Chapter 21 - Mensuration - II (Part - 3), Class 8, Maths RD Sharma Solutions | RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Mathematics PDF Download
PAGE NO 21.22:
Question 1:
Find the surface area of a cuboid whose
(i) length = 10 cm, breadth = 12 cm, height = 14 cm
(ii) length = 6 dm, breadth = 8 dm, height = 10 dm
(iii) length = 2 m, breadth = 4 m, height = 5 m
(iv) length = 3.2 m, breadth = 30 dm, height = 250 cm.
ANSWER:
(i)Dimension of the cuboid:Length = 10 cm
Breadth = 12 cm
Height = 14 cm
Surface area of the cuboid = 2 × (length × breadth + breadth × height + length × height)
= 2 × (10 × 12 + 12 × 14 + 10 × 14) = 2 × (120 + 168 + 140) = 856 cm²
(ii)Dimensions of the cuboid:Length = 6 dm
Breadth = 8 dm
Height = 10 dm
Surface area of the cuboid = 2 × (length × breadth + breadth × height + length × height)
= 2 × (6 × 8 + 8 × 10 + 6 × 10)
= 2 × (48 + 80 + 60) = 376 dm²
(iii) Dimensions of the cuboid:
Length = 2 m Breadth = 4 m
Height = 5 m
Surface area of the cuboid = 2 × (length × breadth + breadth × height + length × height)
= 2 × (2 × 4 + 4 × 5 + 2 × 5) = 2 × (8 + 20 + 10) = 76 m²
(iv)Dimensions of the cuboid:
Length = 3.2m
= 3.2 × 10 dm (1 m = 10 dm)
= 32 dm
Breadth = 30 dm
Height = 250 cm
= 250 × 1/10dm (10cm = 1 dm)
= 25 dm
Surface area of the cuboid = 2 × (length × breadth + breadth × height + length × height)
= 2 × (32 × 30 + 30 × 25 + 32 × 25)
= 2 × (960 + 750 + 800) = 5020 dm²
Question 2:
Find the surface area of a cube whose edge is
(i) 1.2 m
(ii) 27 cm
(iii) 3 cm
(iv) 6 m
(v) 2.1 m
ANSWER:
(i) Edge of the a cube = 1.2 m
∴ Surface area of the cube = 6 × (side)2 = 6 × (1.2)2 = 6 × 1.44 = 8.64 m².
(ii) Edge of the a cube = 27 cm
∴ Surface area of the cube = 6 × (side)2 = 6 × (27)2 = 6 × 729 = 4374 cm²
(iii) Edge of the a cube = 3 cm
∴ Surface area of the cube = 6 × (side)2 = 6 × (3)2 = 6 × 9 = 54 cm²
(iv) Edge of the a cube = 6 m
∴ Surface area of the cube = 6 × (side)2 = 6 × (6)2 = 6 × 36 = 216 m²
(v) Edge of the a cube = 2.1 m
∴ Surface area of the cube = 6 × (side)2 = 6 × (2.1)2 = 6 × 4.41 = 26.46 m²
Question 3:
A cuboidal box is 5 cm by 5 cm by 4 cm. Find its surface area.
ANSWER:
The dimensions of the cuboidal box are 5 cm × 5 cm × 4 cm.
Surface area of the cuboidal box = 2 × (length × breadth + breadth × height + length × height)
= 2 × (5 × 5 + 5 × 4 + 5 × 4)
= 2 × (25 + 20 + 20) = 130 cm²
Question 4:
Find the surface area of a cube whose volume is
(i) 343 m3
(ii) 216 dm3
ANSWER:
(i)Volume of the given cube = 343 m3
We know that volume of a cube = (side)3
⇒ (side)3 = 343 i.e., side = 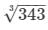 = 7 m
= 7 m
∴ Surface area of the cube = 6 × (side)2 = 6 × (7)2 = 294 m²
(ii)Volume of the given cube = 216 dm3
We know that volume of a cube = (side)3
⇒ (side)3 = 216 i.e., side = 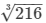 = 6 dm
= 6 dm
∴ Surface area of the cube = 6 × (side)2 = 6 × (6)2 = 216 dm²
Question 5:
Find the volume of a cube whose surface area is
(i) 96 cm²
(ii) 150 m²
ANSWER:
(i)Surface area of the given cube = 96 cm²
Surface area of a cube = 6 × (side)2
⇒ 6 × (side)2 = 96
⇒ (side)2 = 96/6 = 16 i.e., side of the cube = 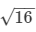 = 4 cm
= 4 cm
∴ Volume of the cube = (side)3 = (4)3 = 64 cm3
(ii)Surface area of the given cube = 150 m²
Surface area of a cube = 6 × (side)2
⇒ 6 × (side)2 = 150
⇒ (side)2 = 150/6 = 25
i.e., side of the cube = 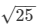 = 5 m
= 5 m
∴ Volume of the cube = (side)3 = (5)3 = 125 m3
Question 6:
The dimensions of a cuboid are in the ratio 5 : 3 : 1 and its total surface area is 414 m². Find the dimensions.
ANSWER:
It is given that the sides of the cuboid are in the ratio 5:3:1.
