Q.1. For a positive integer n, find the value of 
Ans.
We have
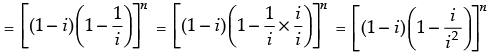 [∵ i2 = - 1]
[∵ i2 = - 1]
= [(1 – i)(1 + i)]n
= [1 – i2]n = [1 + 1]n = 2n
Hence, (1 – i)n
Q.2. Evaluate 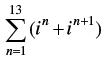 , where n ∈ N .
, where n ∈ N .
Ans.
We have 
= (i + i2) + (i2 + i3) + (i3 + i4) + (i4 + i5) + (i5 + i6) + (i6 + i7) + (i7 + i8) + (i8 + i9) + (i9 + i10) + (i10 + i11) + (i11 + i12) + (i12 + i13) + (i13 + i14)
= i + 2(i2 + i3 + i4 + i5 + i6 + i7 + i8 + i9 + i10 + i11 + i12 + i13) + i14
= i + 2[– 1 – i + 1 + i – 1 – i + 1 + i – 1 – i + 1 + i] + (– 1)
= i + 2(0) – 1 ⇒ 1 + i
Hence,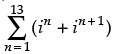 = – 1 + i.
= – 1 + i.
Q.3. If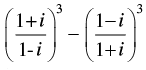 = x + iy, then find (x, y).
= x + iy, then find (x, y).
Ans.
We have 
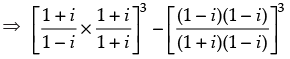 = x + iy
= x + iy

⇒ 
⇒ (i)3 – (- i)3 = x + iy ⇒ i2.i + i2.i = x + iy
⇒ - i – i = x + iy ⇒ 0 – 2i = x + iy
Comparing the real and imaginary parts, we get
x = 0, y = - 2. Hence, (x , y) = (0 , - 2).
Q.4. If 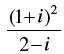 = x + iy, then find the value of x + y.
= x + iy, then find the value of x + y.
Ans.
Given that: 
⇒ 
⇒ 
⇒ 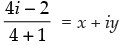 [∵ i2 = - 1]
[∵ i2 = - 1]
⇒ 
Comparing the real and imaginary parts, we get

Hence, 
Q.5. If 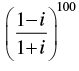 = a + ib, then find (a, b).
= a + ib, then find (a, b).
Ans.
We have 

⇒ ( - i)100 = a + bi ⇒ i100 = a + bi
⇒ (i4)25 = a + bi ⇒ (1)25 = a + bi ⇒ 1 = a + bi
⇒ 1 + 0i = a + bi
Comparing the real and imaginary parts, we have
a = 1, b = 0
Hence (a, b) = (1, 0)
Q.6. If a = cos θ + i sinθ, find the value of 
Ans.
Given that: a = cos θ + i sin θ
∴ 





Hence,
Q.7. If (1 + i) z = (1 – i) z , then show that z = – i
Ans.
Given that: (1 + i)z = 
⇒ 

⇒ 
∴ 
Hence proved.
Q.8. If z = x + iy , then show that 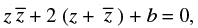 where b ∈ R, represents a circle.
where b ∈ R, represents a circle.
Ans.
Given that: z = x + iy
To prove: 
⇒ (x + iy) (x – iy) + 2(x + iy + x – iy) + b = 0
⇒x2 + y2 – 2(x + x) + b = 0
⇒x2 + y2 – 4x + b = 0 Which represents a circle.
Hence proved.
Q.9. If the real part of 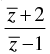 is 4, then show that the locus of the point representing z in the complex plane is a circle.
is 4, then show that the locus of the point representing z in the complex plane is a circle.
Ans.
Let z = x + iy
∴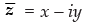
So 


Real part = 4
∴ 
⇒ x2 + y2 + x – 2 = 4[(x – 1)2 + y2]
⇒ x2 + y2 + x – 2 = 4[x2 + 1 – 2x + y2]
⇒ x2 + y2 + x – 2 = 4x2 + 4 – 8x + 4y2
⇒ x2 – 4x2 + y2 – 4y2 + x + 8x – 2 – 4 = 0
⇒ – 3x2 – 3y2 + 9x – 6 = 0
⇒ x2 + y2 – 3x + 2 = 0
Which represents a circle. Hence, z lies on a circle.
Q.10. Show that the complex number z, satisfying the condition arg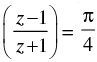 lies on a circle.
lies on a circle.
Ans.
Let z = x + iy
Given that:
⇒ arg (z – 1) – arg (z + 1) =

⇒ arg [x + iy – 1] – arg [x + iy + 1] =
⇒ arg [(x – 1) + iy] – arg [(x + 1) + iy] = 
⇒ 

⇒ 
⇒ 
⇒ 
⇒ x2 + y2 – 1 = 2y
⇒ x2 + y2 – 2y – 1 = 0 which is a circle.
Hence, z lies on a circle.
Q.11. Solve the equation 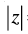 = z + 1 + 2i.
= z + 1 + 2i.
Ans.
Given that: 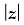 = z + 1 + 2i
= z + 1 + 2i
Let z = x + iy
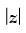 = (z + 1) + 2i
= (z + 1) + 2i
Squaring both sides

