Geometry Class 4 Notes Maths
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Geometry? |

|
| Basic Geometrical Terms |

|
| Types of Lines |

|
| Measuring a Line Segment |

|
| Drawing a Line Segment |

|
| Angle |

|
| Tangrams |

|
| Polygons |

|
| Circles |

|
What is Geometry?
Geometry is a branch of mathematics that deals with shapes, sizes, and the properties of space. It's all about understanding and working with different figures and objects that you see around you every day, like squares, circles, triangles, and more. Let's see some geometrical shapes : 
Open and Closed Shapes
1. Open Shapes
The shapes which do not begin and end at the same point are called open shapes.
Look at the following open shapes:
2. Closed Shapes
The shapes which begin and end at the same point are called closed shapes.
Observe the following closed shapes:
(i) Simple Closed Figures
Look at the following figures:
Which of the figures given above could you draw by starting at some point, never lifting your pencil from the paper and ending at the starting point?
Obviously, A, B, C, D, E, G and H. Such figures are called closed figures.
Out of these, which figures can you draw without having the figure crossed itself?
Ans:A, B, D, G and H. Such figures are calledsimple closed figures.
Basic Geometrical Terms
1. Point
A dot (.) represents a point.
It represents an exact location in a plane or space.
It has no length and breadth. We represent a point with a capital letter, as shown below. 2. Line Segment
2. Line Segment
Mark two points on a sheet of paper and name them as A and B. Join these points using a ruler. The figure so obtained is called a line segment. A line segment has two endpoints. It is named by the endpoints, as line segment AB or
Join these points using a ruler. The figure so obtained is called a line segment. A line segment has two endpoints. It is named by the endpoints, as line segment AB or 
 3. Line
3. Line
A line segment extended on both the sides without an end is called a line.
A line has no endpoints. A line is denoted by taking any two points on it. For example, consider the line 
To name this line, we mark any two points on it, say, A and B. Then, it is named as (line AB) and represented, as shown alongside.
(line AB) and represented, as shown alongside. Generally, we use the word line for a straight line.
Generally, we use the word line for a straight line.
Straight line can be vertical, horizontal or slanting.
4. Ray
A ray is a straight path that has one endpoint and goes on and on in one direction.
This ray begins at point A and goes through point B.
It does not stop at point B. We name the given ray as (ray AB), where the first letter is always the endpoint.
(ray AB), where the first letter is always the endpoint.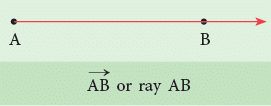 The symbol → shows that a ray has a fixed endpoint and extends forever in the other direction.
The symbol → shows that a ray has a fixed endpoint and extends forever in the other direction.
The rays of light from a torch and the rays of sun are the most common examples of a ray. 5. Plane
5. Plane
A plane is a flat surface.
In mathematics, a plane means one that goes on and on, in all directions without an end. We usually work with just a part of a plane. Points and lines lie on a plane. A plane can be named by using any three points on it. The given figure shows plane PQR. The order of the points does not matter. Some representations of a plane surface from your everyday life are:
Some representations of a plane surface from your everyday life are: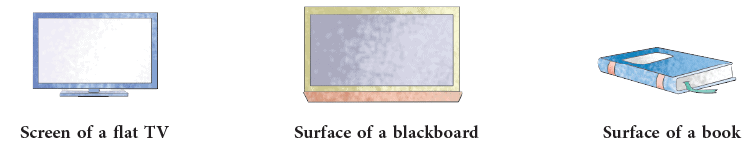
