Important Questions for Class 8 Maths - Rational Numbers
Q1: Mention the commutativity, associative and distributive properties of rational numbers. Also, check a × b = b × a and a + b = b + a for a = ½ and b = ¾
Sol: Commutative property:
Let a and b be the two rational numbers,
a + b = b + a.
Let a and b be the two rational numbers,
a × b = b × a.
Associative Property:
For any three rational numbers a, b and c,
(a + b) + c = a + (b + c)
Distributive property states that for any three numbers x, y and z,
x × ( y + z ) = (x × y) + ( x × z)
a x b = b x a
a x b = ½ x ¾ = 3/8
b x a = ¾ x ½ = 3/8
a + b = ¾ + ½ = 5/4
b + a = ½ + ¾ = 5/4
Q2: Verify commutativity of addition of rational numbers 4/9 and -7/12.
Sol:
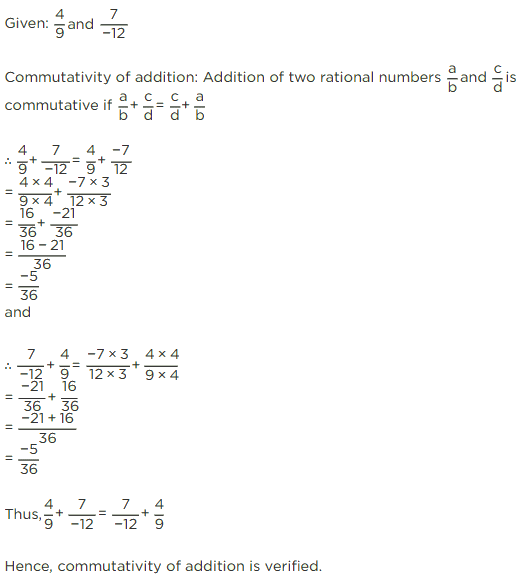
Q3: The equivalent rational number of 7/9, whose denominator is 45, is.
Sol: From the given question,
The equivalent rational number of 7/9 = Numerator/45
To get 45 in the denominator,
It is essential to multiply both the numerator and denominator by 5,
= (7 × 5)/ (9 × 5)
= 35/45
So, the equivalent rational number of 7/9, whose denominator is 45, is (35/45)
Q4: If the product of two rational numbers is 2 and one of them is 15, find the other.
Sol: Consider the two rational numbers as “a” and “b”.
Given, a = 15 and a × b = 2
So, 15 × b = 2
⇒ b = 2/15
Therefore, the other rational number is 2/15.
Q5: 2/5 × (- 3 / 7 ) – 1 / 6 × 3 / 2 + 1 / 14 × 2 / 5
Sol: 2 / 5 × ( – 3/ 7) – 1/6 × 3/ 2 + 1 / 14 × 2 / 5
= 2/5 × (- 3/7) + 1/14 × 2/5 – (1/6 × 3/2) (by commutativity)
= 2/5 × (- 3 / 7 + 1 / 14) – 3/12
= 2/5 × {(- 6 + 1)/14} – 3/12
= 2 / 5 × ((- 5)/14)) – 1/4
= (-10/70) – 1/4
= – 1/7 – 1/4
= (– 4– 7)/28
= – 11/28
Q6: Verify associativity of addition of rational numbers when, x=12, y=13, z=-15
Sol: We need to show that, (x + y) + z = x + (y + z).
x = 12, y = 13, z = -15
(x + y) + z = (12 + 13) + -15
= (12 + 13) + -15
= 25 + (-15)
= 10
x + (y + z) = 12 + (13 + -15)
= 12 + (-2)
= 12 - 2
= 10
As LHS = RHS
Hence verified.
Q7: Three numbers are in the ratio 2 : 3: 4. The sum of their cubes is 0.334125. Find the numbers.
Sol: Given, the ratio of the three numbers is 2 : 3: 4.
Let 2x, 3x and 4x be the three numbers.
According to the given details,
( 2x )³ + ( 3x)³ + ( 4x )³ = 0.334125
8x³ + 27x³ + 64x³ = 0.334125
99x³ = 0.334125
x³ = 334125/(1000000 × 99)
= 3375/1000000
x = ∛(3375/1000000)
= ∛[(15 × 15 × 15)/(100 × 100 × 100)]
= 15/100
= 0.15
2x = 2(0.15) = 0.3
3x = 3(0.15) = 0.45
4x = 4(0.15) = 0.6
Therefore, the three numbers are 0.3, 0.45 and 0.6.