Suppose that its sides are x multiple of each other, then we have:Length = 5x m
Breadth = 3x m
Height = x m
Also, total surface area of the cuboid = 414 m²
Surface area of the cuboid = 2 × (length × breadth + breadth × height + length × height)
⇒ 414 = 2 × (5x × 3x + 3x × 1x + 5x × x)
⇒ 414 = 2 × (15x2 + 3x2 + 5x2)
⇒ 414 = 2 × (23x2)
⇒ 2 × (23 × x2) = 414
⇒ (23 × x2) = 414/2 = 207
⇒ x2 = 207/23 = 9
⇒ x = √9 = 3
Therefore, we have the following:
Lenght of the cuboid = 5 × x = 5 × 3 = 15 m
Breadth of the cuboid = 3 × x = 3 × 3 = 9 m
Height of the cuboid = x = 1 × 3 = 3 m
Question 7:
Find the area of the cardboard required to make a closed box of length 25 cm, 0.5 m and height 15 cm.
ANSWER:
Length of the box = 25 cm
Width of the box = 0.5 m
= 0.5 × 100 cm (∵ 1 m = 100 cm)
= 50 cm
Height of the box = 15 cm
∴ Surface area of the box = 2 × (length × breadth + breadth × height + length × height)
= 2 × (25 × 50 + 50 × 15 + 25 × 15)
= 2 × (1250 + 750 + 375)
= 4750 cm²
Question 8:
Find the surface area of a wooden box whose shape is of a cube, and if the edge of the box is 12 cm.
ANSWER:
It is given that the side of the cubical wooden box is 12 cm.
∴ Surface area of the cubical box = 6 × (side)2 = 6 × (12)2
= 864 cm²
It is given that the side of the cubical wooden box is 12 cm.
∴ Surface area of the cubical box = 6 × (side)2 = 6 × (12)2
= 864 cm²
Question 9:
The dimensions of an oil tin are 26 cm × 26 cm × 45 cm. Find the area of the tin sheet required for making 20 such tins. If 1 square metre of the tin sheet costs Rs 10, find the cost of tin sheet used for these 20 tins.
ANSWER:
Dimensions of the oil tin are 26 cm × 26 cm × 45 cm.
So, the area of tin sheet required to make one tin = 2 × (length × breadth + breadth × height + length × height)
= 2 × (26 × 26 + 26 × 45 + 26 × 45)
= 2 × (676 + 1170 + 1170)
= 6032 cm²
Now, area of the tin sheet required to make 20 such tins = 20 × surface area of one tin = 20 × 6032 = 120640 cm²
It can be observed that 120640 cm² = 120640 × 1cm × 1cm
= 120640 × 1/100m × 1/100m (∵ 100 cm = 1 m)
= 12.0640 m²
Also, it is given that the cost of 1 m² of tin sheet = Rs 10
∴ The cost of 12.0640 m² of tin sheet = 12.0640 × 10 = Rs 120.6
Question 10:
A cloassroom is 11 m long, 8 m wide and 5 m high. Find the sum of the areas of its floor and the four walls (including doors, windows, etc.)
ANSWER:
Lenght of the classroom = 11 m
Width = 8 m
Height = 5 m
We have to find the sum of the areas of its floor and the four walls (i.e., like an open box).
∴ The sum of areas of the floor and the four walls = (length × width) + 2 × (width × height + length × height)
= (11 × 8) + 2 × (8 × 5 + 11 × 5)
= 88 + 2 × (40 + 55)
= 88 + 190 = 278 m²
Question 11:
A swimming pool is 20 m long 15 m wide and 3 m deep. Find the cost of repairing the floor and wall at the rate of Rs 25 per square metre.
ANSWER:
Length of the swimming pool = 20 m
Breadth = 15 m
Height = 3 m
Now, surface area of the floor and all four walls of the pool = (length × breadth) + 2 × (breadth × height + length × height)
= (20 × 15) + 2 × (15 × 3 + 20 × 3)
= 300 + 2 × (45 + 60)
= 300 + 210 = 510 m²
The cost of repairing the floor and the walls is Rs 25/m².
∴ The total cost of repairing 510 m² area = 510 × 25 = Rs 12750
Question 12:
The perimeter of a floor of a room is 30 m and its height is 3 m. Find the area of four walls of the room.
ANSWER:
Perimeter of the floor of the room = 30 m
Height of the oom = 3 m
Perimeter of a rectangle = 2 × (length + breadth) = 30 m
So, area of the four walls = 2 × (length × height + breadth × height)
= 2 × (length + breadth) × height = 30 × 3 = 90 m²
Question 13:
Show that the product of the areas of the floor and two adjacent walls of a cuboid is the square of its volume.
ANSWER:
Suppose that the length, breadth and height of the cuboidal floor are l cm, b cm and h cm, respectively.Then, area of the floor = l × b cm²
Area of the wall = b × h cm²
Area of its adjacent wall = l × h cm²
Now, product of the areas of the floor and the two adjacent walls = (l × b) × (b × h) × (l × h) = l2 × b2 × h2 = (l × b × h)2
Also, volume of the cuboid = l × b × h cm²
∴ Product of the areas of the floor and the two adjacent walls = (l × b × h)2 = (volume)2
Question 14:
The walls and ceiling of a room are to be plastered. The length, breadth and height of the room are 4.5 m, 3 m and 350 cm, respectively. Find the cost of plastering at the rate of Rs 8 per square metre.
