NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Geography - Motions of The Earth
Q1. Answer the following questions briefly.
(a) What is the angle of inclination of the earth’s axis with its orbital plane?
Ans: The angle of inclination of the earth’s axis with its orbital plane is 66 ½º.
- The axis of the Earth is tilted at an angle of 23 ½° from a perpendicular to the orbital plane. This tilting of the axis is called the inclination of the Earth's axis.
- Due to this inclination, the axis of the Earth makes an angle of 66 ½º with the plane of the Earth's orbit.
 Inclination of Earth's Axis & Orbital Plane
Inclination of Earth's Axis & Orbital Plane
(b) Define rotation and revolution.
Ans: Rotation and revolution are two fundamental motions of the Earth in its celestial environment: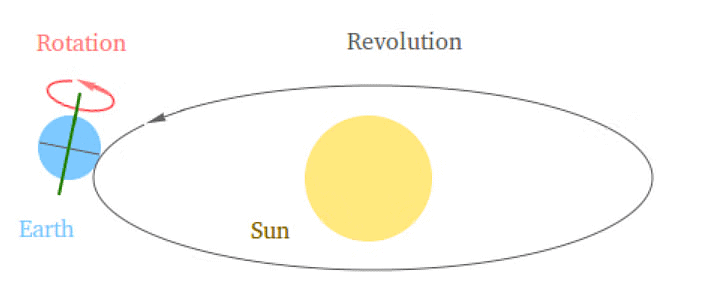 Rotation & Revolution of Earth
Rotation & Revolution of Earth
1. Rotation:
- Definition: Rotation refers to the spinning or turning of the Earth around its own axis. The Earth completes one full rotation approximately every 24 hours.
- Axis: The imaginary line around which the Earth rotates is called its axis. The Earth's axis is an imaginary line that runs from the North Pole to the South Pole.
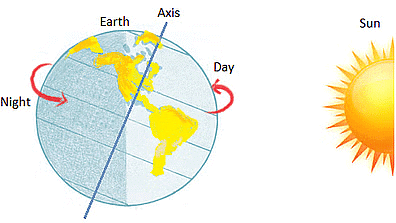
- Effects: Rotation is responsible for day and night. As the Earth rotates, different parts of it face the Sun, experiencing daylight, while the opposite side experiences darkness.
 Day and Night due to the Rotation of Earth
Day and Night due to the Rotation of Earth
2. Revolution:
- Definition: Revolution refers to the Earth's orbit around the Sun. The Earth completes one full orbit around the Sun approximately every 365.25 days.
- Orbit: The Earth follows an elliptical (oval-shaped) path around the Sun.
- Effects: Revolution is responsible for the changing seasons. As the Earth orbits the Sun, the tilt of its axis causes different parts of the Earth to receive varying amounts of sunlight at different times of the year.
 Seasons due to the Revolution of Earth
Seasons due to the Revolution of Earth
(c) What is a leap year?
Ans: Every fourth year, February has 29 days instead of 28 days. Such a year with 366 days is called a leap year.
- A leap year is like a bonus year we get every four years. Normally, a year is 365 days, but the Earth takes a bit more time, about 365 days and 6 hours, to go around the Sun.
- Since it's hard to have a year with 6 extra hours, we just say a year is 365 days to keep it simple. But, those extra hours add up over four years, and we end up with almost a full day left over. So, to catch up, we add that extra day to February in a leap year.
- That's why, every four years, February gets 29 days instead of 28. This helps our calendars match up with how long it really takes for the Earth to complete its trip around the Sun.
(d) Differentiate between the Summer and Winter Solstice.
Ans: Here is the detailed difference between Summer and Winter Solstice:

 Summer & Winter Solstice
Summer & Winter Solstice
(e) What is an equinox?
Ans: On 21st March and September 23rd, direct rays of the sun fall on the equator. At this position, neither of the poles is tilted towards the sun. Therefore, the whole earth experiences equal days and equal nights. This is called an equinox.
(f) Why does the Southern Hemisphere experience Winter and Summer Solstice at different times than that of the Northern Hemisphere?
