Class 6 Social Studies (SST): CBSE Sample Question Paper with Solutions Term I – 1 | Sample Papers For Class 6 PDF Download
Section A (History)
Q1. Records of the past are arranged in which order? [1 mark]
a) Mathematical
b) Chronological
c) Geometrical
d) None of the above
Correct answer is Option (b).
Explanation: History is a record of people, places and events of the past arranged in chronological order. Chronology is the arrangement of events or dates in the order of their occurrence.
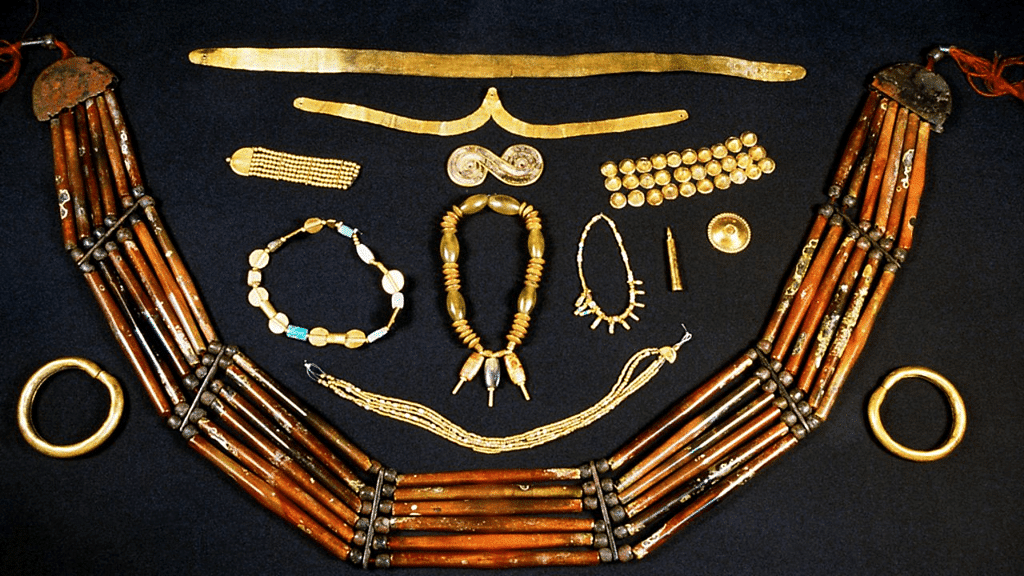 Artifacts From the Past
Artifacts From the Past
Q2. When did humans first appear on Earth? [1 mark]
a) 10000 years ago
b) 20000 years ago
c) 30000 years ago
d) 40000 years ago
Correct answer is Option (d).
Explanation: Homo sapiens emerged around 300,000 years ago, evolving from Homo erectus and migrating out of Africa, gradually replacing local populations of archaic humans. Early humans were hunter-gatherers, before settling in the Fertile Crescent and other parts of the Old World.
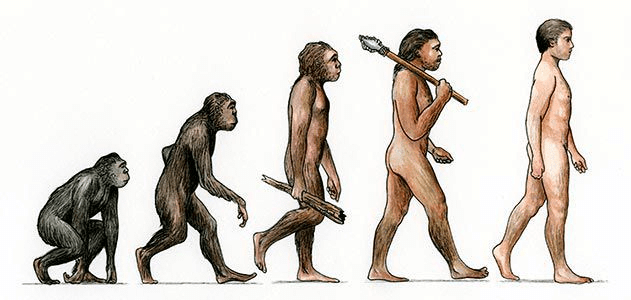 Evolution of Humans
Evolution of Humans
Q3. Which crop requires more water to grow compared to wheat and barley? [1 mark]
a) Rice
b) Bajra
c) Jowar
d) Maize
Correct answer is Option (a).
Explanation: Rice is sown at the beginning of the rainy season. Rice is a Kharif crop. These crops are also referred to as monsoon crops. Hot weather and huge quantity of water is the main requirement for such crops. Rice plants need to maintain the perfect temperature, humidity which is present generally in summer otherwise they won't be able to survive.
Wheat needs less water, excessive water causes root infection in wheat and some other rabi crops. That's why they are planted in the winter season.
Q4. How many years back were the Harappan cities developed? [1 mark]
a) 4700 years ago
b) 4000 years ago
c) 3500 years ago
d) 2500 years ago
Correct answer is Option (a).
Explanation: The Harappan Civilization developed around 4700 years ago. The earliest city to be developed in India was Harappa in Punjab, in present day Pakistan. Further down the Indus valley, another city was excavated and this was Mohenjo-Daro in Sind.