Q8: Verify – (-x) = x for x = 35
Sol: – x = -35
– (-x) = – (-35)
x = 35
Hence verified
Q9: Simplify each of the following by using suitable properties. Also, name the property.
(1212) + (132)
Sol: 12 x (101 + 11) (taking out 12 as common)
= 12 x (112)
=1344
The distributive property of multiplication over the distributive property of addition is used in this part.
Q10: Find ten rational numbers between -13 and 13.
Sol: Multiply the numerator and denominator of both the fractions by any whole number, say 10.
We get,
-13 = -130/10
13 =130/10
Therefore, the equivalent fractions are -130/10 and 130/10.
Ten rational numbers between them are -129/10,-128/10,-127/10,-126/10,-125/10,-124/10,-123/10,-122/10,-121/10,-120/10 .
Q11: Find ten rational numbers between 3/5 and ¾.
Sol: Let us make the denominators the same, say 80.
3/5 = (3 × 16)/(5× 16) = 48/80
3/4 = (3 × 20)/(4 × 20) = 60/80
Ten rational numbers between 3/5 and ¾ = ten rational numbers between 48/80 and 60/80
Therefore, ten rational numbers between 48/80 and 60/80 = 49/80, 50/80, 51/80, 52/80, 54/80, 55/80, 56/80, 57/80, 58/80, 59/80
Q12: 2/5 of the number of students of a school come by car, while 1/4 of students travel by bus to school. The remaining students walk to school, out of which 1/3 walk on their own accord and the rest are escorted by their own parents. If 224 out of all students come to school walking on their own accord, how many students study in that school?
Sol: Let the total number of students in school be x.
From the question, it is given that,
The number of students coming by car = (2/5) × x
The number of students coming by bus = (1/4) × x
The remaining students walk to school = x – ((2x/5) + (1x/4))
= x – ((8x – 5x)/20)
= x – (13x/20)
= (20x – 13x)/20
= 7x/20
Then, the number of students who come to school walking on their own
= (1/3) of (7x/20)
= 7x/60
Since 224 students come to school walking on their own.
As per the given conditions,
= (7x/60) = 224
x = (224 × 60)/7
x = 32 × 60
x = 1920
∴ The total number of students in that particular school is 1920.
Q13:

Sol: We have to find out the difference between the wingspan of a golden eagle and the wingspan of a blue jay.
Length of the wingspan of a golden eagle = 2½ = 5/2 m
Length of the wingspan of a blue jay = 41/100 m
Difference of both = (5/2) – (41/100)
= (250 – 41)/ 100
= 209/100 m
∴ The wingspan of a golden eagle is 209/100 m longer than the wingspan of a blue jay.
Q14: Find the rational number between 2 and 3
Sol: Let us consider the rational number as x
So to find the rational number between 2 and 3
By using the formula x= ½ (a/b + c/d)
x = ½(2 + 3)
x = ½(5)
= 5/2
∴ The rational number between 2 and 3 is 5/2.
Q15: A rectangular piece of paper 12 cm x 5 cm is folded without overlapping to make a cylinder of height 5 cm. Find the volume of the cylinder.
Sol: The length of the rectangular paper = 12 cm
The breadth of the rectangular paper = 5 cm
The circumference of the circular part of the given cylinder = 2πr
Also, given that the paper is rolled along its length.
The circumference of the circular part of the given cylinder = Length of the rectangular paper
2πr = 12 cm
2 × (22/7) × r = 12
r = (12 × 7)/44
r = 84/44
r = 21/11 cm
Height of cylinder = Breadth of the rectangular paper = h = 4 cm
Volume of cylinder = πr2h
= (22/7) × (21/11) × (21/11) × 4
= 45.82 cm³
|
81 videos|452 docs|31 tests
|
FAQs on Important Questions for Class 8 Maths - Rational Numbers
| 1. What are rational numbers? |  |
| 2. How can rational numbers be represented on a number line? |  |
| 3. Can all integers be represented as rational numbers? |  |
| 4. Are decimal numbers rational? |  |
| 5. How can rational numbers be compared and ordered? |  |

