Types of Lines
 Types of Lines
Types of Lines
1. Parallel lines
The lines on the same plane that never meet, no matter how far they are extended, are called parallel lines.
 They are always the same distance apart. The symbol ‘||’ is used to show ‘‘is parallel to’’.
They are always the same distance apart. The symbol ‘||’ is used to show ‘‘is parallel to’’.
Here, line XY is parallel to line PQ and line LM || line AB. The following are some of the representations of parallel lines in everyday life:
The following are some of the representations of parallel lines in everyday life: 2. Intersecting lines
2. Intersecting lines
The lines that cross each other at a point are calledintersecting lines.
 In the figure given alongside,
In the figure given alongside,  intersect at point P.
intersect at point P.
The following are some examples of the intersecting lines or line segments: 3. Perpendicular lines
3. Perpendicular lines
When two intersecting lines meet to form right angles, they are called perpendicular lines.
They are indicated by the symbol  (a square corner) in the diagrams.
(a square corner) in the diagrams.
Line AB is perpendicular to line CD and is written in short as 
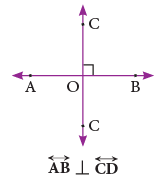 The letter ‘L’ is an example of perpendicular line segments. ‘ ⊥ ’ is the symbol for ‘‘is perpendicular to’’.
The letter ‘L’ is an example of perpendicular line segments. ‘ ⊥ ’ is the symbol for ‘‘is perpendicular to’’.
Measuring a Line Segment
To Measure the Length of a Line Segment using a Ruler
Let us measure the line segment AB shown below. We follow the steps given below.
Step 1: Place the ruler along the line segment AB.
The zero (0) mark of the ruler should coincide with one end, point A of the line segment. Step 2: Read the mark on the ruler at the other end of the line segment, i.e., point B.
Step 2: Read the mark on the ruler at the other end of the line segment, i.e., point B.
Here, point B is at 5.5 cm mark of the ruler. So, the length of the line segment AB is 5.5 cm.
Drawing a Line Segment
To draw a line segment of a given length, say 6.8 cm, we take the following steps.
Step 1: Take a sheet of paper and mark a point, say A, on it with a sharpened pencil. Step 2: Place the ruler with its zero (0) mark at point A, as shown.
Step 2: Place the ruler with its zero (0) mark at point A, as shown.
Step 3:Put your pencil at point A and move the pencil 8 small divisions after 6. This gives a line segment AB of length 6.8 cm.
Angle
An angle is a figure formed by two rays meeting at a common endpoint
The common endpoint is called thevertexof the angle and the two rays are called the arms of the angle.
Looking at these pictures, you can form some idea of an angle:
The symbol for the word angle is ‘∠’.
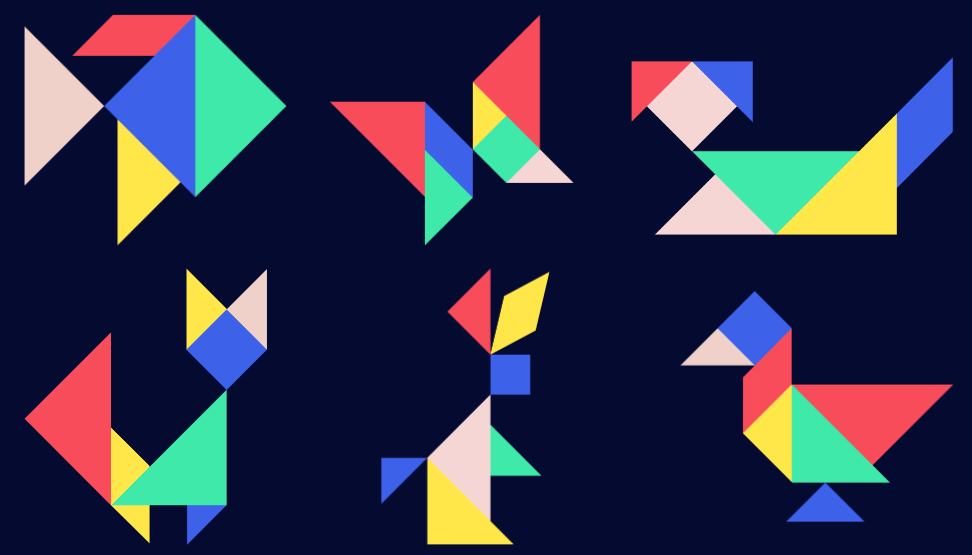
Tangrams
A tangram is a Chinese puzzle created using geometric shapes. You can make tangrams by cutting colourful sheets into five triangles, a square, and a parallelogram. These seven geometric shapes, called tans, can be combined in various ways to create different forms. When you arrange the pieces together, they can represent a wide range of shapes and illustrate many mathematical and geometric ideas. Tangram pieces are commonly used for solving puzzles. Interestingly, all seven pieces can be assembled to create a square. Check out the figure below that illustrates a seven-piece tangram.
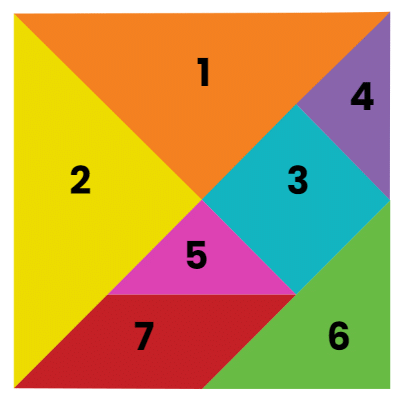 Tangram
Tangram
Why do we use Tangrams?
