NCERT Exemplar Solutions: Light | Science Class 7 (Old NCERT) PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Multiple Choice Questions |

|
| Very Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Short Answer Type Questions |

|
| Long Answer Type Questions |

|
Multiple Choice Questions
Q1. Boojho and Paheli were given one mirror each by their teacher. Boojho found his image to be erect and of the same size whereas Paheli found her image erect and smaller in size. This means that the mirrors of Boojho and Paheli are, respectively
(a) plane mirror and concave mirror.
(b) concave mirror and convex mirror.
(c) plane mirror and convex mirror.
(d) convex mirror and plane mirror.
 Plane Mirror, Concave Mirror and Convex MirrorAns: c
Plane Mirror, Concave Mirror and Convex MirrorAns: c
Explanation:
The plane mirror always forms an image of the same size and erected image. Convex mirror forms erected and smaller image.
Q2. Which of the following can be used to form a real image?
(a) Concave mirror only.
(b) Plane mirror only.
(c) Convex mirror only.
(d) Both concave and convex mirrors
Ans: a
Explanation:
As a concave mirror alone can produce a real image. Plane mirror & convex mirror form a virtual image of an object at all times.
Q3. If an object is placed at a distance of 0.5 m in front of a plane mirror, the distance between the object and the image formed by the mirror will be
(a) 2 m
(b) 1 m
(c) 0.5 m
(d) 0.25 m
Ans: b
Explanation:
The image formed by a plane mirror is at the same distance behind the mirror as the object is in front of it. Therefore, the distance between object and image is given by the distance between object and mirror + distance between mirror and image = 0.5 m+ 0.5 m = 1 m
Q4. You are provided with a concave mirror, a convex mirror, a concave lens and a convex lens. To obtain an enlarged image of an object you can use either
(a) concave mirror or convex mirror.
(b) concave mirror or convex lens.
(c) concave mirror or concave lens.
(d) concave lens or convex lens.
Ans: b
Explanation:
Concave mirror and convex lens form enlarged images whereas convex mirror and concave lens form diminished images.
Q5. A rainbow can be seen in the sky
(a) when the sun is in front of you.
(b) when the sun is behind you.
(c) when the sun is overhead.
(d) only at the time of sunrise.
Ans: b
Explanation:
Rainbow is formed after rain and when the sunlight is low. A rainbow appears when is your back is towards the sun.
Q6. An erect and enlarged image can be formed by
(a) only a convex mirror.
(b) only a concave mirror.
(c) only a plane mirror.
(d) both convex and concave mirrors
Ans: b
Explanation:
The concave mirror always formed a virtual image which is erected and enlarged in size whereas convex mirror forms diminished and erected image.
Q7. You are provided with a convex mirror, a concave mirror, a convex lens and a concave lens. You can get an inverted image from
(a) both the concave lens and convex lens.
(b) both concave mirror and convex mirror.
(c) both concave mirror and convex lens.
(d) both convex mirror and concave lens.
Ans: c
Explanation:
Concave mirror and convex lens can only form a real and inverted image of an object. As a convex mirror and concave lens always form a virtual and erect image of an object.
Q8. An image formed by a lens is erect. Such an image could be formed by a
(a) convex lens provided the image is smaller than the object.
(b) concave lens provided the image is smaller than the object.
(c) concave lens provided the image is larger than the object.
(d) concave lens provided the image is of the same size.
Ans: b
Explanation:
Virtual, erect and diminished image of an object is formed by a concave lens. Convex lens forms magnified, erect and virtual image.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Q1. The image formed by a lens is always virtual, erect and smaller in size for an object kept at different positions in front of it. Identify the nature of the lens.
Ans: The answer is Concave lens
Q2. Fill in the blanks:
(a) The inner surface of a steel spoon acts as a ___________ mirror. (b) The outer surface of a flat steel plate acts as a ___________ mirror. (c) The outer shining surface of a round bottom steel bowl acts as a __________ mirror. (d) The inner surface of the reflector of a torch acts as a __________ mirror.
Ans:
(a) The inner surface of a steel spoon acts as a concave mirror. (b) The outer surface of a flat steel plate acts as a plane mirror. (c) The outer shining surface of a round bottom steel bowl acts as a convex mirror. (d) The inner surface of the reflector of a torch acts as a concave mirror.
Q3. State whether the following statements are True or False.
(a) A concave lens can be used to produce an enlarged and erect image.
(b) A convex lens always produces a real image.
(c) The sides of an object and its image formed by a concave mirror are always interchanged.
(d) An object can be seen only if it emits light.
Ans:
- False- A concave lens can be used to produce a diminished and erect image.
- False- A convex lens always produces a virtual image
- True
- False- An object can be seen if it reflects light falling on it.
Short Answer Type Questions
Q1. What type of mirror is used as a side mirror in a scooter? Why is this type of mirror chosen?
Ans: Convex mirrors are used as a side mirror in a scooter because in Convex mirrors image formed is spread over a large area. This will help the drivers to see the large area behind in the traffic.
Q2. Observe the figures given in Figure carefully.

