Class 9 Science: Sample Question Paper- 5 (With Solutions) PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Section – A |

|
| Section - B |

|
| Section - C |

|
| Section - D |

|
Class IX
Science
Sample Question Paper 2020-21
Max. Marks : 80
Duration : 3 hrs.
General Instructions:
Read the following instructions very carefully and strictly follow them :
1. The question paper comprises four sections A, B, C and D. There are 36 questions in the question paper. All questions are compulsory.
2. Section–A – question no. 1 to 20 - all questions and parts thereof are of one mark each. These questions contain multiple choice questions (MCQs), very short answer questions and assertion - reason type questions. Answers to these questions should be given in one word or one sentence.
3. Section–B – question no. 21 to 26 are short answer type questions, carrying 2 marks each. Answers to these questions should be in the range of 30 to 50 words.
4. Section–C – question no. 27 to 33 are short answer type questions, carrying 3 marks each. Answers to these questions should be in the range of 50 to 80 words.
5. Section–D – question no. 34 to 36 are long answer type questions carrying 5 marks each. Answer to these questions should be in the range of 80 to 120 words.
6. There is no overall choice. However, internal choices have been provided in some questions. A student has to attempt only one of the alternatives in such questions.
7. Wherever necessary, neat and properly labelled diagrams should be drawn.
Section – A
Q.1. Name the gas produced when glucose molecules breakdown using oxygen. (1 Mark)
Ans. Carbon dioxide.
OR
Expand ATP. Where it is produced? (1 Mark)
Ans. Adenosine Triphosphate. It is produced in mitochondria.
Q.2. A ball is thrown vertically upwards. What is its momentum at the highest point? (1 Mark)
Ans. Zero as v = 0.
Q.3. From the given v-t graph (see figure), it can be inferred that the object is (1 Mark)
(a) in uniform motion
(b) at rest
(c) in non-uniform motion
(d) moving with uniform acceleration
Ans. a
Solution. From the given v-t graph, it is clear that the velocity of the object is not changing with time i.e., the object is in uniform motion.
Q.4. How can the velocity of an object be changed? (1 Mark)
Ans. It can be changed by changing either:
(i) the object’s speed,
(ii) direction of motion, or
(iii) both.
Q.5. Write down the electronic distribution of oxygen atom. How many valence electrons does it have? (1 Mark)
Ans. (Atomic number of oxygen is 8)
O(8) = 2, 6
Number of valence electrons = 6
Q.6. Shyam throws a heavy stone out of his boat. As a result, the boat moves in opposite direction. Why? (1 Mark)
Ans. According to IIIrd Law of Motion for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.
OR
In a tug of war, the rope does not move in any direction. Why? (1 Mark)
Ans. Because the forces applied by the two teams are equal and opposite.
Q.7. Identify the type of tissue in the given diagram. (1 Mark)
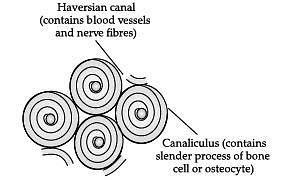
Ans. Bone (Connective tissue)
Q.8. Write the notation of an atom ‘X‘, if the mass number is A and the atomic number is Z. (1 Mark)
Ans. The notation of an atom is represented as: 
Q.9. Name the particles that have no charge and their mass is equal to that of proton. (1 Mark)
Ans. Neutrons have no charge and their mass is equal to that of a proton. i.e., 1 unit.
OR
Name the building blocks of all the matters. (1 Mark)
Ans. Atoms are building blocks of all matters.
Q.10. Seema tried to push a heavy rock of 100 kg for 200 s but could not move it. Find the work done by Seema at the end of 200 s. (1 Mark)
Ans. Work done = 0, Since displacement, s = 0
Q.11. What is the work done against the gravity when a body is moved horizontally along a frictionless surface? (1 Mark)
Ans. W = 0.
OR
A student is writing a three hours science paper. How much work is done by the student ? Give reason for your answer. (1 Mark)
Ans. Zero, as there is no displacement.
Q.12. Define formula unit mass. (1 Mark)
Ans. Sum of atomic masses of all the atoms in a formula unit of a compound is called formula unit mass.