We use tangrams because they are like special building blocks that help us get better at solving problems and thinking smartly. Tangrams also make us good at understanding shapes, figuring out how things fit together, and being creative. They teach us important math ideas like matching shapes, making things symmetrical, finding the space inside shapes, and understanding the size around shapes. Kids who use tangrams can even do better in math tests, and there are lots of fun shapes and pictures, more than 6,500 of them, that we can make with tangrams!
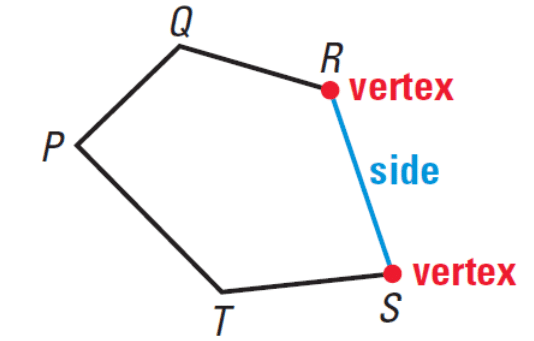
Polygons
- A polygon is a shape that is closed and made up of three or more straight lines.
- The straight lines that make up the polygon are known as its sides.
- Where two sides of a polygon meet, that point is called a vertex of the polygon.
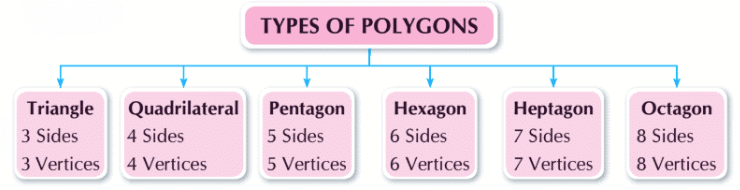
Let's learn about the types of polygons:
Triangle
- A triangle is a closed figure bounded by 3 line segments.
- It’s one of the most common shapes you see in the world around you, like on a road sign or a slice of pizza.
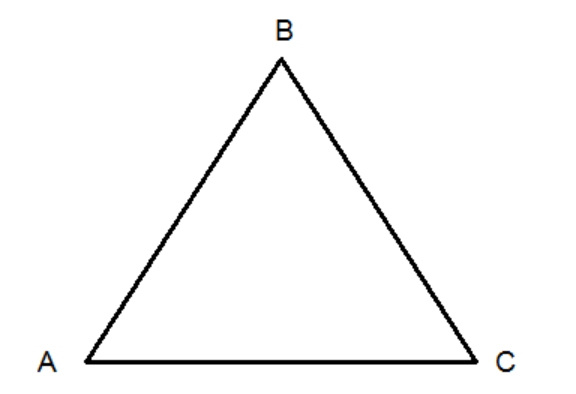
- The triangle ABC has 3 sides: AB, BC and CA
- It has three vertices: A, B and C
Circles
A circle is a shape that is perfectly round, like a ball or a clock face! It doesn’t have any corners or straight edges. Imagine a big round pizza, or the wheels on a bicycle—they are all circles!
Drawing a Circle
We can draw a circle using any one of these methods.
Method
- Take any circular object such as a coin, bottle cap, bangle, etc., and trace its outline. You will get the shape of a circle.
- Take a piece of thread and tie a pencil to one end of the thread. Fix the other end of the thread to the paper with a pin. Hold the thread tightly and rotate the pencil. The shape you get will be a circle.
- Using compasses which has a metal-pointed edge at A circle is not a polygon as it is not made up of straight lines. one end and a pencil holder on the other end.
To draw a circle using compasses:
Step 1: Fix the pencil to the compasses tightly. Adjust the pencil such that the needle and the pencil edge are at the same level. Step 2: Fix the needle of the compasses on the sheet of paper.
Step 2: Fix the needle of the compasses on the sheet of paper.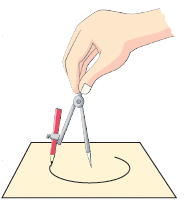 Step 3: Stretch the other arm of the compasses which is holding the pencil.
Step 3: Stretch the other arm of the compasses which is holding the pencil.
Step 4: Move the pencil around to draw a circle.
Parts of a Circle
- Centre
In the figure given alongside, O is the point where we put the metal end of the compasses to draw a circle. O is called the centreof the circle. We name the circle with its centre.
We name the circle with its centre. - Radius
The line segment joining the centre of the circle to any point on the circle is called the radius of the circle. In the figure, line segment OB is the radius of the circle.
In the figure, line segment OB is the radius of the circle. - Chord
The line segment joining any two points on a circle is called achord. In the figure, XY and MN are the chords of the circle.
In the figure, XY and MN are the chords of the circle. - Diameter
A chord that passes through the centre is called adiameterof the circle. Here, AB and CD are the diameters of the circle O.
Here, AB and CD are the diameters of the circle O. - Circumference
The length of the boundary of a circle is called its circumference.
Relation between Radius and Diameter of a Circle
In the given figure, AB is the diameter of the circle. AO and OB are the two radii of the circle.
Measure OA, OB and AB. OA = ____ cm, OB = ____ cm, AB = ___ cm
You will find that AB = 2OA or 2OB = 2 × radius