The given figures show the path of light through lenses of two different types, represented by rectangular boxes A and B. What is the nature of lenses A and B?
Ans:
- Convex lens
- Concave lens
Q3. Boojho made light from a laser torch to fall on a prism. Will he be able to observe a band of seven colours? Explain with a reason.
Ans: No, Boojho cannot observe a band of colours because laser light gives torch of only one colour.
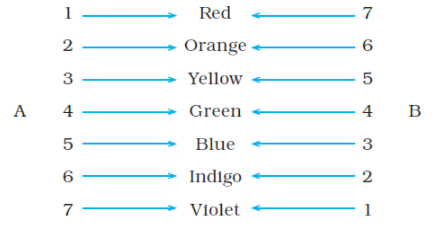
Q4. State the correct sequence (1-7) of colours in the spectrum formed by the prisms A and B, shown in Figure.
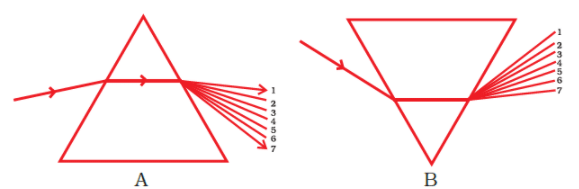
Ans:
Q5. The side mirror of a scooter got broken. The mechanic replaced it with a plane mirror. Mention any inconvenience that the driver of the scooter will face while using it?
Ans: A driver cannot see the traffic spread over the large area behind him.
Q6. The concave reflecting surface of a torch got rusted. What effect would this have on the beam of light from the torch?
Ans: If the concave reflecting surface of a torch got rusted, a beam of light will be diffused with lower intensity.
Q7. An erect and enlarged image of an object is formed on a screen. Explain how this could be possible.
Ans: An erect and enlarged image of an object is formed on a screen if the object is placed upside down between F and 2F of the lens.
Q8. Two different types of lenses are placed on a sheet of newspaper. How will you identify them without touching?
Ans: The lens is a convex lens if the letters appear magnified and the lens is concave if the image appears shortened.
Q9. A shopkeeper wanted to fix a mirror which will give a maximum view of his shop. What type of mirror should he use? Give reason.
Ans: Shopkeeper fixes convex mirror because forms images of object spread from large areas.
Q10. The distance between an object and a convex lens is changing. It is noticed that the size of the image formed on a screen is decreasing. Is the object moving in a direction towards the lens or away from it?
Ans: An object is moving away from the lens.
Long Answer Type Questions
Q1. Suppose we wish to obtain the real image of a distant tree. Explain two possible ways in which we can do it.
Ans: Two possible ways in which the real image of a distant tree can be obtained are given below :
By using a concave mirror and a screen- By using a concave mirror, a real image is formed if the distance between the mirror and the object is beyond the focus.
By using a convex lens and a screen- In a convex lens, when the object is far away from the lens, the image is very close to the lens forming a real and inverted image.
Q2. It was observed that when the distance between an object and a lens decreases, the size of the image increases. What is the nature of this lens? If you keep on decreasing the distance between the object and the lens, will you still able to obtain the image on the screen? Explain.
Ans: It is a convex lens.
No, when the object is placed close to a convex lens then the image formed is virtual which cannot be obtained on the screen.
Q3. You are given three mirrors of different types. How will you identify each one of them?
Ans: We can identify the mirrors by forming images of an object which are given as below:
- Plane mirror: In case of a plane mirror, the image will be virtual, erect and of the same size as that of an object.
- Concave mirror: In case of a concave mirror, an image may be real or virtual, inverted or erect and magnified or diminished depending upon the position of the object.
- Convex mirror: In case of a convex mirror, an image formed will always be virtual, erect and diminished in spite of the position of the object.
|
112 videos|286 docs|28 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar Solutions: Light - Science Class 7 (Old NCERT)
| 1. What is the definition of light? |  |
| 2. How does light travel? |  |
| 3. What is the speed of light? |  |
| 4. How does light interact with objects? |  |
| 5. What are the different colors of light? |  |
