⇒ 
⇒ 0 = – 3 + 2z + 4(z + 1)i
⇒ 3 – 2z – 4(z + 1)i = 0
⇒ 3 – 2(x + yi) – 4[x + yi + 1]i = 0
⇒ 3 – 2x – 2yi – 4xi – 4yi2 – 4i = 0
⇒ 3 – 2x + 4y – 2yi – 4i – 4xi = 0
⇒ (3 – 2x + 4y) – i(2y + 4x + 4) = 0
⇒ 3 – 2x + 4y = 0 ⇒ 2x - 4y = 3 ...(i)
and 4x + 2y + 4 = 0 ⇒ 2x + y = - 2 ...(ii)
Solving eqn. (i) and (ii), we get
y = – 1 and x =
Hence, the value of z = x + yi =
LONG ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS
Q.12. If 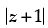 = z + 2 (1 + i), then find z.
= z + 2 (1 + i), then find z.
Ans.
Given that: 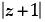 = z + 2(1 + i)
= z + 2(1 + i)
Let z = x + iy
So, 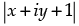 = (x + iy) + 2(1 + i)
= (x + iy) + 2(1 + i)
⇒ 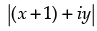 = x + iy + 2 + 2i
= x + iy + 2 + 2i
⇒ 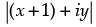 = (x + 2) + (y + 2)i
= (x + 2) + (y + 2)i
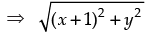 = (x + 2) + (y + 2)i
= (x + 2) + (y + 2)i

Squaring both sides, we get
(x + 1)2 + y2 = (x + 2)2 + (y + 2)2.i2 + 2(x + 2)(y + 2)i
⇒ x2 + 1 + 2x + y2 = x2 + 4 + 4x – y2 – 4y – 4 + 2(x + 2)(y + 2)i
Comparing the real and imaginary parts, we get
x2 + 1 + 2x + y2 = x2 + 4x – y2 – 4y and 2(x + 2)(y + 2) = 0
⇒ 2y2 – 2x + 4y + 1 = 0 ...(i)
and (x + 2)(y + 2) = 0 ...(ii)
x + 2 = 0 or y + 2 = 0
∴ x = – 2 or y = – 2
Now put x = – 2 in eqn. (i)
2y2 – 2 × (- 2) + 4y + 1 = 0
⇒ 2y2 + 4 + 4y + 1 = 0
⇒ 2y2 + 4y + 5 = 0
b2 – 4ac = (4)2 – 4 × 2 × 5
= 16 – 40 = - 24 < 0 no real roots.
Put y = – 2 in eqn. (i)
2(– 2)2 – 2x + 4(– 2) + 1 = 0
8 - 2x - 8 + 1 = 0 ⇒ x = 1/2 and y = -2
Hence, z = x + iy = (1/2 - 2i)
Q.13. If arg (z – 1) = arg (z + 3i), then find x – 1 : y. where z = x + iy
Ans.
Given that: arg (z – 1) = arg (z + 3i)
⇒ arg [x + yi – 1] = arg [x + yi + 3i]
⇒ arg [(x – 1) + yi] = arg [x + (y + 3)i]
⇒ 
⇒ 
⇒ xy = (x – 1)(y + 3) ⇒ xy = xy + 3x – y – 3
⇒ 3x – y = 3 ⇒ 3x - 3 = y
⇒ 3(x – 1) = y ⇒ 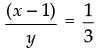 ⇒ x – 1 : y = 1 : 3
⇒ x – 1 : y = 1 : 3
Hence, x – 1 : y = 1 : 3.
Q.14. Show that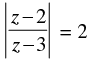 represents a circle. Find its centre and radius.
represents a circle. Find its centre and radius.
Ans.
Given that: 
Let z = x + iy
∴ 
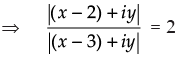



Squaring both sides, we get
(x – 2)2 + y2 = 4[(x – 3)2 + y2]
⇒ x2 + 4 – 4x + y2 = 4[x2 + 9 – 6x + y2]
⇒ x2 + y2 – 4x + 4 = 4x2 + 4y2 – 24x + 36
⇒ 3x2 + 3y2 – 20x + 32 = 0

Here g = 

Hence, the required equation of the circle is

Q.15. If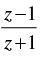 is a purely imaginary number (z ≠ – 1), then find the value of
is a purely imaginary number (z ≠ – 1), then find the value of  .
.
Ans.
Given that 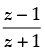 is purely imaginary number
is purely imaginary number
Let z = x + yi


