Class 8 Science Question Answers - Materials : Metals and Non-metals (Old Syllabus)
Q1: Differentiate between metals and non-metals.
Ans:
Metals | Non - metals |
|
|
Q2: Why we use aluminium foil to wrap food items?
Ans: The property of metals by which they can be beaten into thin sheets, is called malleability. Aluminium is a metal. Aluminium foils are made by using this property of aluminium. They keep food items warm and prevent them from getting contaminated.
Q3: Why can't we store lemon pickles in an aluminium container?
Ans: As we know metals react with acids and produce metal salts and hydrogen gas, aluminium is a metal and lemon contains citric acid. So if we store lemon pickle in an aluminium utensil after some time utensil metal will get corroded due to reaction and lemon pickle inside will not be fit for human consumption.
Q4: Explain malleability in metals and non-metals.
Ans: The property of metals by which they can be beaten into thin sheets is called malleability. This is the characteristic property of metals which is exploited to make silver foil for decorating food items and aluminium foil to store food items.
Non-metals do not show this property, on beating a coal or wood they get break down into small pieces, thus we can say that metals are malleable and non-metals are not malleable.
Q5: Explain ductility in metals and non-metals.
Ans: The property of metals by which it can be drawn into wires is called ductility, thus we can see aluminium or copper wires around us. Non-metal do not show this property so we never see plastic wires around us, they are not ductile.
Q6: Why there is difference in sound on dropping a metal coin and a piece of coal?
Ans: This is because metals produce ringing sound and are called sonorous while non-metals do not show this property.
Q7: State some of the chemical properties of metals.
Ans:
- Reaction with oxygen:-
Metals react with oxygen to form metallic oxides. These are basic oxides because they react with water to form bases.
Eg. Magnesium burns in air to form magnesium oxide.
2 Mg + O2 → 2 MgO - Reaction with water:-
Metals react with water to form metal hydroxides and hydrogen.
Eg. Sodium reacts with water to form sodium hydroxide and hydrogen.
2Na + 2H2O → 2NaOH + H2
E.g. Magnesium reacts with water to form magnesium hydroxide and hydrogen.
Mg + H2O → Mg(OH)2+ H2 - Reaction with acids:-
Metals react with acids to form metallic salts and hydrogen.
Eg. Zinc reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid to form zinc chloride and hydrogen.
Zn + 2HCl → ZnCl2+ H2 - Metals replace metals:-
A more reactive metal replaces a less reactive metal from its salt solution.
Eg. Magnesium replaces copper from copper sulphate solution to form magnesium sulphate and copper.
Mg + CuSO4 → MgSO4+ Cu
Zinc replaces copper from copper sulphate solution to for zinc sulphate and copper.
Zn + CuSO4 → ZnSO4 + Cu
Q8: State some of the chemical properties of non-metals.
Ans:
1. Reaction with oxygen:
Non-metals react with oxygen to form non-metallic oxides. These oxides are acidic oxides because they react with water to form acids.
Eg. Sulphur burns in air to form sulphur dioxide. Sulphur dioxide reacts with water to form sulphurous acid.
S + O2 → SO2
SO2+ H2O → H2SO3
2. Reaction with water:
Non-metals do not react with water
3. Reaction with acids:
Most non-metals do not react with acids.
Some non-metals like sulphur react with concentrated nitric acid to form sulphur dioxide, nitrogen dioxide and water.
S + 4HNO3→ SO2 + 4NO2+ 2H2O
Q9: Explain the process of rusting of iron.
Ans: The surface of some metals gets corroded when exposed to moist air for a long time. This is called corrosion. Rusting of iron is an example of corrosion, here an oxide is formed and the chemical equation for rusting of iron is
2Fe + 3/2O2 → Fe2O3.xH2O
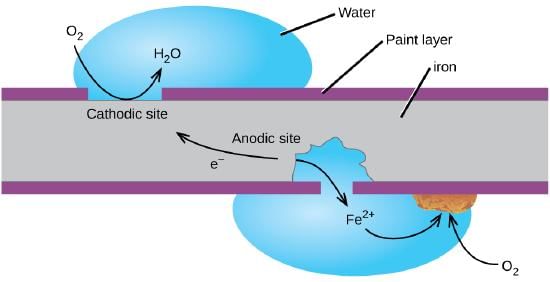 Corrosion
Corrosion
Q10: Explain the process of rusting of copper.
