Class 9 SST: Sample Question Paper- 6 (With Solutions) PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Section - A |

|
| Section - B |

|
| Section - C |

|
| Section - D |

|
Section - A
Q.1. Match the following items given in Column I with those in Column II.
Ans. (A)-3, (B)-1, (C)-2, (D)-4
Q.2. The food procured by FCI is distributed to the______through the Public Distribution System.
OR
The Green Revolution during the late 1960s and early 1970s, helped India significantly to achieve_____.
Ans. Poorer sections of society
OR
Self-sufficiency in foodgrains.
Q.3. Which one of the following describes the drainage patterns resembling the branches of a tree?
(a) Radial
(b) Dendritic
(c) Centrifugal
(d) Trellis
Ans. (b) Dendritic. Drainage PatternsQ.4. Why the Godavari river is known as 'Dakshin Ganga’?
Drainage PatternsQ.4. Why the Godavari river is known as 'Dakshin Ganga’?
Ans. The Godavari river is known as ‘Dakshin Ganga’ because of its length and large area covered by it.
Q.5. In which type of forests were the villagers forbidden from taking anything?
OR
Which species of trees are Suitable for building ships and railways?
Ans. The villagers were forbidden from taking anything from the reserved forests.
OR
The species of trees suitable for building ships and railways are Teak and Sal.
Q.6. _______is a dry forested area below the foothills of Garhwal and Kumaon.
Ans. Bhabhar
Q.7. What is the age group of the population, which is regarded as the workforce?
OR
Who said that food security means access to food through entitlements?
Ans. In India, the workforce population includes people from the age of 15 to 53 years.
OR
Amartya Sen is the speaker here. Amartya SenQ.8. In geographical terms, Indian landmass is called a Peninsula. Why?
Amartya SenQ.8. In geographical terms, Indian landmass is called a Peninsula. Why?
Ans. Peninsula is a landmass that is bounded by the sea on three sides. As India has water bodies on its three sides, it is called, a peninsula.
Q.9. _________ and threshers are provided by Iron industry.
Ans. Tractors.
Q.10. The famous book, 'Two Treatises of Government' is written by_______.
Or The two Indians who responded to the ideas coming from revolutionary France are_____and______.
Ans. John Locke
OR
Tipu Sultan, Raja Rammohan Roy
Q.11. Robert Mugabe was the President of
(a) Ethiopia
(b) Zimbabwe
(c) Algeria
(d) Mozambique
Ans. (b) Zimbabwe
Q.12. The Godavari is the longest river of Peninsular India.
Ans. True
Q.13. Bhabar is
(a) Vast meadows in the low mountains.
(b) Vast meadows in the high mountains.
(c) A dry forested area below the foothills of Garhwal and Kumaon.
(d) None of the above
Ans. (c) A dry forested area below the foothills of Garhwal and Kumaon.
- To the east, in Garhwal and Kumaon, the Gujjar cattle herders came down to the dry forests of the bhabar in the winter and went up to the high meadows – the bugyals – in summer. Many of them were originally from Jammu and came to the UP hills in the nineteenth century in search of good pastures.
Q.14. The makers of the Constitution of India made a provision of______ to ensure representation of every section of society.
Ans. Reserved constituencies
Q.15. Forestry comes under secondary sector.
Ans. False
- When we produce a good by exploiting natural resources, it is an activity of the primary sector. Since most of the natural products we get are from agriculture, like dairy, fishing, forestry, this sector is also called agriculture and related sector.
- Manufacturing comes under the secondary sector.
Q.16. The colonial government started commercial forestry in India in the____.
Or In_______the Mataram Kingdom of Java Split.
Ans. Early 19th century
OR
1775
Q.17. Find the incorrect option.
Successful slogans given by political parties in various elections are as follows:
(a) "India shining" by the Congress Party in the 1971 Lok Sabha elections
(b) "Land to the Tiller" by the Left Front in the 1977 West Bengal Assembly elections
(c) "Save democracy" by the Janata Party in the 1977 Lok Sabha elections
(d) "Protect the Self-Respect of the Telugus" by the Telugu Desam Party in the 1983 Andhra Pradesh Assembly elections
Ans. (a) "India shining” by the Congress Party in the 1971 Lok Sabha elections
Q.18. What do you understand by ‘people as a resource’?
Ans. People as a resource is a way of referring to a country’s working people in terms of their existing productive skills and abilities.
Q.19. In the question given below, there are two statements marked assertion (A) and Reason (R). Read the statement and choose the correct option.