Since, the number is purely imaginary, then real part = 0
∴ 
⇒ x2 + y2 – 1 = 0 ⇒ x2 + y2 = 1
⇒ 
Q.16. z1 and z2 are two complex numbers such that 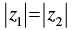 and arg (z1) + arg (z2) = π, then show that z1 =
and arg (z1) + arg (z2) = π, then show that z1 =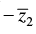 .
.
Ans.
Let z1 = r1 (cos θ1 + i sin θ1) and z2 = r2 (cos θ2 + i sin θ2) are polar form of two complex number z1 and z2.
Given that: |z1| =|z2| ⇒ r1 = r2 ….(i)
and arg (z1) + arg (z2) = π
⇒ θ1 + θ2 = π
⇒ θ1 = π – θ2
Now z1 = r1 [cos (π – θ2) + i sin (π – θ2)]
⇒ z1 = r1 [- cos θ2 + i sin θ2]
⇒ z1 = - r1 (cos θ2 – i sin θ2) ….(i)
z2 = r2 [cos θ2 + i sin θ2]
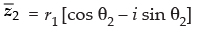 [∴ r1 = r2]…(ii)
[∴ r1 = r2]…(ii)
From eqn. (i) and (ii) we get,

Hence proved.
Q.17. If 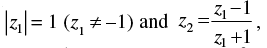 then show that the real part of z2 is zero.
then show that the real part of z2 is zero.
Ans.
Let z1 = x + yi
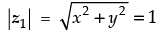

⇒ x2 + y2 = 1 ...(i)
Now 



Hence, the real part of z2 is 0.
Q.18. If z1, z2 and z3, z4 are two pairs of conjugate complex numbers, then find 
Ans.
Let the polar form of z1 = r1 (cos θ1 + i sin θ1)
∴ 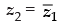 = r1 (cos θ1 – i sin θ1) = r1 [cos (– θ1) + i sin (– θ1)]
= r1 (cos θ1 – i sin θ1) = r1 [cos (– θ1) + i sin (– θ1)]
Similarly, z3 = r2 (cos θ2 + i sin θ2)
∴ 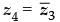 = r2 (cos θ2 – i sin θ2) = r2 [cos (– θ2) + i sin (– θ2)]
= r2 (cos θ2 – i sin θ2) = r2 [cos (– θ2) + i sin (– θ2)]
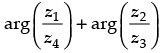 = arg (z1) – arg (z4) + arg (z2) – arg (z3)
= arg (z1) – arg (z4) + arg (z2) – arg (z3)
= θ1 – (- θ2) + (- θ1) – θ2
= θ1 + θ2 – θ1 – θ2 = 0
Hence, 
Q.19. If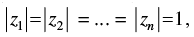 then
then
show that 
Ans.
We have
⇒ 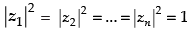 ...(i)
...(i)
⇒
⇒ 



L.H.S. = R.H.S. Hence proved.
Q.20. If for complex numbers z1 and z2, arg (z1) – arg (z2) = 0, then show that

Ans.
Given that for z1 and z2, arg (z1) – arg (z2) = 0
Let us represent z1 and z2 in polar form
z1 = r1 (cos θ1 + i sin θ1) and z2 = r2 (cos θ2 + i sin θ2)
arg (z1) = θ1 and arg (z2) = θ2
Since arg (z1) – arg (z2) = 0
⇒ θ1 – θ2 = 0 ⇒ θ1 = θ2
Now z1 – z2 = r1 (cos θ1 + i sin θ1) – r2 (cos θ2 + i sin θ2)
= r1 cos θ1 + i r1 sin θ1 – r2 cos θ1 – i r2 sin θ1
[∴ θ1 = θ2]
= (r1 cos θ1 – r2 cos θ1) + i(r1 sin θ1 – r2 sin θ1)


Hence, 
Q.21. Solve the system of equations Re (z2) = 0,
Ans.
Given that: Re(z2) = 0 and
Let z = x + yi
∴ 
⇒ 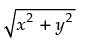 = 2 ⇒ x2 + y2 = 4 ...(i)
= 2 ⇒ x2 + y2 = 4 ...(i)
Since, z = x + yi
z2 = x2 + y2i2 + 2xyi
⇒ z2 = x2 – y2 + 2xyi
∴ Re(z2) = x2 – y2
⇒ x2 – y2 = 0 ...(ii)
From eqn. (i) and (ii), we get x
x2 + y2 = 4 ⇒ 2x2 = 4 ⇒ x2 = 2 ⇒ x =
Hence, z = 
Q.22. Find the complex number satisfying the equation
Ans.
Given that: 
Let z = x + yi
∴ 


⇒ x2 = 2(x2 + 2x + 1 + y2)
⇒ x2 = 2x2 + 4x + 2 + 2y2
⇒ x2 + 4x + 2 + 2y2 = 0
⇒ x2 + 4x + 2 + 2(– 1)2 = 0 [∴ y = – 1]
⇒ x2 + 4x + 4 = 0
⇒ (x + 2)2 = 0
⇒ x + 2 = 0 ⇒ x = – 2
Hence, z = x + yi = – 2 – i.
Q.23. Write the complex number 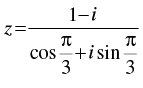 in polar form.
in polar form.
Ans.
Given that:


So r = √2
Now arg(z) =

Hence, the polar is

Q.24. If z and w are two complex numbers such that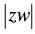 =1 and arg (z) – arg (w) =
=1 and arg (z) – arg (w) =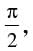 then show that
then show that
Ans.
Let z = r1 (cos θ1 + i sin θ1) and w = r2 (cos θ2 + i sin θ2)
zw = r1r2 [(cos θ1 + i sin θ1)] [(cos θ2 + i sin θ2)]
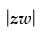 = r1r2 = 1 (given)
= r1r2 = 1 (given)
Now arg (z) – arg (w) = 

