Chapter 3 - Squares and Square Roots (Ex-3.3) - Class 8 Math RD Sharma Solutions | RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Mathematics PDF Download
QUESTION 1: FIND THE SQUARES OF THE FOLLOWING NUMBERS USING COLUMN METHOD. VERIFY THE RESULT BY FINDING THE SQUARE USING THE USUAL MULTIPLICATION:
(I) 25
(II) 37
(III) 54
(IV) 71
(V) 96
ANSWER 1: (i) Here, a = 2, b = 5
Step 1. Make 3 columns and write the values of a2, 2 x a x b, and b2 in these columns.
| Column I | Column II | Column III |
| a2 | 2 x a x b | b2 |
| 4 | 20 | 25 |
Step 2. Underline the unit digit of b2 (in Column III) and add its tens digit, if any, with 2 x a x b (in Column II).
| Column I | Column II | Column III |
| a2 | 2 x a x b | b2 |
| 4 | 20 + 2 | 25 |
| 22 |
Step 3. Underline the unit digit in Column II and add the number formed by the tens and other digits, if any, with a2 in Column I.
| Column I | Column II | Column III |
| a2 | 2 x a x b | b2 |
| 4 + 2 | 20 + 2 | 25 |
| 6 | 22 |
Step 4. Underline the number in Column I.
| Column I | Column II | Column III |
| a2 | 2 x a x b | b2 |
| 4 + 2 | 20 + 2 | 25 |
| 6 | 22 |
Step 5. Write the underlined digits at the bottom of each column to obtain the square of the given number.
In this case, we have:
252 = 625
Using multiplication: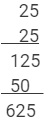
This matches with the result obtained by the column method.
(ii) Here, a = 3, b = 7
Step 1. Make 3 columns and write the values of a2, 2 x a x b, and b2 in these columns.
| Column I | Column II | Column III |
| a2 | 2 x a x b | b2 |
| 9 | 42 | 49 |
Step 2. Underline the unit digit of b2 (in Column III) and add its tens digit, if any, with 2 x a x b (in Column II).
| Column I | Column II | Column III |
| a2 | 2 x a x b | b2 |
| 9 | 42+4 | 49 |
| 46 |
Step 3. Underline the unit digit in Column II and add the number formed by the tens and other digits, if any, with a2 in Column I.
| Column I | Column II | Column III |
| a2 | 2 x a x b | b2 |
| 9 + 4 | 42 + 4 | 49 |
| 13 | 46 |
Step 4. Underline the number in Column I.
| Column I | Column II | Column III |
| a2 | 2 x a x b | b2 |
| 9 + 4 | 42 + 4 | 49 |
| 13 | 46 |
Step 5. Write the underlined digits at the bottom of each column to obtain the square of the given number.
In this case, we have:
372 = 1369
Using multiplication:
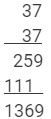
This matches with the result obtained using the column method.
(iii) Here, a = 5, b = 4
Step 1. Make 3 columns and write the values of a2, 2 x a x b and b2 in these columns.
| Column I | Column II | Column III |
| a2 | 2 x a x b | b2 |
| 25 | 40 | 16 |
Step 2. Underline the unit digit of b2 (in Column III) and add its tens digit, if any, with 2 x a x b (in Column II).
| Column I | Column II | Column III |
| a2 | 2 x a x b | b2 |
| 25 | 40 + 1 | 16 |
| 41 |
Step 3. Underline the unit digit in Column II and add the number formed by the tens and other digits, if any, with a2 in Column I.
| Column I | Column II | Column III |
| a2 | 2 x a x b | b2 |
| 25 + 4 | 40 + 1 | 16 |
| 29 | 41 |
Step 4. Underline the number in Column I.
| Column I | Column II | Column III |
| a2 | 2 x a x b | b2 |
| 25 + 4 | 40 + 1 | 16 |
| 29 | 41 |
Step 5. Write the underlined digits at the bottom of each column to obtain the square of the given number.