Ans:
The Southern Hemisphere undergoes Winter and Summer Solstices at different times than the Northern Hemisphere due to the tilt of the Earth's axis.
- During the Northern Hemisphere's Summer Solstice, the North Pole is inclined toward the Sun, resulting in summer for the Northern Hemisphere. Simultaneously, the South Pole is tilted away from the Sun, causing Winter Solstice in the Southern Hemisphere.
- Conversely, during the Northern Hemisphere's Winter Solstice, the North Pole is tilted away from the Sun, leading to winter in the Northern Hemisphere. At the same time, the South Pole is tilted toward the Sun, resulting in the Summer Solstice for the Southern Hemisphere. This axial tilt accounts for the seasonal variations experienced in each hemisphere.
(g) Why do the poles experience about six months of day and six months of night?
Ans: The reason why the North and South Poles have about six months of day and six months of night is because the Earth is a bit tilted, like a spinning top.
- When the top part (Northern Hemisphere) is leaning toward the Sun, the North Pole gets a lot of daylight, and it's summer there. At the same time, the bottom part (Southern Hemisphere) is leaning away from the Sun, so the South Pole has lots of nighttime and it's winter there.
- After some months, it's the other way around. The bottom part (Southern Hemisphere) leans toward the Sun, so the South Pole gets lots of daylight and has its summer. Meanwhile, the top part (Northern Hemisphere) is tilted away, so the North Pole has more nighttime and it's winter there. This happens because the Earth is always spinning and going around the Sun.
 6 Month Day and 6 Month Night at Poles
6 Month Day and 6 Month Night at Poles
Learn in detail about all the important terms related to the earth and its motion through this video:
Q2. Tick the correct answers.
(a) The movement of the earth around the sun is known as
(i) Rotation
(ii) Revolution
(iii) Inclination
Ans: (ii) Revolution
Explanation: The Earth's movement around the Sun is called revolution. Rotation is the Earth's spin on its own axis.
(b) Direct rays of the sun fall on the equator on
(i) 21 March
(ii) 21 June
(iii) 22 December
Ans: (i) 21 March
Explanation: Around March 21st, during the vernal equinox, the Sun's rays fall directly on the equator.
(c) Christmas is celebrated in summer in
(i) Japan
(ii) India
(iii) Australia
Ans: (iii) Australia
Explanation: Australia is in the Southern Hemisphere, and December 25th falls during their summer season.
(d) Cycle of the seasons is caused due to
(i) Rotation
(ii) Revolution
(iii) Gravitation
Ans: (ii) Revolution
Explanation: The changing seasons are a result of the Earth's revolution around the Sun, causing different parts of the Earth to receive varying amounts of sunlight throughout the year.
Q3. Fill in the blanks.
(a) A leap year has __________ number of days.
Ans: 366
Explanation: A leap year has an extra day, making it 366 days. This extra day is added to keep the calendar year synchronized with the astronomical year.
(b) The daily motion of the earth is _____________.
Ans: rotational
Explanation: The Earth's daily motion is its rotation on its own axis, causing day and night.
(c) The earth travels around the sun in ______________ orbit.
Ans: elliptical
Explanation: The Earth's orbit around the Sun is elliptical, meaning it's shaped like an oval.
(d) The sun’s rays fall vertically on the Tropic of ______________ on 21st June.
Ans: Cancer
Explanation: On June 21st, the Sun's rays fall vertically on the Tropic of Cancer, marking the northern hemisphere's summer solstice.
(e) Days are shorter during _____________ season.
Ans: winter
Explanation: In the winter season, the days are shorter because the Northern Hemisphere is tilted away from the Sun.
|
69 videos|386 docs|80 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 6 Geography - Motions of The Earth
| 1. What are the two main motions of the Earth? |  |
| 2. How does the tilt of the Earth's axis affect seasons? |  |
| 3. What is the significance of the equinoxes and solstices? |  |
| 4. What is the effect of the Earth's rotation on daily life? |  |
| 5. How do time zones relate to the Earth's rotation? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 6 exam
|

|