- Picture coal as a black, rock-like chunk that you might have seen or heard about. It’s tough and looks like stone, but it’s a true powerhouse!
- Coal is like a superhero fuel. It cooks our meals, powers old steam trains, and generates electricity for our homes. It also plays a key role in many industries.
Coal and Petroleum Class 8 Notes Science Chapter 3
| Table of contents |

|
| What are Natural Resources? |

|
| Types of Natural Resources |

|
| Coal |

|
| Petroleum |

|
| Natural Gas |

|
| Why We Need to Save Fossil Fuels ? |

|
What are Natural Resources?
Resources supplied by nature are called natural resources. The sun, air, water, soil, trees and forests, wildlife, coal, petroleum, natural gas and minerals are all natural resources.
Natural resources are something which comes from nature and people cannot make the natural resources, but they can collect it. Many industries, like fishing, mining, hunting, agriculture and forestry, revolve around the sensible use of natural resources.
 Natural Resources
Natural Resources
Types of Natural Resources
Natural resources are classified into two categories:
- Inexhaustible Resources. -These are always available and won’t run out no matter how much we use them. Think of sunlight and air—there’s plenty of these for everyone. As they are unlimited and easily renewed by nature , they are also called Renewable resources
- Exhaustible Resources. -These are limited in amount and can be depleted easily if we’re not careful. Examples include forests, wildlife, minerals, coal, oil, and natural gas. As they are limited and not easily renewed in nature, they are also called Non-renewable resources

This chapter will explore exhaustible resources, like coal, oil, and natural gas.
Fossil fuels
Fossil fuels
These were formed from the remains of ancient plants and animals, so they’re called fossil fuels.
Fossil fuels are exhaustible natural resources such as coal, petroleum, and natural gas, formed from the dead remains of living organisms (fossils).

By understanding how we use these resources and making smarter choices, we can help ensure they last longer and protect our environment!
Coal
Formation of coal:
1. Around 300 million years ago, dense forests in low-lying wetlands were buried by soil due to natural processes like flooding.
2. As more soil accumulated, the forests were compressed.
3. The temperature increased as they sank deeper into earth, and under high pressure and temperature, dead plants gradually transformed into coal.
4. This slow process is known as carbonisation.
5. Because coal originates from the remains of vegetation, it is categorized as a fossil fuel.
So, next time you think of coal, imagine it as an ancient, powerful treasure that fuels our world in many ways!
 Coal mine
Coal mine
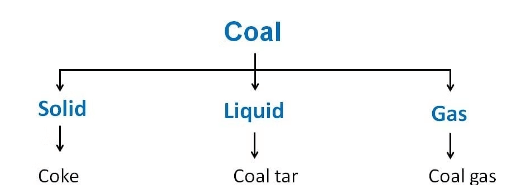
(a) Coke
- Coke is a tough, porous, and black substance. Imagine it as a spongy, rock-like material.
- . It is an almost pure form of carbon.
- Coke helps in making steel and extracting various metals. It’s like a secret ingredient that helps turn raw materials into useful products.
 Coke
Coke
(b) Coal Tar
- Coal tar is a thick, black liquid with a strong unpleasant smell. It's made up of around 200 different substances all mixed together.
- Products obtained from coal tar are key ingredients for making all sorts of things we use daily, like synthetic dyes, medicines, explosives, perfumes, plastics, paints, and even materials for roofing.
- These days, instead of using coal-tar, roads are covered with bitumen, which comes from petroleum.
- One interesting use of coal tar is in making naphthalene balls, which are used in home to keep moths and other bugs away.
 Coal Tar
Coal Tar
(c) Coal Gas
- Coal gas is a gas that's produced when coal is processed to make coke.
- It was first used to light up streets in London in 1810 and in New York around 1820.
- Today, coal gas is mainly used as a heat source for industries near coal processing plants.
- So, while it was used to brighten up the streets before, now it helps power up factories!
 Coal Gas
Coal Gas
Petroleum
You might know that petrol fuels cars and scooters, while diesel powers trucks and tractors.
Both petrol and diesel come from a natural resource called petroleum, which gets its name from "petra" (rock) and "oleum" (oil) because it’s found between rocks deep underground.
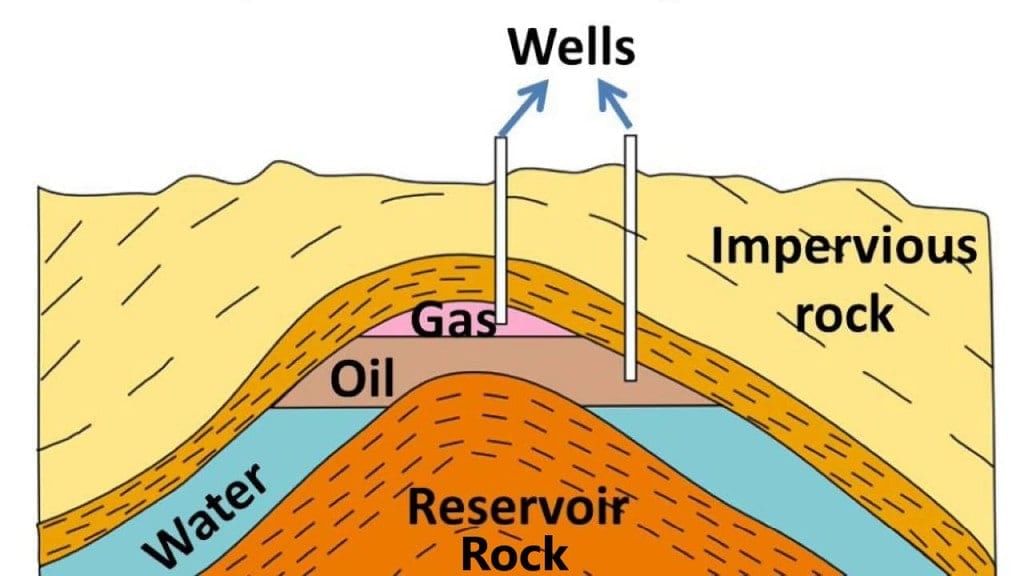 Petroleum and Natural gas deposits
Petroleum and Natural gas deposits
- Formation of petroleum:
1. Petroleum is created from tiny sea organisms that lived millions of years ago. When these organisms died, their bodies sank to the bottom of the sea and were covered by layers of sand and clay.
2. Over millions of years, the absence of air, combined with high temperature and pressure, converted these remains into petroleum and natural gas.
3. In the deposits of petroleum and natural gas, you'll notice that the petroleum and gas layers are above the water layer. This occurs because oil and gas are lighter than water and do not mix with it.
- World’s first oil well was drilled in Pennsylvania, USA, back in 1859
- Just eight years later, in 1867, oil was discovered in Makum , Assam, India! Today, oil can be found in places like Assam, Gujarat, Mumbai High, and the river basins of Godavari and Krishna.
And here’s a cool fact: petroleum and natural gas float on top of water underground because they’re lighter and don’t mix with it.
 Oil Drilling from oil well
Oil Drilling from oil well
Refining of petroleum
Petroleum is a dark, oily liquid with a strong, unpleasant smell. It is made up of a mix of different substances, including petroleum gas, petrol, diesel, lubricating oil, and paraffin wax.
The process used to separate these different components is called refining, and it takes place in a facility known as a petroleum refinery.
 Petroleum refinery
Petroleum refinery
Constituents of Petroleum & their Uses
- Petroleum is separated into useful products known as petrochemicals like petrol, diesel, kerosene etc .
- These petrochemicals are used to make everyday items like detergents, synthetic fibres (like polyester and nylon), and plastic products.
- Even hydrogen gas obtained from natural gas is important—it's used to make fertilizers like urea.
- Because of all these valuable uses, petroleum is often called "black gold," highlighting its importance and value!
 Various Constituents of Petroleum and their Uses
Various Constituents of Petroleum and their Uses
Natural Gas
- Natural gas is a super handy fossil fuel because it travels easily through pipes. It's stored under high pressure as compressed natural gas (CNG). CNG is great for making electricity and is now used to fuel cars and trucks because it's cleaner and produces less pollution.