Q5. In which age did humans begin farming? [1 mark]
a) Mesolithic Age
b) Neolithic Age
c) Palaeolithic Age
d) None of the above
Correct answer is Option (a).
Explanation: The beginning of farming and herding occurred during the Mesolithic Period i.e. roughly from about 12000 years ago. There were changes in climatic conditions. There was adequate rainfall with better tools and harmonized climate conditions for farming. People no longer depended on hunting, fishing, and gathering. Agriculture and animal husbandry took care of their food.
Q6. What is the Vedic Age also known as? [2 marks]
The Vedic Age is also known as the age of the epics, as the two famous epics, Ramayana and Mahabharata were composed during this time.
Q7. Who were the untouchables and what kinds of jobs did they do? [2 marks]
Untouchables included some crafts persons, hunters and gatherers as well as people who helped perform burials and cremations. It was believed as per the priest's saying that contact with these groups was polluting.
Q8. What is history? [2 marks]
History can be defined as the study of our past. It is the story of the people who lived in the past. The events which happened in the past, ten or thousand years ago, are part of our history.
Q9. Which plants were cultivated during the Neolithic period? [2 marks]
The plants cultivated during the Neolithic period were wheat, barley, figs, oats and tall grasses.
Q10. What sets of unique objects were found in the cities of the Indus valley civilisation? [2 marks]
Unique objects found in almost all the cities of the Indus Valley civilisation are listed below:
- Red pottery painted with designs in black
- Stone weights
- Seals
- Special beads
- Copper tools
- Long stone blades
Q11. State at least four reasons why hunter-gatherers move from place to place. [5 marks]
The four reasons why hunter-gatherers move from place to place are as follows:
- Staying at one place finishes all available food–plant or animal resources.
- Animals moved from place to place, and hence, this made the hunter-gatherers move along with them for hunting.
- Plants and trees bore fruit in different seasons. Thus, people had to move season to season to find different kinds of plants.
- Plants and animals needed water to survive. Although most of the water bodies (lakes, ponds and streams) were perennial, some were seasonal. Thus, people living on the banks had to go in search of water during the dry seasons.
Q12. Who were Dasas/Dasyus? [5 marks]
- Dasas/Dasyus were a group of people who were different from Aryans (people who composed hymns). They also spoke a different language.
- Most of the dasas were enslaved and so the term ‘dasa’ (and the feminine dasi) came to mean slave. These were women and men who were often captured in war and were treated as the property of their owners.
- They had to do whatever work was given to them by their masters.
Section B (Civics)
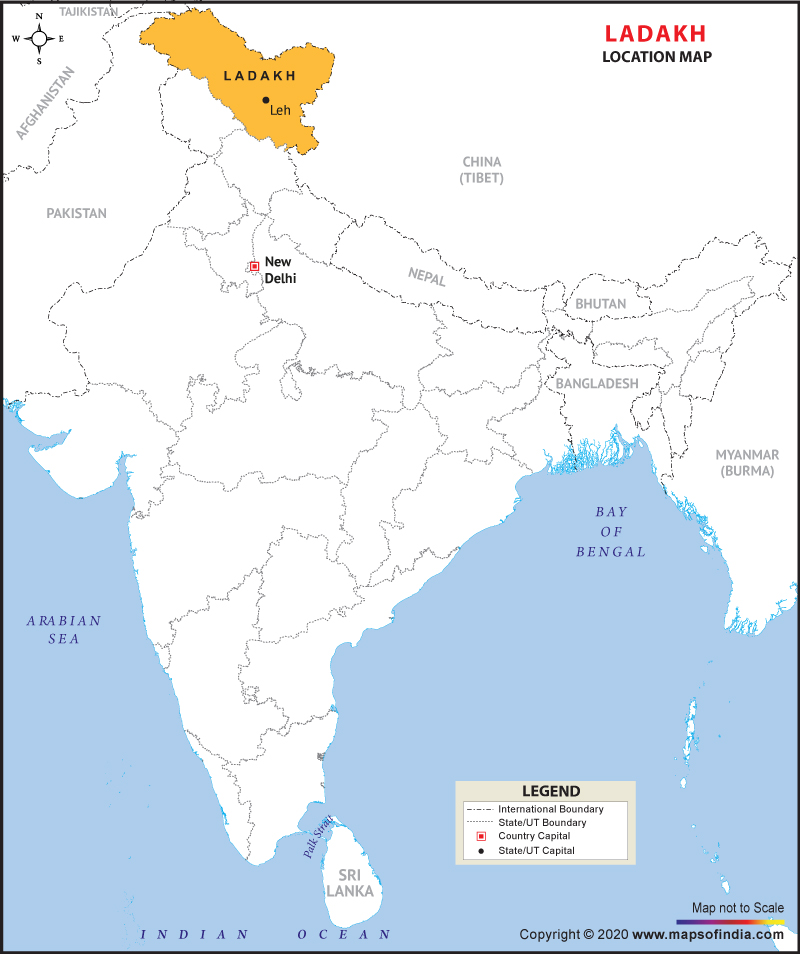
Q1. Ladakh is situated in the eastern part of which state? [1 mark]
a) Himachal Pradesh
b) Punjab
c) Jammu and Kashmir
d) Uttaranchal
Correct answer is Option (c).