Interior and Exterior of a circle

- The points O and P are in the interior of the circle.
- The point M is on the circle.
- The point Q lies to the exterior of the circle.
To Draw a Circle of Given Radius
You must use a pair of compasses to draw neat and accurate circles. Suppose, you have to draw a circle of radius 3 cm. You can do so by following these steps.
Step 1: With the help of your ruler, open the arms of your compasses to 3 cm length. Step 2: Mark any point O on a piece of paper.
Step 2: Mark any point O on a piece of paper. Step 3: Place the steel end of the compasses on the dot marked O. Hold the head of the instrument between the thumb and the forefinger such that the pencil end of the compasses may touch the paper. Now, turn it completely round so that the pencil end traces a circle. You will get a circle of radius 3 cm, with centre O.
Step 3: Place the steel end of the compasses on the dot marked O. Hold the head of the instrument between the thumb and the forefinger such that the pencil end of the compasses may touch the paper. Now, turn it completely round so that the pencil end traces a circle. You will get a circle of radius 3 cm, with centre O.
Conclusion
Geometry is a vital branch of mathematics that deals with shapes, sizes, and the properties of space. It includes understanding open and closed shapes, basic geometrical terms like points, lines, and angles, and the relationships between different geometric figures. By studying geometry, students improve their problem-solving skills, spatial understanding, and logical thinking, which are essential for everyday life.
|
30 videos|110 docs|30 tests
|
FAQs on Geometry Class 4 Notes Maths
| 1. What is geometry and why is it important? |  |
| 2. What are some basic geometrical terms I should know? |  |
| 3. How do I measure a line segment accurately? |  |
| 4. What is an angle and how is it formed? |  |
| 5. What are tangrams and how are they used in geometry? |  |

 We name the circle with its centre.
We name the circle with its centre. In the figure, line segment OB is the radius of the circle.
In the figure, line segment OB is the radius of the circle. In the figure, XY and MN are the chords of the circle.
In the figure, XY and MN are the chords of the circle. Here, AB and CD are the diameters of the circle O.
Here, AB and CD are the diameters of the circle O.


