ANSWER:
Length of a room = 4.5 m
Breadth = 3 m
Height = 350 cm
= 350/100m (∵ 1 m = 100 cm )
= 3.5 m
Since only the walls and the ceiling of the room are to be plastered, we have:
So, total area to be plastered
= area of the ceiling + area of the walls = (length × breadth) + 2 × (length × height + breadth × height)
= (4.5 × 3) + 2 × (4.5 × 3.5 + 3 × 3.5)
= 13.5 + 2 × (15.75 + 10.5) = 13.5 + 2 × (26.25) = 66 m²
Again, cost of plastering an area of 1 m² = Rs 8
∴ Total cost of plastering an area of 66 m² = 66 × 8 = Rs 528
PAGE NO 21.23:
Question 15:
A cuboid has total surface area of 50 m² and lateral surface area is 30 m². Find the area of its base.
ANSWER:
Total surface area of the cuboid = 50 m²
Its lateral surface area = 30 m²
Now, total surface area of the cuboid = 2 × (surface area of the base) + (surface area of the 4 walls)
⇒ 50 = 2 × (surface area of the base) + (30)
⇒ 2 × (surface area of the base) = 50−30 = 20
∴ Surface area of the base = 202 = 10 m²
Total surface area of the cuboid = 50 m²
Its lateral surface area = 30 m²
Now, total surface area of the cuboid = 2 × (surface area of the base) + (surface area of the 4 walls)
⇒ 50 = 2 × (surface area of the base) + (30)
⇒ 2 × (surface area of the base) = 50-30 = 20
∴ Surface area of the base = 20/2 = 10 m²
Question 16:
A classroom is 7 m long, 6 m broad and 3.5 m high. Doors and windows occupy an area of 17 m². What is the cost of white-washing the walls at the rate of Rs 1.50 per m².
ANSWER:
Length of the classroom = 7m
Breadth of the classroom = 6 m
Height of the classroom = 3.5 m
Total surface area of the classroom to be whitewashed = areas of the 4 walls
= 2 × (breadth × height + length × height)
= 2 × (6 × 3.5 + 7 × 3.5) = 2 × (21 + 24.5) = 91 m²
Also, the doors and windows occupy 17 m².
So, the remaining area to be whitewashed = 91−17 = 74 m²
Given that the cost of whitewashing 1 m² of wall = Rs 1.50
∴ Total cost of whitewashing 74 m² of area = 74 × 1.50 = Rs 111
Question 17:
The central hall of a school is 80 m long and 8 m high. It has 10 doors each of size 3 m × 1.5 m and 10 windows each of size 1.5 m × 1 m. If the cost of white-washing the walls of the hall at the rate of Rs 1.20 per m² is Rs 2385.60, find the breadth of the hall.
ANSWER:
Suppose that the breadth of the hall is b m.
Lenght of the hall = 80 m
Height of the hall = 8 m
Total surface area of 4 walls including doors and windows = 2 × (length × height + breadth × height)
= 2 × (80 × 8 + b × 8)
= 2 × (640 + 8b) = 1280 + 16b m²
The walls have 10 doors each of dimensions 3 m × 1.5 m. i.e., area of a door = 3 × 1.5 = 4.5 m²
∴ Area of 10 doors = 10 × 4.5 = 45 m²
Also, there are 10 windows each of dimensions 1.5 m × 1 m.i.e., area of one window = 1.5 × 1 = 1.5 m²
∴ Area of 10 windows = 10 × 1.5 = 15 m²
Thus, total area to be whitwashed = (total area of 4 walls)−(areas of 10 doors + areas of 10 windows)
= (1280 + 16b)−(45 + 15) = 1280 + 16b−60
= 1220 + 16b m²
It is given that the cost of whitewashing 1 m² of area = Rs 1.20
∴ Total cost of whitewashing the walls = (1220 + 16b) × 1.20
= 1220 × 1.20 + 16b × 1.20
= 1464 + 19.2b
Since the total cost of whitewashing the walls is Rs 2385.60, we have:1464 + 19.2b = 2385.60
⇒ 19.2b = 2385.60−1464
⇒ 19.2b = 921.60
⇒ b = 921.60/19.2 = 48 m
∴ The breadth of the central hall is 48 m.
FAQs on Chapter 21 - Mensuration - II (Part - 3), Class 8, Maths RD Sharma Solutions - RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Mathematics
| 1. How can I find the volume of a cylinder using the Mensuration - II concepts? |  |
| 2. What is the difference between surface area and volume in Mensuration - II? |  |
| 3. How can I find the area of a triangle using Mensuration - II concepts? |  |
| 4. What is the formula to calculate the surface area of a cone in Mensuration - II? |  |
| 5. How can I find the volume of a sphere using Mensuration - II concepts? |  |
