Explanation: Ladakh, a large area of the northern and eastern Kashmir region, the northwestern Indian subcontinent. Administratively, Ladakh is divided between Pakistan (northwest), as part of Gilgit-Baltistan, and India (southeast), as part of Ladakh union territory.
Q2. The traveller who wrote about the lives of Muslims in Kerala is one of the writers listed below: [1 mark]
a) Al Beruni
b) Abdul Razzak
c) Afanasy Nikitin
d) Ibn Battuta
Correct answer is Option (d).
Explanation: The Moroccan traveller Ibn Battutah (14th century) has recorded the considerably huge presence of Muslim merchants and settlements of sojourning traders in most of the ports of Kerala.
 Ibn Battutah
Ibn Battutah
Q3. How many major religions are there in the world? [1 mark]
a) Seven
b) Three
c) Eight
d) Five
Correct answer is Option (c).
Explanation: There are 8 major religions in the world and every single one of them is practised in India.
Q4. The term used for disabled children is one of the terms listed below: [1 mark]
a) God’s children
b) Special children
c) Children with special needs
d) All of the above
Correct answer is Option (c).
Explanation: The other term used for disabled children is children with special needs.
Q5. What is a monarchy? [1 mark]
a) Rule by a king or queen
b) Chosen by the people
c) None of them
d) A and B
Correct answer is Option (a).
Explanation: Monarchy is a form of government in which the monarch (king or queen) has the power to make decisions and run the government. The monarch may have a small group of people to discuss matters with, but the final decision-making power remains with the monarch.
Q6. What do we mean by diversity? [2 marks]
Diversity is understanding that each individual is unique and includes recognising our individual differences. The differences can be in race, ethnicity, gender, sexual orientation, socio-economic status, age, physical abilities, religious beliefs, political beliefs or other ideologies.
Q7. After which massacre was the song ‘Don’t forget the days of blood, O friend’ composed? [2 marks]
The song was composed and sung after the Jallianwala Bagh massacre. It was sung in the memory of brave Indian people who lost their lives protesting against the British.
Q8. What do we mean by prejudice? [2 marks]
Prejudice means judging other people negatively or considering them to be inferior.
Example: When we think that only one particular way is the best and right way to do things, we often end up not respecting others who prefer to do the same things differently.
Q9. What are the various levels at which the government works? [2 marks]
The government works at the following three levels:
- Local-level – This level includes village, town or locality.
- State-level – This level covers the entire state.
Example: Haryana or Maharashtra- National-level – This level is related to the whole country.
Q10. Who are the main members of the Gram Sabha? [2 marks]
Gram Sabha consists of the Panchayat president called the Sarpanch and the Panchs who are the members of the Panchayat.
Q11. How is a Gram Panchayat formed? [5 marks]
Gram Panchayat is formed in the following manner:
- Every village Panchayat is divided into wards, i.e. smaller areas.
- Each ward elects a representative who is known as the Ward Member (Panch).
- All the members of the Gram Sabha also elect a Sarpanch who is the Panchayat President.
- The Ward Panch and Sarpanch from the Gram Panchayat.
Q12. How does the government in India promote justice? [5 marks]
- The government recognises and makes special provisions for groups within society that face inequality.
Example: In our society, there is a general tendency to value and care for the boy child more than the girl child.- This means that society does not value the girl and boy child equally, and this is unfair. Hence, the government steps in to promote justice by providing special provisions that can enable girls to overcome the injustice that they are subjected to.
- Thus, it is possible that fees for girls might be waived or lowered in government schools and colleges.
Section C (Geography)
Q1. The major physical divisions of India includes one of the following options: [1 mark]
a) Peninsula Plateau
b) North India plains
c) Great mountains of the North Himalayas North India plains
d) All of the above
Correct answer is Option (d).