Assertion (A): The seasonal hunger affects the landless agricultural labourers most.
Reason (R): The seasonal hunger is the consequence of the seasonal nature of food production and harvesting.
Options:
(a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
(b) Both A and R are true and R is not the correct explanation of A.
(c) A is true but R is false.
(d) A is false but R is true.
Ans. (a) Both A and R are true and R is the correct explanation of A.
Q.20. First, the Constituent assembly decided some basic principles which were agreed upon. Then a Drafting Committee prepared a draft Constitution for discussion. Several rounds of thorough discussion took place on the Draft Constitution, clause by clause. The members deliberated for 114 days spread over three years to finalise the Constitution. Every document presented and every word spoken in the Constituent Assembly has been recorded and preserved. These are called ‘Constituent Assembly Debates’. These debates provide the rationale behind every provision of the Constitution.
Analyse the information given above and consider one of the following as the correct option:
(a) The Constituent Assembly
(b) Constituent Assembly debates
(c) The Preamble to the Indian Constitution
(d) The making of the Constitution of India
Ans. (d) The making of the Constitution of India
Section - B
Q.21. Mention any three merits of democracy.
OR
Why it is said that democracy is possible only if elections are free and fair?
Ans.
The three merits of democracy are as follows:
- Democracy looks after the welfare of all people. The society as a whole benefit under the democratic system. It looks after the interests of the masses.
- Democracy is based on equality, where all citizens are treated without any discrimination of caste, colour, creed, sex or religion.
- Democracy forms a democratic government. It is a strong and responsible government and guarantees liberty of thought and expression, freedom to form associations and even to criticise the government. This is essential for the self-expression and development of people.
OR - Holding free and fair elections is the soul of a democratic setup. In a democracy, people have the choice to remove the existing rulers, if they wish so.
- Those currently in power have a fair chance of losing if there is a free and fair election. Democracy is based on a fundamental principle of political equality.
- Each adult citizen has one vote and each vote has one value.
- In China, only those who are members of the Chinese Communist Party or eight smaller parties allied to it are allowed to contest elections.
- So there is no real choice between political alternatives. Ah, the elections are free and fair, there is no democracy in China.
- Therefore, democracy is possible only if elections are free and fair.
Q.22. What was unique about the apartheid system followed in South Africa?
OR
Explain any three salient features of the Indian Constitution.
Ans.
- Apartheid was the system of racial discrimination on the basis of skin colour. This system was practised in South Africa where the original inhabitants, which were large in number, were seen low in society.
- Europeans who had settled in South Africa and were few in number enjoyed a high rank in society.
- The original inhabitants were termed as blocks (natives) and Europeans were termed as whites.
- The uniqueness was that in spite of the natives who were large in number, were ruled in their own country by a small community of European settlers.
OR
The Indian Constitution is a very long and detailed document, Its three salient features are discussed below:
(i) The Constitution generates a degree of trust and coordination that is necessary for different kinds of people to live together in our country.
(ii) The Indian Constitution suggests a procedure for choosing persons to govern the country. It specifies how the government will be constituted and who will have the power to make which decisions.
(iii) The Indian Constitution needs to be amended quite regularly to keep it updated.
Q.23. The central location of India at the head of the Indian Ocean is considered of great significance. Why? Any three points.
Ans.
The great significance of the central location of India is due to the following reasons:
(i) It is at the centre between East and West Asia.
(ii) India is a southward extension of the Asian Continent. The trans-Indian Ocean routes which connect the countries of Europe in the West and the countries of East Asia provide a strategic central location to India.
(iii) As the Deccan Peninsula protrudes into the Indian Ocean, it helps India to establish close contacts with West Asia, Africa and Europe from the western coast with Southeast and East Asia from the eastern coast.
Q.24. What is the Universal Adult Franchise? State its two characteristics.
OR
Mention some wide-ranging powers of the Election Commission.
Ans.
- In our country, all the citizens aged 18 years and above have the right to vote irrespective of any discrimination on the basis of caste, religion, colour or gender.
- It is known as the Universal Adult Franchise.
- Two characteristics of Universal Adult Franchise are as follows:
(i) Under this system, everyone is treated equally and to give equal opportunity to elect their representatives in the law-making process of the country.
(ii) This also reflects the democratic form of government elected through general elections.
OR
The wide-ranging powers of the Section Commission of India are as follows:
(i) It takes decisions on every aspect of conduct and control or elections from the announcement of elections to tine declaration of results.