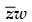 = r1 (cos θ1 – i sin θ1) r2 (cos θ2 + i sin θ2)
= r1 (cos θ1 – i sin θ1) r2 (cos θ2 + i sin θ2)
= r1 r2 [cos θ1 cos θ2 + i cos θ1 sin θ2 – i sin θ1 cos θ2 – i2 sin θ1 sin θ2]
= r1 r2 [(cos θ1 cos θ2 + sin θ1 sin θ2) + i(cos θ1 sin θ2 – sin θ1 cos θ2)]
= r1 r2 [cos (θ2 – θ1) + i sin (θ2 – θ1)]

Here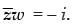 Hence proved.
Hence proved.
Fill in the Blanks
Q.25. (i) For any two complex numbers z1, z2 and any real numbers a, b,
(ii) The value of
(iii) The number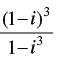 is equal to ...............
is equal to ...............
(iv) The sum of the series i + i2 + i3 + ... upto 1000 terms is ..........
(v) Multiplicative inverse of 1 + i is ................
(vi) If z1 and z2 are complex numbers such that z1 + z2 is a real number, then z2 = ....
(vii) arg (z) + arg 
(viii) If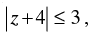 then the greatest and least values of
then the greatest and least values of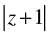 are ............... and ...............
are ............... and ...............
(ix) If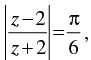 then the locus of z is ............
then the locus of z is ............
(x) If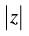 = 4 and arg (z) =
= 4 and arg (z) =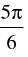 , then z = ............
, then z = ............
Ans.


Hence, the value of the filler is

Hence, the value of the filler is – 15.
(iii) 

(iv) i + i2 + i3 + ... upto 1000 terms
= i + i2 + i3 + ... + i1000 = 0

Hence, the value of the filler is 0.
(v) Multiplicative inverse of

Hence, the value of the filler = 
(vi) Let z1 = x1 + iy1 and z2
= x2 + iy2 z1 + z2
= (x1 + iy1) + (x2 + iy2) z1 + z2
= (x1 + x2) + (y1 + y2)i
If z1 + z2 is real then
y1 + y2 = 0⇒ y1 = – y2
∴ z2 = x2 – iy1
z2 = x1 – iy1 (when x1 = x2)
So z2 = 
Hence, the value of the filler is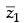 .
.
(vii) arg ( z) + arg 
If arg (z) = θ, then arg ( 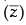 ) = - θ
) = - θ
So θ + (– θ) = 0
Hence, the value of the filler is 0.
(viii) Given that:
For the greatest value of

Hence, the greatest value of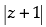 is 6 and for the least value of
is 6 and for the least value of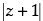 = 0.
= 0.
[∴ The least value of the modulus of complex number is 0] Hence, the value of the filler are 6 and 0.
(ix) Given that:
Let z = x + iy

Which represents are equation of a circle.
Hence, the value of the filler is circle.
(x) Given that:
Let z = x + yi

From eqn. (i) and (ii)

Hence, the value of the filler is
Q.26. State True or False for the following :
(i) The order relation is defined on the set of complex numbers.
(ii) Multiplication of a non zero complex number by – i rotates the point about origin through a right angle in the anti-clockwise direction.
(iii) For any complex number z the minimum value of
(iv) The locus represented by 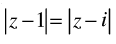 is a line perpendicular to the join of (1, 0) and (0, 1).
is a line perpendicular to the join of (1, 0) and (0, 1).
(v) If z is a complex number such that z ≠ 0 and Re (z) = 0, then Im (z2) = 0.
(vi) The inequality 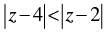 represents the region given by x > 3.
represents the region given by x > 3.
(vii) Let z1 and z2 be two complex numbers such that 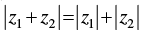 , then arg (z1 – z2) = 0.
, then arg (z1 – z2) = 0.
(viii) 2 is not a complex number.
Ans.
(i) Comparison of two purely imaginary complex numbers is not possible. However, the two purely real complex numbers can be compared.
So it is ‘False’.
(ii) Let z = x + yi
z.i = (x + yi) i = xi – y which rotates at angle of 180°
So, it is ‘False’.
(iii) Let z = x + yi

The value of 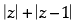 is minimum when x = 0, y = 0 i.e., 1.
is minimum when x = 0, y = 0 i.e., 1.
Hence, it is ‘True’.
(iv) Let z = x + yi
Given that:

⇒(x – 1)2 + y2 = x2 + (1 – y)2
⇒ x2 – 2x + 1 + y2 = x2 + 1 + y2 – 2y
⇒ – 2x + 2y = 0
⇒ x – y = 0 which is a straight line.
Slope = 1
Now equation of a line through the point (1, 0) and (0, 1)