OR
Interpret the number of moles of oxygen atoms in PO43–. (1 Mark)
Ans. Each mole of phosphate ion possesses 4 moles of oxygen atoms as represented by the formula.
Q.13. Shyam throws a heavy stone out of his boat. As a result, the boat moves in opposite direction. Why? (1 Mark)
Ans. According to IIIrd Law of Motion for every action there is an equal and opposite reaction.
For question numbers 14, 15 and 16, two statements are given- one labelled Assertion (A) and the other labelled Reason (R). Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given below:
Q.14. Assertion: Elements and compounds are pure substances.
Reason: Properties of compounds are different from those of its constituent elements. (1 Mark)
(a) Both A and R are true, and R is correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) A is true, but R is false.
(d) A is false, but R is true.
Ans. b
Solution. (i) A pure substance may either contain constituent particles of only one kind or of different kinds. Pure substances can be elements or compounds.
(ii) A compound is a substance composed of two or more different types of elements, chemically combined in a fixed proportion. Properties of a compound are different from its constituent elements.
Q.15. Assertion: Bark of trees are impervious to gases and water.
Reason: Cells of bark have suberin in their walls. (1 Mark)
(a) Both A and R are true, and R is correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) A is true, but R is false.
(d) A is false, but R is true.
Ans. a
Solution. Cells of bark are dead and compactly arranged without intercellular spaces. They have a chemical called suberin in their walls that make them impervious to gases and water.
OR
Assertion: Ciliated epithelium helps in movement of particles.
Reason: Cilia help in movement. (1 Mark)
(a) Both A and R are true, and R is correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) A is true, but R is false.
(d) A is false, but R is true.
Ans. a
Solution. The main function of the cilia is to move particles. It is present in inner surfaces of some hollow organs such as fallopian tubes, bronchioles and small bronchi and help in movement of the particles present there. Thus the function of ciliated epithelium (as it possesses cilia) is the movement of particles.
Q.16. Assertion: If the distance between two bodies of masses m1 and m2 is increased by a factor of 5, the gravitational force is reduced by 1 / 25.
Reason: The gravitational force is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the two bodies. (1 Mark)
(a) Both A and R are true, and R is correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) A is true, but R is false.
(d) A is false, but R is true.
Ans. a
Solution. Gravitational force is given by the formula F = GMm / R2. Gravitational force is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between two bodies.
Q. No 17 - 20 contain five sub-parts each. You are expected to answer any four sub parts in these questions.
Q.17. Read the following and answer any four questions from 17 (i) to 17 (v)
Rahul took 5 moles of carbon atoms in a container and Sohan also took 5 moles of sodium atoms in another container of same weight.
(i) Which container is heavier?
(a) Rahul’s container is heavier.
(b) Sohan’s container is heavier.
(c) Both containers will be of same weight.
(d) None of the container will have any weight
Ans. b
Solution. Mass of container containing 5 moles of C atoms = 5 × 12 = 60 g
Mass of container containing 5 moles of Na atoms = 5 × 23 = 115 g
Hence, Sohan’s container is heavier.
(ii) Whose container has more number of atoms?
(a) Rahul’s container
(b) Sohan’s container
(c) Both containers have same number of atoms
(d) None of the container will have any weight
Ans. c
Solution. Both containers have same number of atoms since they contain same number of moles.
(iii) Avogadro’s constant is:
(a) The exact number of atoms present in one molecule of hydrogen
(b) The exact number of molecules in 1 gm of any element.
(c) The exact number of atoms present in 1 gm of any element
(d) The exact number of atoms present in 12 gm of carbon-12
Ans. d
Solution. The exact number of atoms present in 12 gm of carbon-12.
(iv) How many atoms are there in 1 gm of hydrogen?
(a) 6.020 × 1023 atoms.
(b) 6.220 × 1023 atoms.
(c) 6.0022 × 1023 atoms.
(d) 6.022 × 1023 atoms.
Ans. d
(v) State true or false: 5 moles of carbon atom and 5 moles of sodium atom will have same weight.
Ans. False
Q.18. Read the following and answer any four questions from 18 (i) to 18 (v).