(ii) It implements the code of conduct and punishes any candidate or party that violates it.
(iii) It can order the government to follow some guidelines to prevent the use and misuse of governmental power to enhance its chances to win or to transfer some government officials.
(iv) At the time of election duty, government officers must work under the control of the Election Commission not under the government.
Q.25. "Food security is essential in India." Justify the statement.
Ans.
Food security is essential in India.
Following points justify the given statements:
- The poorest section of the society might be food insecure most of the times. At the same time, persons above the poverty line might also be food insecure during natural calamities, economic recessions etc.
- During natural calamities like drought, earthquake, flood, tsunami etc, total production of foodgrains decreases. It creates a shortage of food and the prices go up. At high prices, some people cannot afford to buy food.
Q.26. “Democracy is a form of government in which the rulers are elected by the people.” In light of this definition, explain the features of democracy.
Ans.
In the light of the above definition of democracy, the features of democracy are explained as mentioned below:
(i) In a democracy, the final decision-making power must rest with those elected by the people.
(ii) Democracy must be based on a free and fair election where those currently in power have a fair chance of losing.
(iii) In a democracy, each adult citizen must have one vote and each vote must have one value.
Q.27. What do you mean by famine? How it occurs and what are its effect?
OR
How is Minimum Support Price (MSP) helpful for farmers and also for ensuring food security in India? Explain.
Ans.
- A famine is characterised by widespread deaths due to starvation and epidemics caused by forced use of contaminated water or decaying food and loss of body resistance due to weakening from starvation.
- This occurs due to severe shortage of food resulting from crop failure or other calamity, which increases the price cf food dramatically. Poor people cannot afford to buy food at these high prices.
- They suffer from food shortage which ultimately leads to starvation.
- The inflation in food prices also affects middle income earners.
- The production of food grain also decreases that results in further increase in food prices. This results in starvation and famine like Bengal famine of 1943.
OR
Minimum Support Price is helpful for farmers and for ensuring food security in the following ways:
(i) It provides an economic assurance to the farmers that motivates them to grow targeted crops. They cannot be exploited by middlemen for lower prices.
(ii) Production of targeted crops increases.
Example: India once an importer of wheat is now one of the largest producers of it and has huge surplus stocks catering to both domestic and international demands.
(iii) Increased production also helped in achieving food security and catering to the requirements of National Food Security Act.
Q.28. Do you think the rich farmers are violating the principle of justice by not giving a fair wage to the labourers? Explain it in Indian context.
Ans.
- It is very common in India that the rich farmers do not give the proper wage to the labourers. Sometimes they are offered only food, but not money.
- The rich farmers take advantage of the helpless condition of the labourers.
- Nowadays, the rate has been fixed by the government based on the evaluation of normal work done by a farm labourer.
- According to Labour Ministry, an unskilled, semi-skilled and skilled labourer can get wages from 300 to 400 respectively, according to their work.
- But there is heavy competition for work, among the farm labourers, so people agree to work for even lower wages.
- This malpractice can be corrected by the local government like the village panchayat intervening and ensuring that the rich farmers should pay the farm labourers the minimum wage fixed by the government.
Section - C
Q.29. Explain the main provisions of the Right to Equality.
OR
How does our Constitution specify the cultural and educational rights of the minorities?
Ans.
The main provisions of the Right to Equality are as follows:
(i) Equality Before Law Article 14 of the Constitution guarantees that all citizens shall be equally protected by the laws of the country. It means that the state cannot discriminate any of the Indian citizens on the basis of his/her caste, creed, colour, sex, gender, religion or place of birth.
(ii) Social Equality and Equal Access to Public Areas Article 15 states that every person shall have equal access to public places like public parks, museums, wells, bathing ghats, temples, etc.
(iii) Equality in Matters of Public Employment Article 16 states that all citizens can apply for government jobs. But this right shall not be conferred to overseas citizens of India.
(iv) Abolition of Untouchability Article 17 of the Constitution abolishes the practice of untouchability and anyone doing so is punishable by law.
(v) Abolition of Titles Article 18 of the Constitution prohibits the state from conferring any title.
OR
- Democracy gives power to majority. Language, culture and religion of minorities need special protection here.
- Otherwise, they feel neglected and undermined under the influence of religion and culture of majority section in the society.
- Thus, Constitution makers specified the cultural and educational rights of the minorities in our society.
- These are as follows:
(i) Any section of citizens with a distinct language or culture has a right to conserve It.