⇒ y = – x + 1 whose slope = – 1.
Now the multiplication of the slopes of two lines = – 1 x 1 = - 1,
so they are perpendicular.
Hence, it is ‘True’.
(v) Let z = x + yi, z ≠ 0 and Re(z) = 0
Since real part is 0 ⇒ x = 0
∴ z = 0 + yi = yi
∴ lm (z2) = y2i2 = - y2 which is real.
Hence, it is ‘False’.
(vi) Given that:
Let z = x + yi

⇒ (x – 4)2 + y2 < (x – 2)2 + y2
⇒ (x – 4)2 < (x – 2)2
⇒ x2 + 16 – 8x < x2 + 4 – 4x
⇒ – 8x + 4x < – 16 + 4
⇒ – 4x < – 12 ⇒ x > 3
Hence, it is ‘True’.
(vii) Let z1 = x1 + y1i and z2 = x2 + y2i

Squaring both sides, we get

Again squares on both sides, we get

∴ arg (z1) = arg (z2)
⇒ arg (z1) – arg (z2) = 0
Hence, it is ‘True’.
(viii) Since 2 has no imaginary part.
So, 2 is not a complex number.
Hence, it is ‘True’.
Q.27. Match the statements of Column A and Column B.

Ans.
(a) Given that z = i + √3
Polar form of z = r [cos θ + i sin θ]

Since x > 0, y > 0
∴ Polar form of z =
Hence, (a) ⇒ 8y = 0 Þ y = 0. Which is the equation of x-axis and it is perpendicular to the line segment joining (0, – 2) and (0, 2).
Hence, (d) ↔ (iv).
(b) Given that 
Here argument (z) = 
So, 
Since x < 0 and y > 0

Hence, (b) ↔ (iii).
(c) Given that: 
Let z = x + yi

⇒ 8y = 0 ⇒ y = 0. Which is the equation of x-axis and it is perpendicular to the line segment joining (0, – 2) and (0, 2).
Hence, (d) ↔ (iv).
(e) Given that:
Let z = x + yi

Which represents a circle on or outside having centre (0, – 4) and radius 3.
Hence, (e) ↔ (ii).
(f) 
Let z = x + yi

Which is a circle having centre (– 4, 0) and r=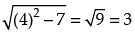 and is on or inside the circle.
and is on or inside the circle.
Hence, (f) ↔ (vi).
(g) Let

∴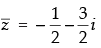 which lies in third quadrant.
which lies in third quadrant.
Hence, (g) ↔ (viii).
(h) Given that: z = 1 – i

Which lies in first quadrant.
Hence, (h)↔ (vii).
Hence, the correct matches are (a) ↔ (v), (b) ↔ (iii), (c) ↔ (i), (d) ↔ (iv), (e) ↔ (ii), (f) ↔ (vi), (g) ↔ (viii), (h) ↔ (vii).
Q.28. What is the conjugate of
Ans.
Given that 



Q.29. If 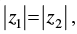 is it necessary that z1 = z2?
is it necessary that z1 = z2?
Ans.
Let z1 = x1 + y1i and z2 = x2 + y2i

⇒ x1 = ± x2 and y1 = ± y2
So z1 = x1 + y1i and z2 = ± x2 ± y2i
⇒ z1 ≠ z2
Hence, it is not necessary that z1 = z2.
Q.30. If 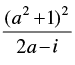 = x + iy, what is the value of x2 + y2?
= x + iy, what is the value of x2 + y2?
Ans.
Given that: 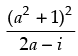 = x + iy ...(i)
= x + iy ...(i)
Taking conjugate on both sides
⇒ 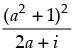 = x – iy ...(ii)
= x – iy ...(ii)
Multiplying eqn. (i) and (ii) we have

Hence, the value of x2 + y2 = 
Q.31. Find z if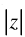 = 4 and arg (z) =
= 4 and arg (z) =
Ans.
Given that:
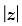 = 4 ⇒ r = 4
= 4 ⇒ r = 4
So Polar form of z = r [ cos θ + i sin θ]


= - 2 √3 + 2i
Hence, z = - 2 √3 + 2i .
Q.32. Find
Ans.


= 1
Hence,
Q.33. Find principal argument of (1 + i √3 )2 .
Ans.
Given that: (1 + i √3 )2 = 1 + i2 . 3 + 2 √3i
= 1 - 3 + 2 √3i = - 2 + 2 √3i

⇒ 
⇒ 
Now Re(z) < 0 and image (z) > 0.
∴ 
Hence, the principal arg =
Q.34. Where does z lie, if
Ans.
Given that:
Let z = x + yi
∴ 
⇒ 
⇒ x2 + (y – 5)2 = x2 + (y + 5)2
⇒(y – 5)2 = (y + 5)2
⇒ y2 + 25 – 10y = y2 + 25 + 10y
⇒ 20y = 0⇒ y = 0
Hence, z lies on x-axis i.e., real axis.
Choose the correct answer from the given four options
Q.35. sinx + i cos 2x and cos x – i sin 2x are conjugate to each other for:
(A) x = nπ