Study the given diagram of bacterial cell and answer the following questions.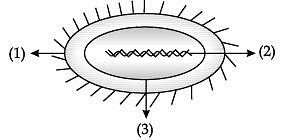
(i) Label the parts marked 1, 2, and 3. (1 Mark)
(a) 1- Nucleus, 2-Cell wall, 3- Plasma membrane.
(b) 1-Cell wall, 2- Nucleoid, 3- Plasma membrane.
(c) 1- Cytoplasm ,2- Nucleus, 3- Cell wall.
(d) 1- Nucleus, 2-Cytoplasm, 3- Cell wall.
Ans.
(ii) Which structure present in the region 2 of a living cell bear genes? (1 Mark)
(a) Chromosome
(b) Plasma membrane
(c) Cytoplasm
(d) Cell wall
Ans.
(iii) How nuclear region of a bacterial cell and nuclear region of an animal cell is different from each other? (1 Mark)
(a) Nuclear region of bacterial cell is well defined but lacks any covering while nuclear region of an animal cell is poorly defined and membrane bound.
(b) Nuclear region of bacterial cell is poorly defined and has a covering while nuclear region of an animal cell is poorly defined and membrane bound.
(c) Nuclear region of bacterial cell is poorly defined and lacks any covering while nuclear region of an animal cell is well defined and membrane bound.
(d) Nuclear region of bacterial cell is poorly defined and lack any covering while nuclear region of an animal cell is well defined and membrane bound.
Ans.
(iv) Can a single cell live independently on its own? (1 Mark)
(a) No, single cell cannot perform all the life processes independently.
(b) Yes, single cell can perform all the life processes.
(v) Identify an example of single celled organism. (1 Mark)
(a) Bird
(b) Fish
(c) Snake
(d) Amoeba
Ans.
Q.19. Read the following and answer any four questions from 19 (i) to 19 (v)
Although Sonia has been suffering from cold and cough she decided to appear for her class test. Classmates seated close to her had an exposure to the infection being carried by Sonia. However, only one of them actually suffered from cold and cough.
(i) Is cold and cough an acute or chronic disease? (1 Mark)
(a) Cold and cough last for only short periods. Hence, it is an acute disease.
(b) Cold and cough last for only short periods. Hence, it is a chronic disease.
(c) Cold and cough last for long periods. Hence, it is an acute disease.
(d) Cold and cough last for long periods. Hence, it is chronic disease.
Ans. a
(ii) Explain, what prevented rest of those classmates catching cold and cough inspite of their exposure to the infection. (1 Mark)
(a) The excretory system of those who did not suffer with cold and cough successfully fought against the microbes to which they were exposed.
(b) The digestive system of those who did not suffer with cold and cough successfully fought against the microbes to which they were exposed.
(c) The immune system of those who did not suffer with cold and cough successfully fought against the microbes to which they were exposed.
(d) The nervous system of those who did not suffer with cold and cough successfully fought against the microbes to which they were exposed.
Ans. c
(iii) Why taking an antibiotic is not effective in common cold? (1 Mark)
(a) Since common cold is a disease caused due to malarial parasite, antibiotics are not effective in common cold.
(b) Since common cold is an infection caused due to protozoa, antibiotics are not effective in common cold.
(c) Since common cold is a bacterial disease antibiotic are not effective in common cold.(d) Since common cold is a viral disease, antibiotics are not effective in common cold.
Ans. d
(iv) What precautions can you take in your school to reduce the incidence of infectious diseases? (1 Mark)
(a) We should keep our surroundings unclean and unhygienic.
(b) We should consume junk food.
(c) There should be provision of safe drinking water.
(d) We should not take any medicine.
Ans. c
(v) Which of the following is an infectious disease? (1 Mark)
(a) Diabetes
(b) Malaria
(c) Vitamin deficiency diseases
(d) Asthma
Ans. b
Q.20. Read the following and answer any 4 questions from 20 (i) to 20 (v).
According to a newspaper report, some areas in Delhi received grey coloured water in their taps. It was reportedly due to mixing of contents at some points due to leakage in sewer and water supply pipes.