(ii) Admission to any educational institution maintained by government or receiving government aid cannot be denied to any citizen on the ground of religion or language.
(iii) All minorities have the right to establish and administer educational institutions of their own choice.
Q.30. Read the extract and answer the questions that follow:
Due to the curvature of Earth, the amount of solar energy received varies according to latitude. As a result, air temperature decreases from the equator towards the poles. As one goes from the surface of Earth to higher altitudes, the atmosphere becomes less dense and temperature decreases. Thus, the hills are cooler during summers.
The pressure and wind system of any area depend on the latitude and altitude of the place. Thus, it influences the temperature and rainfall pattern. The sea exerts a moderating influence on climate as the distance from the sea increases, its moderating influence decreases and the people experience extreme weather conditions. This condition is known as continentality, meaning that the summers are very hot and the winters are very cold.
Ocean currents, along with onshore winds affect the climate of coastal areas. For instance, any coastal area with warm or cold currents flowing past it will be warmed or cooled if the winds are onshore.
Questions:
(a) Why are the hills cooler than the plains in summers?
(b) Where do people experience continentality and why?
(c) What factors affect the climate of coastal areas?
Ans.
(a) The hills are cooler than the plains in summers because the temperature decreases as one goes from the surface of Earth to higher altitudes.
(b) Continentality, meaning that the summers are very hot and the winters are very cold, is experience in land areas far from the sea. The reason for this is that the sea exerts a moderating influence on climate.
(c) Two factors affect the climate of coastal areas; the nature of currents flowing past them and the presence of onshore winds. Thus, a coastal area with a warm current flowing past it will be warmed if onshore winds are present. Similarly, a coastal area with a cold current flowing past it will be cooled if onshore winds are present.
Q.31. Compare the powers and position of Ministers and the bureaucracy, i.e., the civil servants in India.
OR
Describe the Right to Equality as guaranteed under the Constitution of India. What are various exceptions to it?
Ans.
Or
(a) Main features of the Right to Equality are as mentioned below:
(i) Equality before the law or equal protection of laws.
(ii) No discrimination on account of religion, caste, sex etc.
(iii) Access to all public places like shops, cinema halls etc.
(iv) No restrictions on use of wells, bathing ghats etc.
(v) Equal opportunity in matters of employment or appointment in the government.
(vi) Abolition of untouchability,
(vii) Abolition of titles except provided on account of academic and military distinctions.
(b) Exceptions:
(i) Reservations for SC/ST.
(ii) Preference to women or physically handicapped.
(iii) Special treatment to ensure equal opportunity.
Q. 32. Read the extract and answer the questions that follows:
Nazi ideology was synonymous with Hitler's worldview. According to this, there was no equality between people, but only a racial hierarchy. In this view blond, blue-eyed, Nordic German Aryans were at the top, while jews were located at the lowest rung. They came to be regarded as an anti-race, the arch-enemies of the Aryans. All other coloured people were placed in between depending upon their external features. Hitler's racism borrowed from thinkers like Charles Darwin and Herbert Spencer.
Darwin was a natural scientist who tried to explain the creation of plants and animals through the concept of evolution and natural selection. Herbert Spencer later added the idea of survival of the fittest. According to this idea, only those species survived on earth that could adapt themselves to changing climatic conditions. We should bear in mind that Darwin never advocated human intervention in what he thought was a purely natural process of selection. However, his ideas were used by racist thinkers and politicians to justify imperial rule over conquered peoples.
(a) What is the main point in Nazi ideology?
(b) What is the source of Hitler's inspiration for racism?
(c) What is the similarity between the view of Hitler and natural scientists? (5 Mark)
Ans.
(a) Hitler’s worldview is known as Nazi ideology.
- According to it, there was no equality between people, but only a racial hierarchy in which Nordic German Aryans were at the top and Jews were located at the lowest place.
(b)
- Natural scientists Charles Darwin and Herbert Spencer’s view inspired Hitler to develop his racism.
- Darwin explained the creation of plants and animals through the concept of evolution and natural selection.
- Herbert Spence gave the idea of the survival of the fitted!, i.e. only those species survived on Earth that could adapt themselves to changing climatic conditions.
(c) Darwin never suggested that the purely natural process of selection was applicable to human beings. His ideas were used by Hitler to justify his imperial racist rule over conquered people. As such, there is no similarity between the two.
Q.33. India has a long advantageous coastline. Explain.
Ans.