In this case, we have:
542 = 2916
Using multiplication:

This matches with the result obtained using the column method.
(iv) Here, a = 7, b = 1
Step 1. Make 3 columns and write the values of a2, 2 x a x b and b2 in these columns.
| Column I | Column II | Column III |
| a2 | 2 x a x b | b2 |
| 49 | 14 | 1 |
Step 2. Underline the unit digit of b2 (in Column III) and add its tens digit, if any, with 2 x a x b (in Column II).
| Column I | Column II | Column III |
| a2 | 2 x a x b | b2 |
| 49 | 14 + 0 | 1 |
| 14 |
Step 3. Underline the unit digit in Column II and add the number formed by the tens and other digits, if any, with a2 in Column I.
| Column I | Column II | Column III |
| a2 | 2 x a x b | b2 |
| 49 + 1 | 14 + 0 | 1 |
| 50 | 14 |
Step 4. Underline the number in Column I.
| Column I | Column II | Column III |
| a2 | 2 x a x b | b2 |
| 49 + 1 | 14 + 0 | 1 |
| 50 | 14 |
Step 5. Write the underlined digits at the bottom of each column to obtain the square of the given number.
In this case, we have:
712 = 5041
Using multiplication:
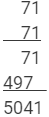
This matches with the result obtained using the column method.
(v) Here, a = 9, b = 6
Step 1. Make 3 columns and write the values of a2, 2 x a x b and b2 in these columns.
| Column I | Column II | Column III |
| a2 | 2 x a x b | b2 |
| 81 | 108 | 36 |
Step 2. Underline the unit digit of b2 (in Column III) and add its tens digit, if any, with 2 x a x b (in Column II).
| Column I | Column II | Column III |
| a2 | 2 x a x b | b2 |
| 81 | 108 + 3 | 36 |
| 111 |
Step 3. Underline the unit digit in Column II and add the number formed by the tens and other digits, if any, with a2 in Column I.
| Column I | Column II | Column III |
| a2 | 2 x a x b | b2 |
| 81 + 11 | 108 + 3 | 36 |
| 92 | 111 |
Step 4. Underline the number in Column I.
| Column I | Column II | Column III |
| a2 | 2 x a x b | b2 |
| 81 + 11 | 108 + 3 | 36 |
| 92 | 111 |
Step 5. Write the underlined digits at the bottom of each column to obtain the square of the given number.
In this case, we have:
962 = 9216
Using multiplication:
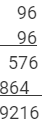
This matches with the result obtained using the column method.
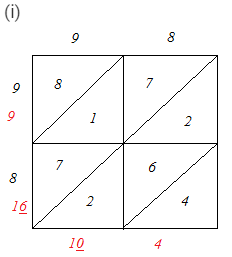
Question 2: Find the squares of the following numbers using diagonal method:
(i) 98
(ii) 273
(iii) 348
(iv) 295
(v) 171
Answer 2:
∴ 982 = 9604

∴ 2732 = 74529
(iii)
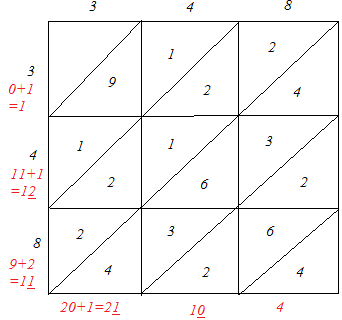
∴ 3482 = 121104
(iv)

∴ 2952 = 87025
(v)
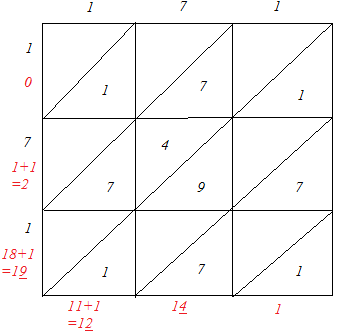
∴ 1712 = 29241
QUESTION 3: FIND THE SQUARES OF THE FOLLOWING NUMBERS:
(I) 127
(II) 503
(III) 451
(IV) 862
(V) 265
ANSWER 3: We will use visual method as it is the most efficient method to solve this problem.