(i) Which kind of diseases are likely to spread due to such problems? (1 Mark)
(a) Air borne diseases
(b) Water borne diseases
(c) Mainly viral diseases
(d) Mainly vector borne diseases only
Ans. b
(ii) Why do water borne diseases are more likely to be spread in such cases? (1 Mark)
(a) Only the dirt present in sewage will enter drinking water supply and causes diseases.(b) Damaged water supply pipes cause diseases.
(c) The pathogens present in sewage will enter drinking water supply and can cause diseases.
(d) Grey colour of water causes diseases.
Ans. c
(iii) Give two specific names of diseases that can thus be spread. (1 Mark)
(a) Cholera, typhoid
(b) Diabetes, Cardiac diseases
(c) AIDS, Pneumonia
(d) Tuberculosis, common cold mainly
Ans. a
(iv) What precaution should we take to avoid onset of water borne diseases? (1 Mark)
(a) Always use mineral water available in market.
(b) Drink water which is boiled and cooled.
(c) We should keep the sewage pipelines near water supply pipes.
(d) Always cover mouth while sneezing and coughing.
Ans. b
(v) State True or False: Water borne diseases are not at all communicable. (1 Mark)
(a) True
(b) False
Ans. b
Section - B
Q.21. Write the chemical formulae of the following : (i) Aluminium nitrate (ii) Magnesium hydrogen carbonate (2 Mark)
Ans. (i) Al(NO3)3
(ii) Mg(HCO3)2
OR
Calculate the mass of 0.72 g molecule of CO2. (Atomic mass of C = 12 u, O = 16 u) (2 Mark)
Ans. Gram molecular mass of CO2 = 44 grams
1 gram molecule of CO2 = 44 grams
0.72 gram molecule of CO2 = 44 × 0.72 grams
= 31.68 grams
Q.22. The velocity-time graph of an object is shown in the following figure : (2 Mark)

(i) State the kind of motion that the object has from A to B and from B to C.
(ii) Identify the part of graph where the object has zero acceleration. Give reason for your answer.
Ans. (i) Uniform motion from A to B and non-uniform motion from B to C.
(ii) AB because velocity remains constant from A to B.
Q.23. Define weight of a body. Mention the direction in which it acts. (2 Mark)
Ans. Weight of an object is the force with which a body is attracted towards the Earth. Its direction is vertically downwards.
OR
Define uniformly accelerated motion and uniform motion. (2 Mark)
Ans. (i) When a body travels equal distances in equal intervals of time, its motion is called uniform motion.
(ii) If an object travels in a straight line and its velocity increases or decreases by equal amounts in equal intervals of time, then the acceleration of the object is said to be uniform and motion is said to be uniformly accelerated motion.
Q.24. List two differences between properties of metals and non-metals. (2 Mark)
Ans. Metals: Metals are sonorous i.e., they produce sound. Metals can be beaten into thin sheets i.e., malleable.
Non-metals: Non-metals are non-sonorous as they do not produce any sound. Non metals cannot be beaten into thin sheets.
Q.25. State the law of conservation of momentum. (2 Mark)
Ans. When two or more bodies act upon one another their total momentum remains constant, provided no external forces are acting.
Q.26. Explain in brief, why is an immune system essential for our good health. (2 Mark)
Ans. Immune system in our body is a kind of defence mechanism to fight against pathogenic microbes. It has cells that are specialised to kill infectious microbes and keep our body healthy.
Section - C
Q.27. A man’s weight when taken at the poles is 600 N. Will his weight remain the same when measured at the equator? Will there be an increase or decrease in his weight ? Explain. (3 Mark)
Ans. No, his weight will not remain same as that at the poles. There will be a decrease in his weight at the equator. As the radius of the earth increases from the poles to the equator, the value of ‘g’ becomes greater at poles decreasing towards the equator. Also, the force of gravity decreases from poles to the equator.
OR
Give reasons : (3 Mark)
(i) A piece of paper takes much longer to fall than a stone through the same distance, when both are dropped simultaneously from roof.
(ii) The mass is constant everywhere the weight keeps changing.
(iii) The value of ‘g’ keeps changing as we move away from the earth whereas value of ‘G’ remains constant all over the universe.
Ans. (i) This is because a piece of paper has larger surface area and therefore experiences more friction due to air than a stone which has less surface area.
