Chapter 15 - Understanding Shapes-I (Polygons), Class 8, Maths RD Sharma Solutions | RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Mathematics PDF Download
PAGE NO 15.5:
Question 1:
Draw rough diagrams to illustrate the following:
(i) Open curve
(ii) Closed curve
ANSWER:
(i) Open curve: A curve in which the beginning and the end points does not cut each other or are different.
(ii) Closed curve: A curve in which the beginning and the end points are the same and cuts each other.
Question 2:
Classify the following curves as open or closed:
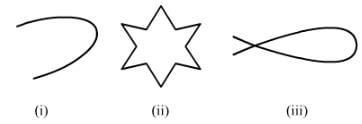
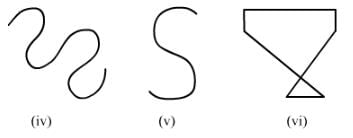
ANSWER:
Open curve: A curve in which the beginning and end points are different or do not cut each other.
Closed curve: A curve in which the beginning and end points are the same and cut each other.
By the above definitions, we can classify the given figures as follows:
(i) Open curve
(ii) Closed curve
(iii) Closed curve
(iv) Open curve
(v) Open curve
(vi) Closed curve
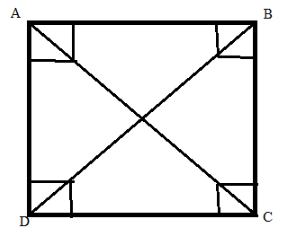
Question 3:
Draw a polygon and shade its interior. Also draw its diagonals, if any.
ANSWER:
In polygon ABCD, AC and BD are the diagonals.
PAGE NO 15.6:
Question 4:
Illustrate, if possible, each one of the following with a rough diagram:
(i) A closed curve that is not a polygon.
(ii) An open curve made up entirely of line segments.
(iii) A polygon with two sides.
ANSWER:
(i) Polygons are made up of straight lines, not curves.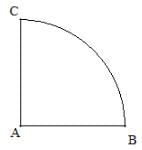
(ii) An open curve made up entirely of line segments: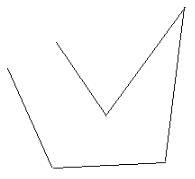
(iii) Not possible because polygons are closed figures.
Question 5:
Following are some figures: Classify each of these fugures on the basis of the following:
(i) Simple curve
(ii) Simple closed curve
(iii) Polygon
(iv) Convex polygon
(v) Concave polygon
(vi) Not a curve
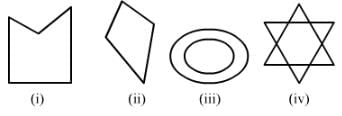
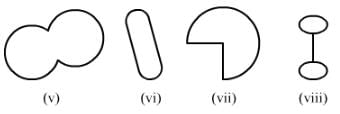
ANSWER:
(i) It is a simple closed curve and a concave polygon.
(ii) It is a simple closed curve and a convex polygon.
(iii) It is not a curve; hence, it is not a polygon.
(iv) It is not a curve; hence, it is not a polygon.
(v) It is a simple closed curve but not a polygon.
(vi) It is a simple closed curve but not a polygon.
(vii) It is a simple closed curve but not a polygon.
(viii) It is a simple closed curve but not a polygon.
Question 6:
How many diagonals does each of the following have?
(i) A convex quadrilateral
(ii) A regular hexagon
(iii) A triangle
ANSWER:
An n-sided convex polygon has 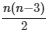 diagonals.
diagonals.
(i) A quadrilateral has 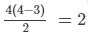 diagonals.
diagonals.
There are 2 diagonals in the convex quadrilateral.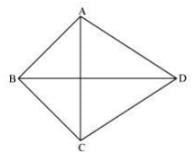
(ii) A regular hexagon has 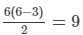 diagonals.
diagonals.
There are 9 diagonals in a regular hexagon.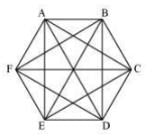
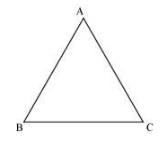
(iii) A triangle does not have any diagonal in it.
Question 7:
What is a regular polygon? State the name of a regular polygon of
(i) 3 sides
(ii) 4 sides
(iii) 6 sides
ANSWER:
A polygon that has equal sides and equal angles is called a regular polygon.
(i) Equilateral triangle: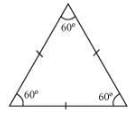
(ii) Square:
(iii) Regular hexagon:
FAQs on Chapter 15 - Understanding Shapes-I (Polygons), Class 8, Maths RD Sharma Solutions - RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Mathematics
| 1. What is a polygon? |  |
| 2. How many sides does a polygon have? |  |
| 3. What is the sum of the interior angles of a polygon? |  |
| 4. How do you classify polygons based on their sides? |  |
| 5. How do you classify polygons based on their angles? |  |
