(i) We have:
127 = 120 + 7
Hence, let us draw a square having side 127 units. Let us split it into 120 units and 7 units.
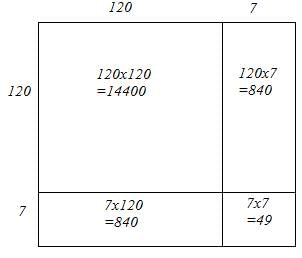
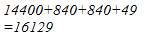
Hence, the square of 127 is 16129.
(ii) We have:
503 = 500 + 3
Hence, let us draw a square having side 503 units. Let us split it into 500 units and 3 units.
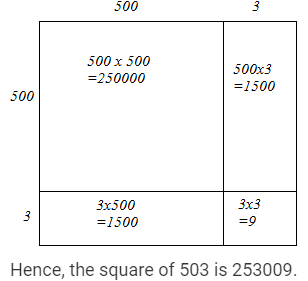
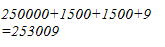
Hence, the square of 503 is 253009.
(iii) We have:
451 = 450 + 1
Hence, let us draw a square having side 451 units. Let us split it into 450 units and 1 units.
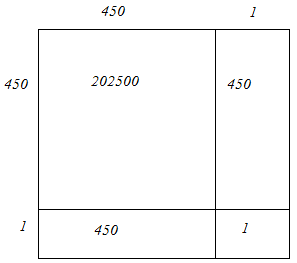
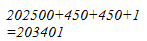
Hence, the square of 451 is 203401.
(iv) We have:
862 = 860 + 2
Hence, let us draw a square having side 862 units. Let us split it into 860 units and 2 units.
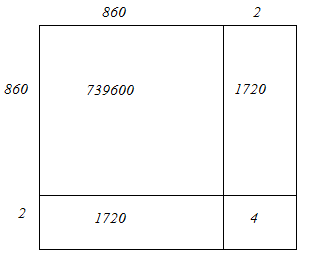
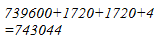
Hence, the square of 862 is 743044.
(v) We have:
265 = 260 + 5
Hence, let us draw a square having side 265 units. Let us split it into 260 units and 5 units.
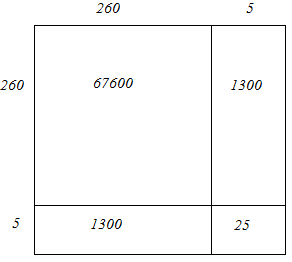
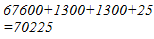
Hence, the square of 265 is 70225.
Question 4: Find the squares of the following numbers:
(i) 425
(ii) 575
(iii) 405
(iv) 205
(v) 95
(vi) 745
(vii) 512
(viii) 995
Answer 4: Notice that all numbers except the one in question (vii) has 5 as their respective unit digits. We know that the square of a number with the form n5 is a number ending with 25 and has the number n(n + 1) before 25. Notice that all numbers except the one in question (vii) has 5 as their respective unit digits. We know that the square of a number with the form n5 is a number ending with 25 and has the number n(n + 1) before 25.
