Natural Disasters Class 5 Notes SST
| Table of contents |

|
| What is a Natural Disaster? |

|
| Earthquake |

|
| Flood |

|
| Drought |

|
| Cyclone |

|
| Tsunami |

|
| Volcano |

|
What is a Natural Disaster?
Natural disasters are strong and sudden events in nature that cannot be controlled by humans. They are caused by the forces of nature and may result in loss of life, injury, and damage to property. Natural disasters can be caused by things like bad weather, earthquakes, landslides, or other events that happen on or inside the Earth. No place on Earth is completely safe from natural disasters, but some types of disasters happen more often in certain areas. Natural Disasters
Natural Disasters
- The best way to tell when natural disasters will occur is to study ones that have already happened. This gives important information about the events that led up to disasters.
- Most natural disasters are impossible to prevent. The forces of nature that cause them are beyond the control of humans. Their effects, however, may be reduced in several ways.
Earthquake
- An earthquake is the shaking of the surface of the Earth due to the sudden release of energy in the Earth’s crust.
- The seismic activities in an area determine the type and intensity of the earthquake.
 Earthquake
Earthquake - The sudden movement under the surface of the earth causes vibrations on the surface of the earth. It may lead to a minor or major disaster.
- The place where an earthquake start is called the focus.
- The point directly above the focus on the surface of the earth is called the epicentre.
- The effect of an earthquake is greatest at its epicentre.

Causes
- Most earthquakes are caused by the rapid release of energy stored within the rocks of the crust.
- Earthquakes occur due to internal pressures within the earth.
Consequences
- It causes a great loss of life and property.
- An earthquake that takes place under the ocean can sometimes cause tsunamis.
Precautions
The following precautions should be taken during an earthquake:
- Go to open areas and stay away from buildings.
- If you cannot go out of the building, stand in the corner to avoid things falling on you.
- Do not use a lift during or immediately after an earthquake. Use the staircase.
- Get out of cars or buses if you sense an earthquake.
- If on a road, stay away from trees, poles, electric wires, etc.
- Do not stand near mirrors, shelves, fans, etc.
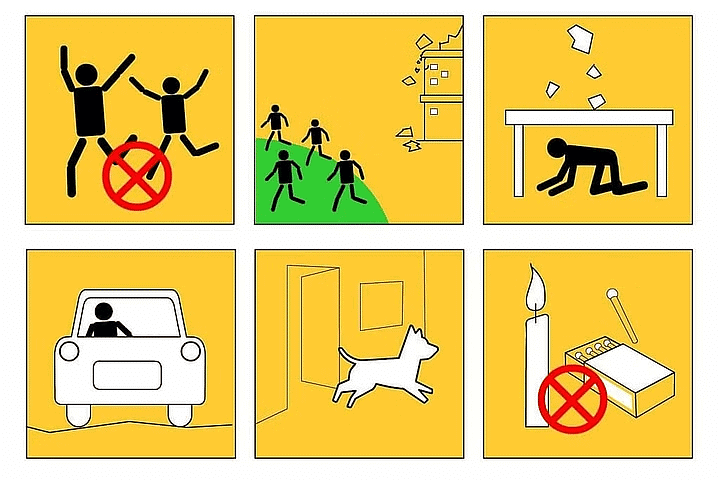 Precautions to take during an Earthquake
Precautions to take during an Earthquake
Major Earthquake
The Bhuj earthquake of 7.6 magnitude (Richter scale) that shook the Indian province of Gujarat on the morning of January 26, 2001 was the deadliest in India’s recorded history.
It is very difficult to predict when an earthquake will occur. Japan and the Philippines are the most earthquake-prone countries in the world.
Flood
- A flood is an overflow of water on land. Sometimes a river might receive extra water, either from heavy rains or other natural disasters.
- When this happens, the water overflows from its normal path in the river bed and onto the dry land.