(C) x = 0
(D) No value of x
Ans.
Let z = sin x + i cos 2x
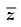 = sin x – i cos 2x
= sin x – i cos 2x
But we are given that 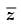 = cos x – i sin 2x
= cos x – i sin 2x
∴ sin x – i cos 2x = cos x – i sin 2x
Comparing the real and imaginary parts, we get
sin x = cos x and cos 2x = sin 2x
⇒ tan x = 1 and tan 2x = 1
⇒ 
∴ 
⇒ x = 2x ⇒ 2x - x = 0 ⇒ x = 0
Hence, the correct option is (c).
Q.36. The real value of α for which the expression 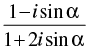 is purely real is :
is purely real is :


(C) n π
(D) None of these, where n ∈N
Ans.
Let 

Since, z is purely real, then

So, α = nπ, n ∈ N.
Q.37. If z = x + iy lies in the third quadrant, then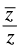 also lies in the third quadrant if
also lies in the third quadrant if
(A) x > y > 0
(B) x < y < 0
(C) y < x < 0
(D) y > x > 0
Ans.
Given that: z = x + iy
If z lies in third quadrant.
So x < 0 and y < 0.


When z lies in third quadrant then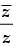 will also be lie in third quadrant
will also be lie in third quadrant
∴
⇒ 2 – y2 < 0 and 2xy > 0
⇒ x2 < y2 and xy > 0
So x < y < 0.
Hence, the correct option is (b)
Q.38. The value of (z + 3)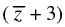 is equivalent to
is equivalent to


(C) z2 + 3
(D) None of these
Ans.
Given that: ( z + 3)
Let z = x + yi
So ( z + 3)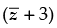 = (x + yi + 3)(x – yi + 3)
= (x + yi + 3)(x – yi + 3)
= [(x + 3) + yi][(x + 3) – yi]
= (x + 3)2 – y2i2 = (x + 3)2 + y2

Hence, the correct option is (a).
Q.39. If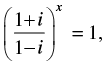 then
then
(A) x = 2n+1
(B) x = 4n
(C) x = 2n
(D) x = 4n + 1, where n ∈N
Ans.
Given that: 

⇒ (i)x = (i)4n
⇒x = 4n, n ∈ N
Hence, the correct option is (b).
Q.40. A real value of x satisfies the equation 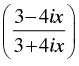 = α − iβ(α, β ∈ R) if α2 + β2 =
= α − iβ(α, β ∈ R) if α2 + β2 =
(A) 1
(B) – 1
(C) 2
(D) – 2
Ans.
Given that:
⇒ 
⇒
⇒ 
⇒ 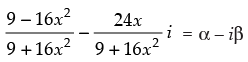 ...(i)
...(i)
⇒ 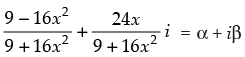 ...(ii)
...(ii)
Multiplying eqn. (i) and (ii) we get

⇒ 
⇒ 
⇒ 
So, α2 + β2 = 1
Hence, the correct option is (a).
Q.41. Which of the following is correct for any two complex numbers z1 and z2?

(B) arg (z1z2) = arg (z1). arg (z2)


Ans.
Let z1 = r1 (cos θ1 + i sin θ1)
∴ 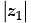 = r1
= r1
and z2 = r2 (cos θ2 + i sin θ2)
∴ 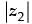 = r2
= r2
z1z2 = r1 (cos θ1 + i sin θ1) . r2 (cos θ2 + i sin θ2)
= r1r2 (cos θ1 + i sin θ1) . (cos θ2 + i sin θ2)
= r1r2 (cos θ1 cos θ2 + i sin θ2 cos θ1 + i sin θ1 cos θ2 + i2 sin θ1 sin θ2)
= r1r2 [(cos θ1 cos θ2 – sin θ1 sin θ2) + i(sin θ1 cos θ2 + cos θ1 sin θ2)]
= r1r2 [cos (θ1 + θ2) + i sin (θ1 + θ2)]

Hence, the correct option is (a).
Q.42. The point represented by the complex number 2 – i is rotated about origin through an angle 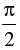 in the clockwise direction, the new position of point is:
in the clockwise direction, the new position of point is:
(A) 1 + 2i
(B) –1 – 2i
(C) 2 + i
(D) –1 + 2 i
Ans.
Given that: z = 2 – i
If z rotated through an angle of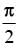 about the origin in clockwise direction.
about the origin in clockwise direction.
Then the new position = z.e– (π/2)
= (2 – i) e– (π/2)

= (2 – i) (0 – i) = – 1 – 2i
Hence, the correct option is (b).
Q.43. Let x, y ∈ R, then x + iy is a non real complex number if:
(A) x = 0
(B) y = 0
(C) x ≠ 0
(D) y ≠ 0
Ans.
x + yi is a non-real complex number if y ≠ 0. If x, y ∈ R.
Hence, the correct option is (d).
Q.44. If a + ib = c + id, then
(A) a2 + c2 = 0
(B) b2 + c2 = 0
(C) b2 + d2 = 0
(D) a2 + b2 = c2 + d2
Ans.
Given that: a + ib = c + id

Squaring both sides, we get a2 + b2 = c2 + d2
Hence, the correct option is (d).
Q.45. The complex number z which satisfies the condition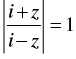 lies on
lies on
(A) circle x2 + y2 = 1
(B) the x-axis
(C) the y-axis
(D) the line x + y = 1.
Ans.
Given that: 
Let z = x + yi