- The best part about CNG is that it can be delivered straight to homes and factories through pipelines. Cities like Vadodara and parts of Delhi have these pipelines set up. Natural gas is also used to make chemicals and fertilizers.
- CNG Pipeline in India
- India has a lot of natural gas, found in places like Tripura, Rajasthan, Maharashtra, and the Krishna-Godavari delta.
- We can't make coal, petroleum, or natural gas in a lab from dead organisms. These resources take millions of years to form naturally, so we can't recreate those conditions in the lab.
Here is an interesting video about the above topics.
Why We Need to Save Fossil Fuels ?
- Fossil fuels like coal and oil come from ancient plants and animals that turned into these resources over millions of years.
- The amount we have now will only last a few hundred years if we keep using them the way we do.
- Also, burning these fuels makes the air dirty and contributes to global warming.

To protect our planet and make sure we have these fuels for longer, we need to use them wisely.
Here are some easy tips from the Petroleum Conservation Research Association (PCRA) to save fuel while driving:
- Drive at a steady speed and maintain a constant speed whenever possible.
- Avoid sudden acceleration and hard braking as it consumes more fuel.
- Turn off the engine at red lights or during long stops to save fuel.
- Drive Smoothly: Keep a steady speed as much as you can.
- Turn Off the Engine: If you’re waiting at a light or parked for a while, switch off the engine.
- Check Tire Pressure: Make sure your tires are properly inflated.
- Maintain Your Car: Regularly service your vehicle to keep it running efficiently.
By following these tips, we can help reduce pollution, slow down global warming, and save these precious resources for the future!
|
90 videos|273 docs|44 tests
|
FAQs on Coal and Petroleum Class 8 Notes Science Chapter 3
| 1. What are natural resources? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of natural resources? |  |
| 3. How is coal formed and why is it important? |  |
| 4. Why should we save fossil fuels? |  |
| 5. What are the environmental impacts of using petroleum? |  |






