(ii) Mass is constant as it is the amount of matter present in an object. So, it does not change with gravity. Whereas, weight is the force on an object due to gravity. As the gravity varies from place to place so, the weight also varies.
(iii) The value of g depends on latitude of the place and the mass of the earth while G is called universal constant as its value remains constant at all the places in the universe.
Q.28. Define osmosis. In what two ways it is different from diffusion? (3 Mark)
Ans. Osmosis is the movement of solvent (usually water) from a region of high water concentration to a region of low water concentration; it takes place through semi-permeable membrane whereas the diffusion does not require any membrane. In osmosis movement of solvent is involved whereas in diffusion movement of solid, liquid and gases are involved.
Detailed Answer: Osmosis is the process in which there is a movement of solvent (usually water) from a region of high water concentration to a region of low water concentration.
Differences between osmosis and diffusion: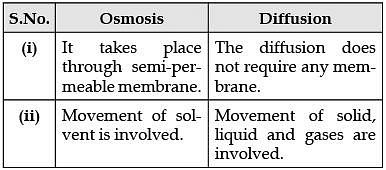 Q.29. Plot velocity-time graph for a body whose initial velocity is 5 m/s and is moving with a retardation of 1 m/s2. Also calculate the distance covered by it. (3 Mark)
Q.29. Plot velocity-time graph for a body whose initial velocity is 5 m/s and is moving with a retardation of 1 m/s2. Also calculate the distance covered by it. (3 Mark)
Ans. u = 5 m/s
v = 0
a = –1m/s2
t = v – u/a
t = 0 – 5/ –1
t = 5 sec
Graph:
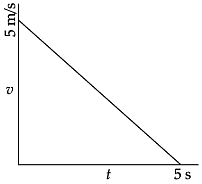
Distance, s = area under the graph
= ½ × 5 × 5 = 12.5 m
Q.30. (i) Draw a labelled diagram of longitudinal section of sclerenchyma.
(ii) Name any two regions in the plant, where this tissue is present. (3 Mark)
Ans. (i)
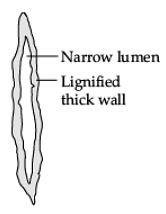 Longitudinal section of Sclerenchyma
Longitudinal section of Sclerenchyma
(ii) Two regions: Stems / Around vascular bundles / Veins of leaves / Hard covering of seeds and nuts.
Q.31. (i) A woman draws water from a well of 15 m depth in 15 s. If the mass of her bucket drawn is 10 kg, calculate power used by her.
(ii) When an arrow is shot from a bow, from where will the arrow acquire its kinetic energy? (3 Mark)
Ans. (i) m = 10 kg, t = 15 s, d = 15 m.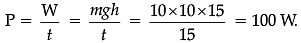
(ii) Potential energy from the stretched string of the bow.
Q.32. (i) Which of these is an acute ailment and why?
Tuberculosis, Cancer, Diarrhoea, Elephantiasis.
(ii) State any two internal, non-infectious causes of a disease.
(iii) Name the organ that is targeted by the virus that causes jaundice. (3 Mark)
Ans. (i) Diarrhoea, since it is a short-term disease and does not cause drastic long-term effect on the person’s general health.
(ii) Genetic abnormalities, excessive weight, lack of exercise.
(iii) Liver.
Q.33. Study the given figure and answer the following questions:
(i) What is the potential energy of the object of mass (m) at point B and C when it is raised from point A to B and B to C.
(ii) Calculate the potential energy of the object when raised directly from point A to C.
(iii) Calculate whether the same amount of work is done against the gravity in each case.
Write your inference. (3 Mark)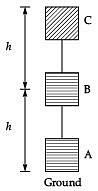 Ans. (i) AB, BC
Ans. (i) AB, BC
P. E. = mgh, P. E. = mgh (same)
The potential energy of the object in both the cases would be same.
(ii) A to C P. E. = m × g × 2h = 2 mgh
(iii) Work done = F × distance
In (A), W = mgh + mgh = 2 mgh
In (B), W = mg × 2h = 2 mgh
W(AC) = 2(AB) = 2(BC)
Here, the work done is equal in each case.
Section - D
Q.34. (i) Differentiate between distance and displacement.
(ii) Under what condition is distance and the magnitude of the displacement equal ?