Explanation: The physical features of India can be grouped under the following physiographic divisions:
- The Himalayan Mountains
- The Northern Plains
- The Peninsular Plateau
- The Indian Desert
- The Coastal Plains
- The Islands
Q2. Which two major rivers flow into the Arabian Sea? [1 mark]
a) Brahmaputra and Kaveri
b) Krishna and Godavari
c) Ganga and Yamuna
d) Narmada and Tapi
Correct answer is Option (d).
Explanation: The two prominent rivers which drain into the Arabian Sea are Narmada and Tapi.
The Narmada River is known as the "Life Line of Madhya Pradesh and Gujarat". This is because it has played a huge role for these states in several ways. Narmada arises from Amarkantak Plateau in Madhya Pradesh.
The Tapti River flows through central India between the Godavari and Narmada rivers. It flows westwards before draining into the Arabian Sea. The river has its origin in the eastern Satpura Range of southern part of Madhya Pradesh.
Q3. At which position do the Earth experience equal days and equal nights? [1 mark]
a) Summer Solstice
b) Equinox
c) Winter Solstice
d) None of the above
Correct answer is Option (b).
Explanation: On 21st March and September 23rd, direct rays of the sun fall on the equator. At this position, neither of the poles is tilted towards the sun; so, the whole earth experiences equal days and equal nights. This is called an equinox.
Q4. How many time zones are there in Russia? [1 mark]
a) 2 time zones
b) 10 time zones
c) 11 time zones
d) 12 time zones
Correct answer is Option (c).
Explanation: There are eleven time zones in Russia, which currently observe times ranging from UTC+02:00 to UTC+12:00.
Q5. Which of the following is the natural habitat of the Indian lion? [1 mark]
a) Kaziranga
b) Periyar
c) Sunderbans
d) Gir forest
Correct answer is Option (d).
Explanation: Gir Forest National Park and Wildlife Sanctuary is a forest found in Gujarat and it is the sole home for the Indian Lion.
Q6. Describe the Great Indian Desert. [2 marks]
The Great Indian Desert lies in the western part of India in Rajasthan. It is a dry, hot and sandy stretch of land. It has very little vegetation.
Q7. What would happen if the Earth did not rotate? [2 marks]
If the Earth did not rotate, the portion of the Earth facing the Sun would always experience day and would be hot continuously. The other half would remain in darkness and be freezing cold. Life would not be possible in such extreme conditions.
Q8. What are the special features of a globe? [2 marks]
A globe is a true model (miniature form) of the Earth. It may be small or big in size. It shows countries, continents and oceans in their correct size. In addition, it is not fixed but can be rotated.
Q9. Define climate? What type of climate does India have? [2 marks]
The average weather condition of a place measured over many years is called the climate. India has a monsoon type of climate.
Q10. What are migratory birds? Name a few of them. [2 marks]
Birds that move from one country to another country in winters are called migratory birds. Examples include Siberian Crane, Stork, Pintail Duck and Curlew.
Q11. Explain summer solstice? [5 marks]
- On the 21st of June, the Northern Hemisphere is tilted towards the Sun, while the Southern Hemisphere is turned away from the Sun.
- The rays of the Sun fall vertically over the Tropic of Cancer and a large portion of the Northern Hemisphere receives the heat and light of the Sun.
- Days are longer than the nights in the Northern Hemisphere and they experience the summer season.
- The longest day and the shortest night occur on 21st June in the Northern Hemisphere.
- At this time, all the conditions are reversed in the Southern Hemisphere and they experience winter. This position of the Earth is called the Summer Solstice.
Q12. Why does the amount of heat reduce as we go from the Equator to the North Pole or the South Pole? [5 marks]
- As the Earth is spherical in shape, the Equator receives direct sun rays and the North Pole and the South Pole receive slanting sun rays.
- Places located in the Torrid Zone experience vertical rays of the Sun at least twice a year, and this region receives maximum heat.
- Places in the temperate zone receive slanting rays of the Sun and less heat, while the Frigid Zone is very cold receiving the extremely slanting rays of the Sun.
- Hence, the amount of heat received in the areas of the North Pole or the South Pole is lesser than in areas located in the Equator.
FAQs on Class 6 Social Studies (SST): CBSE Sample Question Paper with Solutions Term I – 1 - Sample Papers For Class 6
| 1. What is the CBSE Sample Question Paper for Class 6 Social Studies (SST) Term I? |  |
| 2. How can students use the CBSE Sample Question Paper for Class 6 Social Studies (SST) Term I? |  |
| 3. What is the importance of studying Social Studies in Class 6? |  |
| 4. How can parents help their child prepare for the CBSE Class 6 Social Studies (SST) exam? |  |
| 5. What are some effective study tips for students to prepare for the CBSE Class 6 Social Studies (SST) exam? |  |



