Causes
- Floods also occur when a dam falls or when a sea rises above its level.
- When heavy rain takes place.
- Melting of a large amount of snow on mountains during the summer season.
- Cyclones and tsunamis in coastal areas.
- Strong tides in the sea.
- Blocking of the river channel by landslides.
Consequences
- A flood causes huge damage to life and property.
- It causes many water-borne diseases.
- Clean water gets contaminated, which leads to water scarcity.
Precautions
- Banks of rivers should be repaired if they develop cracks.
- All electrical equipments should be disconnected if there is a danger of flood.
Major Flood
The death toll in the Assam floods on July 5, 2012 rose to 100 even as the water started to recede in most of the 27 affected districts, except Dhemaji. However, the rising water level of the Jiadhal river submerged several villages in the morning. The surging waters also affected parts of National Highway number 52 in the district.
Floods are common in India during the monsoon season. Some areas get flooded due to their proximity to rivers. Bihar, West Bengal and Assam experience floods almost every year.
Drought
- Drought is a long period when there is very little or no rain.
- Drought-affected areas have very few natural sources of water.
- Farmers are the worst affected during droughts.
- A drought can last for days, months or years

Causes
- Lack of rainfall.
- Insufficient water supply to meet everybody’s needs.
- Lack of snowfall in mountain regions (not in India, but in very cold regions of the world).
Precautions
- Water storage should be constructed to store rainwater.
- Farmers should be educated to avoid over-cropping and over-grazing.
- Steps should be taken by the government to limit human settlements in drought-prone areas.
- Rainwater harvesting, which involves collecting rainwater, should be encouraged.
Consequences
- In a country like India, where farmers depend on monsoon rains for agriculture, cultivation is not possible in dry conditions.
- Drought causes scarcity of food.
- It also leads to death of human beings and animals.
India has many drought-prone states, like Maharashtra, Karnataka, Gujarat, Rajasthan, Andhra Pradesh and Orissa.
Cyclone
- A cyclone is a rotating mass of air with minimum pressure in its centre.
- During a cyclone, the wind blows at a very high speed followed by heavy rainfall.
- Cyclones are formed with huge amount of energy from the ocean to the atmosphere.
 Cyclone
Cyclone
Causes
- Cyclones are caused by warm tropical moisture bearing clouds, which develop above oceans or seas. They occur in areas of very low pressure, when air heated by the sun rises rapidly and becomes saturated with moisture.
- This air then condenses into thunder-clouds. When the cyclone continues its course and winds blow strongly, they may cause heavy damage to life and property.
Consequences
- A cyclone causes heavy floods. Flooding may result in the spread of diseases like cholera and malaria.
- It damages the electricity supply system and tele-communication system.
Precautions
- Watch weather forecasts and warnings.
- Move to a safe place before the cyclone hits.
- Do not go near the sea.
- Keep phone numbers of hospitals, relatives and help agencies handy.
Major Cyclone