(iii) The minute hand of a wall clock is 10 cm long. Find its displacement and the distance covered from 10 a.m. to 10.30 a.m. (5 Mark)
Ans. (i) Distance is the length of actual path travelled by a body in a given time. Displacement is the shortest distance between the initial and final positions of the body in a known direction.
(ii) Distance and magnitude of displacement are equal if an object is travelling on a straight line in one direction.
(iii) Length of the minute hand (l) = 10 cm
Distance covered by minute hand from 10 am to 10 : 30 am
= 1/2 x circumference of circle of radius 10 cm
= 1/2 × 2πr = 22/7 x 10 = 220/7= 31·43 cm
Displacement = Diameter of circle of radius 10 cm = 2π = 20 cm.
Q.35. (a) Look at the diagram above and answer the following questions: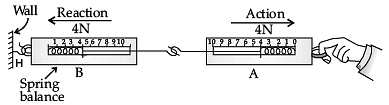 (i) When a force is applied through the free end of the spring balance A the reading on the spring balance A, is 20 gwt. What will be the reading shown by the spring balance B?
(i) When a force is applied through the free end of the spring balance A the reading on the spring balance A, is 20 gwt. What will be the reading shown by the spring balance B?
(ii) Write reasons for your answer.
(b) Observe the following diagram and answer the questions given below: (i) Which direction does the balloon move when the thread tied to its neck is removed and why?
(i) Which direction does the balloon move when the thread tied to its neck is removed and why?
(ii) State the conclusion drawn from this activity. (5 Mark)
Ans. (a) (i) Spring balance B will also show 20 gwt.
(ii) It is because of Newton’s III law of motion, when spring balance A exerts force on the balance B then the balance B pulls the balance A with an equal force of 20 gwt, but in the opposite direction. Balance A exerts a force of action on balance B then balance B exerts an equal and opposite force of reaction on balance A.
(b) (i) Air from inside the balloon escapes from the mouth of the balloon. Balloon moves in opposite direction that is from left to right.
(ii) Forces of action and reaction are equal and opposite.
Q.36. Describe Rutherford’s α-particle scattering experiment and mention the important observations and conclusions drawn from this experiment. (5 Mark)
Ans. In this experiment fast moving α-particles were made to fall on a thin gold foil.
The following observations were made :
(i) Most of the fast moving α-particles passed straight through the gold foil.
(ii) Some of the α-particles were deflected by the foil by small angles.
(iii) One out of every 12000 particles appeared to rebound.
Conclusions:
(i) Most of the space inside the atom is empty because most of the α-particles passed through the gold foil without getting deflected.
(ii) Very few particles were deflected from their path, indicating that the positive charge of the atom occupies very little space.
(iii) A very small fraction of α-particles was deflected by 180°, indicating that all the positive charge and mass of the gold atom were concentrated in a very small volume within the atom.
OR
(i) Write the chemical formula and name of the compounds formed between :
(a) Barium and nitrate ions
(b) Ferrous and sulphide ions
(ii) State the law of definite proportion.
(iii) Calculate the number of moles for the following:
(a) 36 gm of water
(b) 4 gm of oxygen gas
Atomic number of oxygen and hydrogen is 16 u and 14 u respectively. (5 Mark)
Ans. (a) (i) Ba(NO3)2 (Barium Nitrate)
(ii) FeS (Ferrous Sulphide)
(b) A chemical compound is always made up of the same elements combined together in the same fixed proportion by mass.
(c) (i) 18 g of H2O = 1 mole
36 g of H2O = 1 / 18 x 32 = 2 moles
(ii) 32 g of oxygen = 1 mole
4 g of oxygen = 1 / 32 x 4 = 0.125 mole
FAQs on Class 9 Science: Sample Question Paper- 5 (With Solutions)
| 1. What is the importance of studying different sections in Class 9 Science? |  |
| 2. How can I prepare effectively for the Class 9 Science exam? |  |
| 3. Can I score well in Class 9 Science without understanding the different sections? |  |
| 4. Are there any specific strategies to remember the content from different sections in Class 9 Science? |  |
| 5. Can I skip studying certain sections in Class 9 Science if I find them difficult? |  |


















