each time to form a new principal is called the _______.
Answer: Conversion period
Q30: ______ expenses are the additional expenses incurred by a buyer for an item over and above its cost of purchase.
Answer: Overhead
Q31: The discount on an item for sale is calculated on the _______.
Answer: Marked price
Q32: When principal P is compounded semi-annually at r % per annum for t years, then Amount = ______.
Answer: A = P(1+R/200)2t
Q33: Percentages are equal to fractions with _________ equal to 100.
Answer: Denominator
Q34: The marked price of an article when it is sold for Rs. 880 after a discount of 12% is ______.
Answer: Rs.1000
Solution: Selling price = Rs.880
Discount percentage = 12%
Let x be the marked price.
Since, discount is calculated on marked price, thus;
x – x × (12/100) = 880
88x /100 = 880
x = 10 × 100 = 1000
Q35: The compound interest on Rs 8,000 for one year at 16% p.a. compounded half yearly is ______, given that (1.08)2 = 1.1664.
Answer: Rs. 9331.2
Solution: Principal = Rs.8000
Time period = 1 year
Rate = 16% = 16/100 = 0.16
Amount = P ( 1+r/n)nt
n = 2 (compounded half yearly in a year)
A = 8000(1+0.16/2)2×1 = 8000 (1+0.08)2 = 8000 (1.08)2
A = 8000 × 1.1664
A = 9331.2
Q36: In the first year on an investment of Rs. 6,00,000 the loss is 5% and in the second year the gain is 10%, the net result is ____.
Answer: 627000
Solution: Investment amount = 600000
Loss in first year = 5%.
So, investment in first year = 600000 – (5/100) x 600000 = 600000 – 30000 = 570000
In second year, the gain is 10%.
So, net result = 570000 + (10/100) x 570000 = 570000 + 57000 = 627000
Q37: If amount on the principal of Rs 6,000 is written as 6000 [1+5/100]3 and compound interest payable half yearly, then rate of interest p.a. is ____ and time in years is ______.
Answer: Rate – 10% and 1.5 years
Q38: By selling an article for Rs 1,12,000 a girl gains 40%. The cost price of the article was _______.
Answer: Rs.80000
Solution: Selling price of the article = ₹112000
Gain% = 40%
Say, x is the cost price of the article.
Since, cost price = selling price – profit % on cost price
Therefore, Selling price = cost price + profit % on cost price
Hence,
112000 = x + x × (40/100)
112000 = x + (2/5)x
112000 = 7x/5
x = (112000 × 5)/7
x = 80000
Q39: The loss per cent on selling 140 geometry boxes at the loss of S.P. of 10 geometry boxes is equal to ______.
Answer: 20/3%
Solution: Say, the selling price of one geometry box = Rs.1
So, the selling price of 140 geometry boxes = 1 × 140 = Rs.140
Selling price of 10 geometry boxes = Rs.10
Loss = Rs. 10
Loss percentage = Loss/CP × 100
= 10/(140+10) × 100
= 10/150 × 100
= 20/3%
Q40: The cost price of 10 tables is equal to the sale price of 5 tables. The profit per cent in this transaction is ______.
Answer: 100%
Solution: Say, the cost price of one table is Rs.1
Cost price of 10 tables = Sale price of 5 tables (Given)
Sale price of 5 tables profit = cost price of 5 tables = Rs. 5
Profit percentage = Profit/CP × 100
= 5/5 × 100 = 100%
Q41: Abida bought 100 pens at the rate of Rs 3.50 per pen and pays a sales tax of 4%. The total amount paid by Abida is ______.
Answer: Rs.364
Solution: Number of pens = 100
Rate of per pen = Rs.3.50
Cost of 100 pens = 100 × 3.50 = 350
Sales tax on pen = 4%
Total amount paid = 350 × (4/100) + 350
= 350 × 1/25 + 350
= 14 + 350
= 364
Q42: The cost of a tape-recorder is Rs 10,800 inclusive of sales tax charged at 8%. The price of the tape-recorder before sales tax was charged is _______.
Answer: Rs.10000
Solution: Cost of tape recorder = Rs.10800
Say, the cost before including the tax = x
Therefore,
x + x×(8/100) = 10800
(100x+8x)/100 = 10800
108x = 1080000
x = 10000
Q43: 2500 is greater than 500 by _______.
Answer: 400%
Solution: 2500 – 500 = 2000
Percentage increase in 500 to 2500 = (2000/500) × 100
= 2000/5 = 400
Q44: Four times a number is a ____ increase in the number.
Answer: 300%
Solution: Let the number be x
Four times of number = 4x
4x is greater than x by = 4x – x = 3x
Percentage increase in x = 3x/x × 100 = 300%
Q45: 5% sales tax is charged on an article marked Rs 200 after allowing a discount of 5%, then the amount payable is ______.
Answer: Rs.199.50.
Solution: Marked price = Rs. 200
Discount = 5%
Selling price = 200 – (5/100) × 200
= 200-10
= 190
Selling price including 5% tax = 190+(5/100)×190
= 190 + 9.5
= Rs. 199.5
True Or False
Q46: To calculate the growth of a bacteria if the rate of growth is known, the formula for calculation of amount in compound interest can be used.
Answer: True
Q47: Additional expenses made after buying an article are included in the cost price and are known as Value Added Tax.
Answer: False
Q48: Discount is a reduction given on cost price of an article.
Answer: False
Q49: Compound interest is the interest calculated on the previous year’s amount.
Answer: True
Q50: C.P. = M.P. – Discount.
Answer: False
|
79 videos|408 docs|31 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar Solutions: Comparing Quantities - Mathematics (Maths) Class 8
| 1. What are the key concepts covered in the NCERT Exemplar Solutions for Comparing Quantities? |  |
| 2. How can I use the NCERT Exemplar Solutions to improve my understanding of comparing quantities? |  |
| 3. Are the NCERT Exemplar Solutions beneficial for exam preparation? |  |
| 4. What types of questions can I expect in the Comparing Quantities chapter of the exam? |  |
| 5. How can I effectively solve problems related to profit and loss using NCERT Exemplar Solutions? |  |