Diffusion in Plants | Biology for JAMB PDF Download
- The study of various vital activities and metabolism of plants is known as Plant physiology.
- Stephan Hales is known as the father of plant physiology.
 Fig: Stephen Hales
Fig: Stephen Hales - J.C. Bose is known as the Father of Indian Plant physiology.
- Plants grow in soil and absorb water and minerals, which are available in the soil. So that water has great importance for plants. Water forms 80-90% of the fresh weight of the plant body. The method or technique, plant cells obtain water, comes under the heading of Water relation.
To understand the plant water relations, we should know the following process-
Diffusion
“The movement of molecules or atoms or ions of materials from an area of higher concentration to an area of their lower concentration is called diffusion.
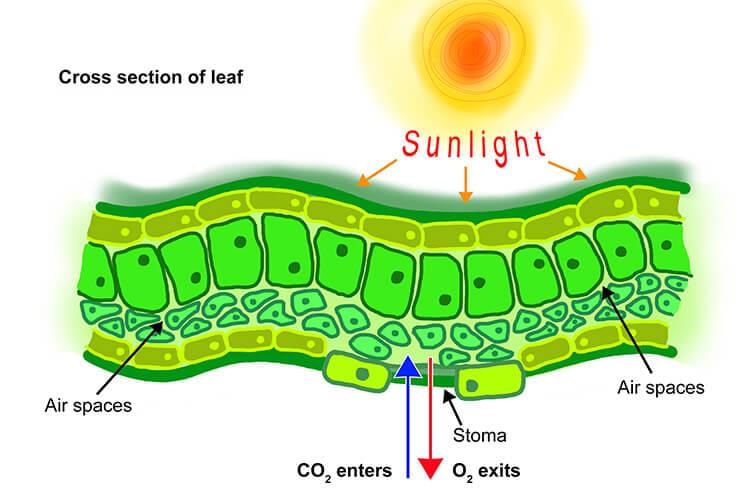
Fig: Diffusion
The diffusion is continue till the dynamic equilibrium is established. At this stage, the net movement of the molecule is equal in both directions.
- The kinetic energy, which is present in the molecules of material is distributed equally in their available space by their nature.
Diffusion rate → Gas > Liquid > Solid
Diffusion pressure:
“The diffused molecules or ions exert a pressure on the substance or medium in which diffusion take place, known as Diffusion pressure.”
- This is developed due to differences in the concentration of molecules of the material. The diffusion pressure of a pure solvent (1236 atm) is always higher than its solution.
- Water molecules move from their higher concentration to their lower concentration in plants.
- The rate of diffusion decrease with the increasing size of molecules.
Factors affecting Diffusion in Plants
2. Temperature: The rate of diffusion is directly proportional to the increase in temperature.
3. Density: The rate of diffusion is inversely proportional to the square root of the density of the gas.
Significance of diffusion
- The exchange of gases like CO2, O2 takes place through diffusion.
- The distribution of hormones in the plants takes place through diffusion.
- The process of transpiration is a diffusion process. The evaporation of water from the intercellular spaces is linked with diffusion during transpiration.
- The ions of the minerals may diffuse into the plant body.
- The process of osmosis is a special type of diffusion of solvent molecules through a semi-permeable membrane.
|
224 videos|175 docs|151 tests
|
FAQs on Diffusion in Plants - Biology for JAMB
| 1. What is diffusion and how does it occur in plants? |  |
| 2. What are the factors that affect diffusion in plants? |  |
| 3. How is diffusion significant for plants? |  |
| 4. How does diffusion occur in leaves of plants? |  |
| 5. How does diffusion contribute to the movement of water in plants? |  |

|
Explore Courses for JAMB exam
|

|