India has a long coastline on the Indian Ocean. Western side it has the Arabian sea and Eastern side it has the Bay of Bengal.
This long coastline is really advantageous for the following reasons:
(i) This coastline provided a significant boost to India’s maritime trade. Almost 90% of India’s international trade is done through sea.
(ii) The Deccan Peninsula extends towards the Indian Ocean, thus, helping India to establish close contact with West Asia, Africa and Europe from the Western coast and with South-East Asia and East Asia from the Eastern coast.
(iii) No other country has such a long coastline on the Indian Ocean, it justifies the naming of an ocean after it.
(iv) India has developed many coasts like Mumbai, Chennai, Kochi, Vishakapatnam etc which have become major centres for international business.
Q.34. What are the different ways of increasing production on the same piece of land? Give examples to explain.
Or
Modern farming methods require more inputs which are manufactured by industry. Do you agree?
Ans.
The production may be increased in the following ways:
(a) Multiple Cropping
- It is the most common way of increasing production on a given piece of land. No land is left idle.
Example: In Palampur, during the rainy season (kharif) farmers grow jawar and bajra. - It is followed by cultivation of potato between October and December. In the winter season (rabi) wheat is produced.
- A part of the land area is also devoted to sugarcane which is harvested once every year.
(b) Modern farming methods for higher yield: The farmers can increase production by using High-Yielding Varieties (HYV) seeds, chemical fertilisers, pesticides, tubewells for irrigation, tractors, threshers. In Palampur, the yield of wheat grown from the traditional varieties was 1300 kg per hectare. With HYV seeds, the yield went up to 3,200 kg per hectare.
OR
I agree with the statement that modern farming methods require more inputs which are manufactured by industry.
The modem farming methods consist of the following inputs:
(i) Tubewells for irrigation- Provided by iron industry.
(ii) HYV seeds
(iii) Chemical fertilisers- Provided by chemical industry.
(iv) Pesticides.
(v) Tractors and threshers - Provided by iron industry make ploughing and harvesting faster.
Almost all the above machines etc. are manufactured by industry. Thus, with the help of industry, a farmer cannot get high yields of wheat/rice or other grain production.
Example: In Palampur, the yield of wheat grown from traditional varieties was 1300 kg per hectare. With modem farming methods - HYV seeds etc. - the yield went up to 3200 kg per hectare.
Thus, modem farming methods require many inputs which are manufactured by industry.
Section - D
Q.35. (a) Two items (i) and (ii) are shown in the given outline map of France. Identify these items with the help of following information and write their correct names on the lines marked on the map.
(i) The present capital of France.
(ii) The port of France enriched due to slave trade. Ans. The answer map is given below:
Ans. The answer map is given below: (b) Six features (i), (ii), (iii), (iv), (v) and (vi) are marked on the given outline map of India. Identify any four of these features with the help of the following information and write their correct names on the lines marked in the map.
(b) Six features (i), (ii), (iii), (iv), (v) and (vi) are marked on the given outline map of India. Identify any four of these features with the help of the following information and write their correct names on the lines marked in the map.
(i) A plateau rich in minerals.
(ii) An area of black soil formed by a vast outpouring of lava, from many fissures developing in Earth's crust.
(iii) A mountain range
(iv) Famous national park in Uttarakhand
(v) Bird Sanctuary in Rajasthan
(vi) Lake in Jammu and Kashmir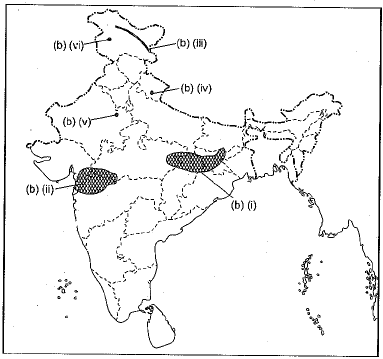 Ans. The answer map is given below:
Ans. The answer map is given below:
FAQs on Class 9 SST: Sample Question Paper- 6 (With Solutions)
| 1. What is the format of the Class 9 SST Sample Question Paper- 6? |  |
| 2. How many questions are there in the Class 9 SST Sample Question Paper- 6? |  |
| 3. Are there any solutions provided for the Class 9 SST Sample Question Paper- 6? |  |
| 4. What is the level of complexity of the questions in the Class 9 SST Sample Question Paper- 6? |  |
| 5. How can I access the Class 9 SST Sample Question Paper- 6? |  |



