The coastal areas of Andhra Pradesh were hit by a cyclone in May 1990. Winds blew at a speed of over 250 km per hour. The cyclone affected nearly 6,000 villages. About 10 lakh houses were destroyed.
Tsunami
- Tsunamis are big waves caused by underwater earthquakes or volcanoes.
- They start small in deep water but grow taller and more powerful as they approach the shore.
- A tsunami is a series of large waves that are created when the water in an ocean is displaced rapidly.
 Tsunami
Tsunami
Causes
- Volcanic eruptions, underwater explosions and underwater earthquakes can generate a tsunami.
- The effects of a tsunami are devastating.
Consequences
- Tsunamis can severely affect coastlines, causing large-scale loss to life and property.
Precautions
- People near the sea or the beach should rush to higher places if a tsunami warning is heard.
- One should stay away from the ocean till it is considered safe by the authorities.
Major Tsunami
On March 11, 2011, off the Pacific coast of Japan, a 9.0 magnitude earthquake produced a tsunami 33 feet (10 m) high waves along Japan’s north eastern coast. The wave caused widespread damage, with an official count of around 20,000 people confirmed to be killed/missing.
Volcano
- A volcano is an opening on the earth’s crust through which molten materials (magma) comes out on the surface from its interior.
- The molten magma which flows out through the vent is called lava. Lava comes out when a volcanic eruption takes place.
- Gases and ashes are forced out of cracks in the crust of the earth.
- When the volcanic eruption stops and the lava cools, it forms a mountain. A bowl-shaped hollow is formed at the top of such mountains and is called a crater.
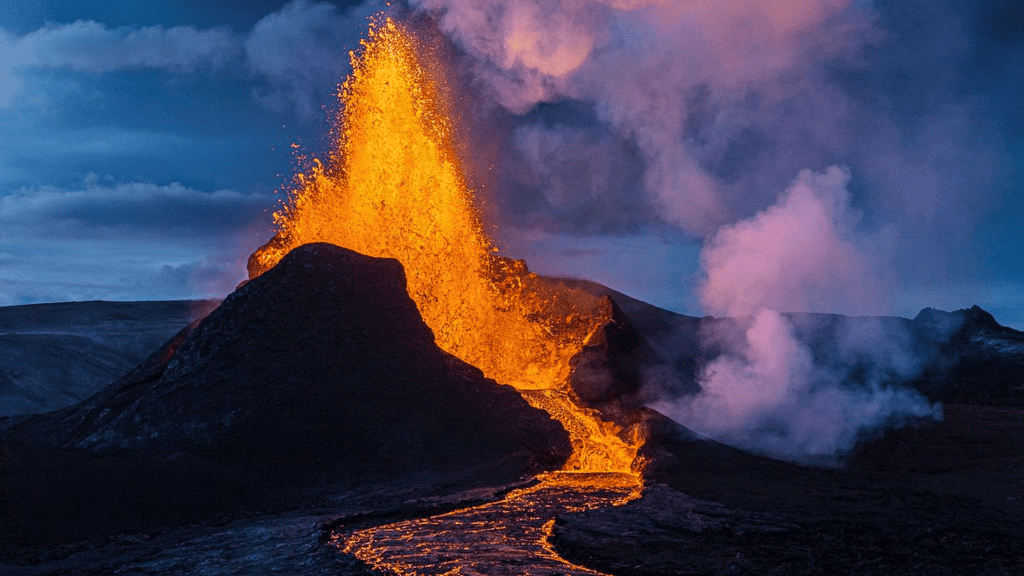 Volcano
Volcano
Causes
- Magma or molten rock is formed beneath the surface due to various reasons.
- Molten rock ruptures the ground and pours out.
- Sometimes, it cools down beneath the ground surface instead of pouring out.
Types of volcanoes
- Extinct or dead volcanoes are those which have not erupted for thousands of years and will probably never erupt. For example, Mt. Kilimanjaro in Africa.
- Dormant or sleeping volcanoes are those that have not erupted for many years but have chance of erupting again. When a vent becomes blocked by hardened lava, it becomes a dormant volcano. For example, Mt. Fujiyama in Japan.
- The third and the most dangerous are the active volcanoes. They often erupt and lead to destruction. For example, Mt. Etna in Italy.
We should never forget that an extinct volcano may become active. For example, Mt. Vesuvius in Italy was an extinct volcano, but it erupted after many years and destroyed Pompeii in 79 AD.
Consequences
- Volcanoes can destroy entire cities and change the landscape of a place.
- They cause vast damage to human life and property.
Precautions
- In many places where volcanoes are active, people should move to other far-off places till the volcanoes have stopped erupting.
- Food and water should be stored for such emergencies.
Major Volcano
Barren Island, located in the Andaman Sea, is the only confirmed active volcano in South Asia. It erupted recently on May 2, 2006.
|
33 videos|264 docs|50 tests
|
FAQs on Natural Disasters Class 5 Notes SST
| 1. What is a natural disaster? |  |
| 2. What causes earthquakes? |  |
| 3. How do floods occur? |  |
| 4. What is a drought and what causes it? |  |
| 5. How do tsunamis form? |  |





