⇒ x2 + (y + 1)2 = x2 + (y – 1)2
⇒ (y + 1)2 = (y – 1)2
⇒ y2 + 2y + 1 = y2 – 2y + 1
⇒ 2y = – 2y
⇒ 4y = 0 ⇒ y = 0 ⇒ x-axis.
Hence, the correct option is (b).
Q.46. If z is a complex number, then




Ans.
Let z = x + yi

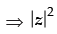 = x2 + y2 ...(i)
= x2 + y2 ...(i)
Now z2 = x2 + y2i2 + 2xyi
z2 = x2 – y2 + 2xyi


Hence, the correct option is (b).
Q.47. 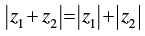 is possible if
is possible if


(C) arg (z1) = arg (z2)

Ans.
Let z1 = r1 (cos θ1 + i sin θ1) and z2 = r2 (cos θ2 + i sin θ2)
Since
z1 + z2 = r1 cos θ1 + i r1 sin θ1 + r2 cos θ2 + i r2 sin θ2


Squaring both sides, we get

⇒ 2r1r2 – 2r1r2 cos (θ1 – θ2) = 0
⇒ 1 – cos (θ1 – θ2) = 0 ⇒ cos (θ1 – θ2) = 1
⇒ θ1 – θ2 = 0 ⇒ θ1 = θ2
So, arg (z1) = arg (z2)
Hence, the correct option is (c).
Q.48. The real value of θ for which the expression 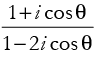 is a real number is:
is a real number is:



(D) none of these.
Ans.
Let


If z is a real number, then

⇒ 3 cos θ = 0 ⇒ cos θ = 0
∴ 
Hence, the correct option is (c).
Q.49. The value of arg (x) when x < 0 is:
(A) 0
(B) π/2
(C) π
(D) none of these
Ans.
Let z = – x + 0i and x < 0
∴ 
Since, the point (–x, 0) lies on the negative side of the real axis
(∴ x < 0).
∴ Principal argument (z) = π
Hence, the correct option is (c).
Q.50. If f (z) =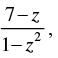 where z = 1 + 2i, then
where z = 1 + 2i, then



(D) none of these.
Ans.
Given that: z = 1 + 2i

Now 


So 

Hence, the correct option is (a).


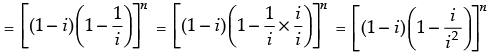 [∵ i2 = - 1]
[∵ i2 = - 1]
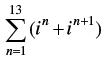 , where n ∈ N .
, where n ∈ N .
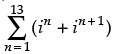 = – 1 + i.
= – 1 + i.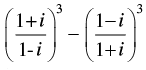 = x + iy, then find (x, y).
= x + iy, then find (x, y).
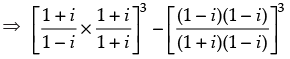 = x + iy
= x + iy

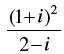 = x + iy, then find the value of x + y.
= x + iy, then find the value of x + y.


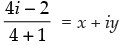 [∵ i2 = - 1]
[∵ i2 = - 1]


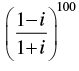 = a + ib, then find (a, b).
= a + ib, then find (a, b).















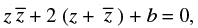 where b ∈ R, represents a circle.
where b ∈ R, represents a circle.
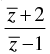 is 4, then show that the locus of the point representing z in the complex plane is a circle.
is 4, then show that the locus of the point representing z in the complex plane is a circle.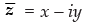




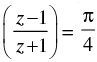 lies on a circle.
lies on a circle.









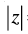 = z + 1 + 2i.
= z + 1 + 2i.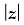 = z + 1 + 2i
= z + 1 + 2i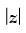 = (z + 1) + 2i
= (z + 1) + 2i



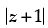 = z + 2 (1 + i), then find z.
= z + 2 (1 + i), then find z.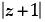 = z + 2(1 + i)
= z + 2(1 + i)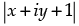 = (x + iy) + 2(1 + i)
= (x + iy) + 2(1 + i)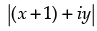 = x + iy + 2 + 2i
= x + iy + 2 + 2i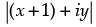 = (x + 2) + (y + 2)i
= (x + 2) + (y + 2)i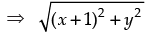 = (x + 2) + (y + 2)i
= (x + 2) + (y + 2)i


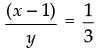 ⇒ x – 1 : y = 1 : 3
⇒ x – 1 : y = 1 : 3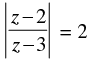 represents a circle. Find its centre and radius.
represents a circle. Find its centre and radius.

