Chapter 18 - Practical Geometry (Constructions) (Part - 2), Class 8, Maths RD Sharma Solutions | RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Mathematics PDF Download
PAGE NO 18.13:
Question 1:
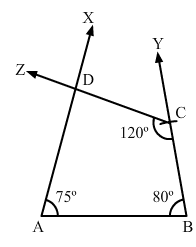
Construct a quadrilateral ABCD given that AB = 4 cm, BC = 3 cm, ∠A = 75°, ∠B = 80° and ∠C = 120°.
ANSWER:
Steps of construction:
Step I: Draw AB = 4 cm.
Step II: Construct ∠XAB = 75° at A and ∠ABY = 80° at B.
Step III: With B as the centre and radius 3 cm, cut off BC = 3 cm.
Step IV: At C, draw ∠BCZ = 120° such that it meets AX at D.
The quadrilateral so obtained is the required quadrilateral.
Question 2:
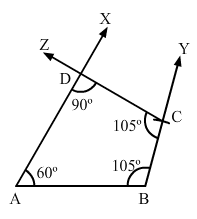
Construct a quadrilateral ABCD, where AB = 5.5 cm, BC = 3.7 cm, ∠A = 60°, ∠B = 105° and ∠D = 90°.
ANSWER:
We know that the sum of all the angles in a quadrilateral is 360.
i.e., ∠A + ∠B + ∠C + ∠D = 360°
⇒ ∠C = 105°
Steps of construction:
Step I: Draw AB = 5.5 cm.
Step II: Construct ∠XAB = 60° at A and ∠ABY = 105°.
Step III: With B as the centre and radius 3.7 cm, cut off BC = 3.7 cm.
Step IV: At C, draw ∠BCZ = 105° such that it meets AX at D.
The quadrilateral so obtained is the required quadrilateral.
Question 3:
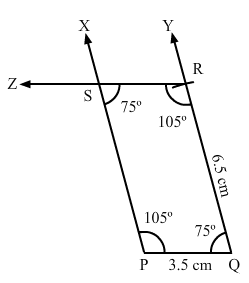
Construct a quadrilateral PQRS, where PQ = 3.5 cm, QR = 6.5 cm, ∠P = ∠R = 105° and ∠S = 75°.
ANSWER:
We know that the sum of all the angles in a quadrilateral is 360.
i.e., ∠P + ∠Q + ∠R + ∠S = 360°⇒ ∠Q = 75°
Steps of construction:
Step I: Draw PQ = 3.5 cm.
Step II: Construct ∠XPQ = 105° at P and ∠PQY = 75° at Q.
Step III: With Q as the centre and radius 6.5 cm, cut off QR = 6.5
Step IV: At R, draw ∠QRZ = 105° such that it meets PX at S.
The quadrilateral so obtained is the required quadrilateral.
Question 4:
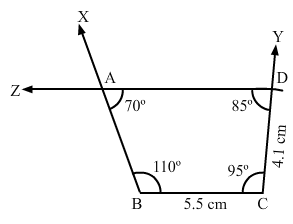
Construct a quadrilateral ABCD when BC = 5.5 cm, CD = 4.1 cm, ∠A = 70°, ∠B = 110° and ∠D = 85°.
ANSWER:
We know that the sum of all the angles in a quadrilateral is 360.
i.e., ∠A + ∠B + ∠C + ∠D = 360°
⇒ ∠C = 95°
Steps of construction:
Step I: Draw BC = 5.5 cm.
Step II: Construct ∠XBC = 110° at A and ∠BCY = 95°.
Step III: With C as the centre and radius 4.1 cm, cut off CD = 4.1 cm.
Step IV: At D, draw ∠CDZ = 85° such that it meets BY at A.
The quadrilateral so obtained is the required quadrilateral.
Question 5:
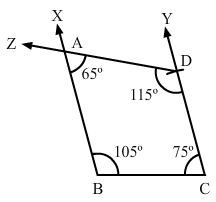
Construct a quadrilateral ABCD, where ∠A = 65°, ∠B = 105°, ∠C = 75° BC = 5.7 cm and CD = 6.8 cm.
ANSWER:
We know that the sum of all the angles in a quadrilateral is 360.
i.e., ∠A + ∠B + ∠C + ∠D = 360°
⇒ ∠D = 115°
Steps of Construction:
Step I: Draw BC = 5.7 cm.
Step II: Construct ∠XBC = 105° at B and ∠BCY = 105° at C.
Step III : With C as the centre and radius 6.8 cm, cut off CD = 6.8 cm.
Step IV: At D, draw ∠CDZ = 115° such that it meets BY at A.
The quadrilateral so obtained is the required quadrilateral.
Question 6:
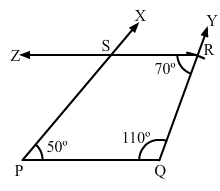
Construct a quadrilateral PQRS, in which PQ = 4 cm, QR = 5 cm, ∠P = 50°, ∠Q = 110° and ∠R = 70°.
ANSWER:
Steps of construction:
Step I: Draw PQ = 4 cm.
Step II: Construct ∠XPQ = 50° at P and ∠PQY = 110° at Q.
Step III : With Q as the centre and radius 5 cm, cut off QR = 5 cm.
Step IV: At R, draw ∠QRZ = 70° such that it meets PX at S.
The quadrilateral so obtained is the required quadrilateral.
FAQs on Chapter 18 - Practical Geometry (Constructions) (Part - 2), Class 8, Maths RD Sharma Solutions - RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Mathematics
| 1. What are the different types of constructions covered in Chapter 18 of RD Sharma Solutions? |  |
| 2. How can I construct a tangent to a circle using RD Sharma Solutions? |  |
| 3. How can I construct an equilateral triangle using RD Sharma Solutions? |  |
| 4. How can I construct a square using RD Sharma Solutions? |  |
| 5. How can I construct a regular hexagon using RD Sharma Solutions? |  |


