Ans: When a copper vessel is exposed to moist air for long time, it acquires a dull green coloured coating on its surface; this green material is the mixture of copper hydroxide and copper carbonate. Reaction is as follows:
2Cu+H20+CO2+02→ Cu(OH)2 + CuCO3
Q11: Explain reaction between sulphur and oxygen. What is the nature of its oxide formed?
Ans:
- Reaction with oxygen:
Non-metals react with oxygen to form non-metallic oxides. These oxides are acidic oxides because they react with water to form acids.
Eg. Sulphur burns in air to form sulphur dioxide. Sulphur dioxide reacts with water to form sulphurous acid.
S + O2 → SO2
SO2+ H2O → H2SO3
Q12: Explain activity series of metals.
Ans: The arrangement of metals in decreasing order of their reactivity is called reactivity series of metals. Reactivity series of metals is used to summarize information about the reactions of metals with acids and water, single displacement reactions and the extraction of metals from their ores.
Q13: Explain noble metals and give examples.
Ans: Noble metals are those metals which are not reactive while some are less reactive. There are certain metals that do not react with oxygen, water, moisture or even any of the dilute acids. We can imply that they are very unreactive. For example: gold and platinum.
Q14: State the role played by metals in our daily life.
Ans: Metals plays very important role in our day to day life, metals like iron is used for making pins, nuts, nails, bolts tools, machines etc.
1. Aluminium is used for making utensils, wires, parts of aircraft, vehicle, packaging of food stuffs and medicines etc.
2. Copper is used for making wires, vessels and electrical gadgets.
3. Gold and silver are used in making jewellery, coins and medals and platinum is used for making metals which are used for making jewellery, electrical gadgets, etc.
4. Sodium compounds are used as common salt, calcium compounds are used for making cement, glass etc.
Q15: State the role played by non-metals in our daily life.
Ans: Non-metals are essential for our life. Non-metals like oxygen are used for respiration by living beings and for burning of fuels. Nitrogen is used for making ammonia which is an important constituent of fertilizers used for improving soil quality for crop production. Sulphur is used for making sulphuric acid and salts of metals. Hydrogen is used for making ammonia which is used for making fertilizers and as fuels in rockets. Chlorine is used to kill germs in water and iodine is used as an antiseptic as well as a disinfectant.
Q16: State all possible ways of prevention of corrosion of metals.
Ans: Corrosion of metals can be prevented by :
- Applying oil grease
- Applying paint
- Galvanisation
- Electroplating
- Alloying: (Eg. When iron is alloyed with chromium and nickel, it forms stainless steel which is resistant to corrosion)
Q17: Give an example to illustrate that generally metallic oxides are basic in nature.
Ans: Burn a magnesium ribbon in air, and analyse the ash which is formed. The ash obtained by burning magnesium ribbon is dissolved in water and tested for its acidic or basis nature, we will observe it turns red litmus blue, thus concluded oxides of magnesium is basic in nature, amd in general metallic oxides are basic in nature.
Q18: Have you ever seen a greenish deposit on the surface of copper vessels, what is that?
Ans: When a copper vessel is exposed to moist air for long time, it acquires a dull green coloured coating on its surface;this green material is the mixture of copper hydroxide and copper carbonate. Reaction is as follow:
2Cu+H20+CO2+02 → Cu(OH)2 + CuCO3
|
137 videos|271 docs|60 tests
|
FAQs on Class 8 Science Question Answers - Materials : Metals and Non-metals (Old Syllabus)
| 1. What are the properties of metals and non-metals? |  |
| 2. What are some examples of metals and non-metals? |  |
| 3. How are metals and non-metals used in everyday life? |  |
| 4. What happens when metals react with non-metals? |  |
| 5. Can metals and non-metals form alloys? |  |





