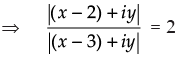







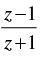 is a purely imaginary number (z ≠ – 1), then find the value of
is a purely imaginary number (z ≠ – 1), then find the value of  .
.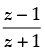 is purely imaginary number
is purely imaginary number



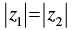 and arg (z1) + arg (z2) = π, then show that z1 =
and arg (z1) + arg (z2) = π, then show that z1 =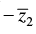 .
.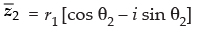 [∴ r1 = r2]…(ii)
[∴ r1 = r2]…(ii)
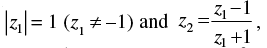 then show that the real part of z2 is zero.
then show that the real part of z2 is zero.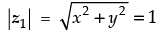






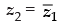 = r1 (cos θ1 – i sin θ1) = r1 [cos (– θ1) + i sin (– θ1)]
= r1 (cos θ1 – i sin θ1) = r1 [cos (– θ1) + i sin (– θ1)]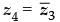 = r2 (cos θ2 – i sin θ2) = r2 [cos (– θ2) + i sin (– θ2)]
= r2 (cos θ2 – i sin θ2) = r2 [cos (– θ2) + i sin (– θ2)]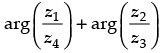 = arg (z1) – arg (z4) + arg (z2) – arg (z3)
= arg (z1) – arg (z4) + arg (z2) – arg (z3)
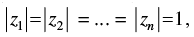 then
then

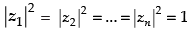 ...(i)
...(i)











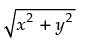 = 2 ⇒ x2 + y2 = 4 ...(i)
= 2 ⇒ x2 + y2 = 4 ...(i)






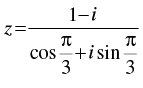 in polar form.
in polar form.




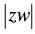 =1 and arg (z) – arg (w) =
=1 and arg (z) – arg (w) =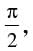 then show that
then show that
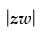 = r1r2 = 1 (given)
= r1r2 = 1 (given)

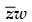 = r1 (cos θ1 – i sin θ1) r2 (cos θ2 + i sin θ2)
= r1 (cos θ1 – i sin θ1) r2 (cos θ2 + i sin θ2)
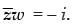 Hence proved.
Hence proved.

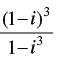 is equal to ...............
is equal to ...............
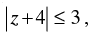 then the greatest and least values of
then the greatest and least values of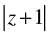 are ............... and ...............
are ............... and ...............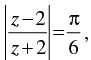 then the locus of z is ............
then the locus of z is ............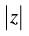 = 4 and arg (z) =
= 4 and arg (z) =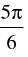 , then z = ............
, then z = ............









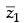 .
.
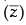 ) = - θ
) = - θ

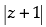 is 6 and for the least value of
is 6 and for the least value of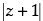 = 0.
= 0.






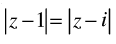 is a line perpendicular to the join of (1, 0) and (0, 1).
is a line perpendicular to the join of (1, 0) and (0, 1).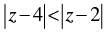 represents the region given by x > 3.
represents the region given by x > 3.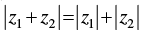 , then arg (z1 – z2) = 0.
, then arg (z1 – z2) = 0.
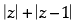 is minimum when x = 0, y = 0 i.e., 1.
is minimum when x = 0, y = 0 i.e., 1.




















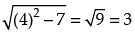 and is on or inside the circle.
and is on or inside the circle.

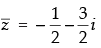 which lies in third quadrant.
which lies in third quadrant.





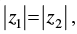 is it necessary that z1 = z2?
is it necessary that z1 = z2?
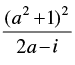 = x + iy, what is the value of x2 + y2?
= x + iy, what is the value of x2 + y2?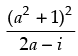 = x + iy ...(i)
= x + iy ...(i)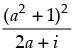 = x – iy ...(ii)
= x – iy ...(ii)

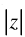 = 4 and arg (z) =
= 4 and arg (z) =

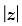 = 4 ⇒ r = 4
= 4 ⇒ r = 4















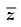 = sin x – i cos 2x
= sin x – i cos 2x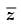 = cos x – i sin 2x
= cos x – i sin 2x

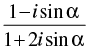 is purely real is :
is purely real is :




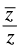 also lies in the third quadrant if
also lies in the third quadrant if

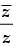 will also be lie in third quadrant
will also be lie in third quadrant 
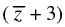 is equivalent to
is equivalent to


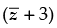 = (x + yi + 3)(x – yi + 3)
= (x + yi + 3)(x – yi + 3)
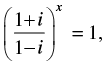 then
then

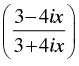 = α − iβ(α, β ∈ R) if α2 + β2 =
= α − iβ(α, β ∈ R) if α2 + β2 =



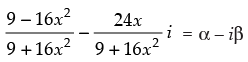 ...(i)
...(i)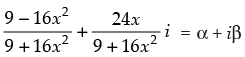 ...(ii)
...(ii)






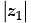 = r1
= r1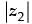 = r2
= r2
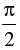 in the clockwise direction, the new position of point is:
in the clockwise direction, the new position of point is: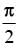 about the origin in clockwise direction.
about the origin in clockwise direction.

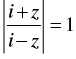 lies on
lies on






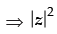 = x2 + y2 ...(i)
= x2 + y2 ...(i)

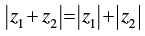 is possible if
is possible if






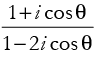 is a real number is:
is a real number is:








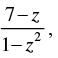 where z = 1 + 2i, then
where z = 1 + 2i, then



