(i) Here, n = 42
∴ n(n + 1) = (42)(43) = 1806
∴ 4252 = 180625
(ii) Here, n = 57
∴ n(n + 1) = (57)(58) = 3306
∴ 5752 = 330625
(iii) Here n = 40
∴ n(n + 1) = (40)(41) = 1640
∴ 4052 = 164025
(iv) Here n = 20
∴∴ n(n + 1) = (20)(21) = 420
∴ 2052 = 42025
(v) Here n = 9
∴ n(n + 1) = (9)(10) = 90
∴ 952 = 9025
(vi) Here n = 74
∴ n(n + 1) = (74)(75) = 5550
∴ 7452 = 555025
(vii) We know:
The square of a three-digit number of the form 5ab = (250 + ab)1000 + (ab)2
∴ 5122 = (250+12)1000 + (12)2 = 262000 + 144 = 262144
(viii) Here, n = 99
∴ n(n + 1) = (99)(100) = 9900
∴ 9952 = 990025
Question 5: Find the squares of the following numbers using the identity (a + b)2 = a2 + 2ab + b2:
(i) 405
(ii) 510
(iii) 1001
(iv) 209
(v) 605
Answer 5: (i) On decomposing:
405 = 400 + 5
Here, a = 400 and b = 5
Using the identity (a + b)2 = a2 + 2ab + b2:
4052 = (400 + 5)2 = 4002 + 2(400)(5) + 52 = 160000 + 4000 + 25 = 164025
(ii) On decomposing:
510 = 500 + 10
Here, a = 500 and b = 10
Using the identity (a + b)2 = a2 + 2ab + b2:
5102 = (500 + 10)2 = 5002 + 2(500)(10) + 102 = 250000 + 10000 + 100 = 260100
(iii) On decomposing:
1001 = 1000 + 1
Here, a = 1000 and b = 1
Using the identity (a + b)2 = a2 + 2ab + b2:
10012 = (1000 + 1)2 = 10002 + 2(1000)(1) + 12 = 1000000 + 2000 + 1 = 1002001
(iv) On decomposing:
209 = 200 + 9
Here, a = 200 and b = 9
Using the identity (a + b)2 = a2 + 2ab + b2:
2092 = (200 + 9)2 = 2002 + 2(200)(9) + 92 = 40000 + 3600 + 81 = 43681
(v) On decomposing:
605 = 600 + 5
Here, a = 600 and b = 5
Using the identity (a + b)2 = a2 + 2ab + b2:
6052 = (600 + 5)2 = 6002 + 2(600)(5) + 52 = 360000 + 6000 + 25 = 366025
Question 6: Find the squares of the following numbers using the identity (a − b)2 = a2 − 2ab + b2:
(i) 395
(ii) 995
(iii) 495
(iv) 498
(v) 99
(vi) 999
(vii) 599
Answer 6: (i) Decomposing: 395 = 400 − 5
Here, a = 400 and b = 5
Using the identity (a − b)2 = a2 − 2ab + b2:
3952 = (400 − 5)2 = 4002 − 2(400)(5) + 52 = 160000 − 4000 + 25 = 156025
(ii) Decomposing: 995 = 1000 − 5
Here, a = 1000 and b = 5
Using the identity (a − b)2 = a2 − 2ab + b2:
9952 = (1000 − 5)2 = 10002 − 2(1000)(5) + 52 = 1000000 − 10000 + 25 = 990025
(iii) Decomposing: 495 = 500 − 5
Here, a = 500 and b = 5
Using the identity (a − b)2 = a2 − 2ab + b2:
4952 = (500 − 5)2 = 5002 − 2(500)(5) + 52 = 250000 − 5000 + 25 = 245025
(iv) Decomposing: 498 = 500 − 2
Here, a = 500 and b = 2
Using the identity (a − b)2 = a2 − 2ab + b2:
4982 = (500 − 2)2 = 5002 − 2(500)(2) + 22 = 250000 − 2000 + 4 = 248004
(v) Decomposing: 99 = 100 − 1
Here, a = 100 and b = 1
Using the identity (a − b)2 = a2 − 2ab + b2:
992 = (100 − 1)2 = 1002 − 2(100)(1) + 12 = 10000 − 200 + 1 = 9801
(vi) Decomposing: 999 = 1000 - 1
Here, a = 1000 and b = 1
Using the identity (a − b)2 = a2 − 2ab + b2:
9992 = (1000 − 1)2 = 10002 − 2(1000)(1) + 12 = 1000000 − 2000 + 1 = 998001
(vii) Decomposing: 599 = 600 − 1
Here, a = 600 and b = 1
Using the identity (a − b)2 = a2 − 2ab + b2:
5992 = (600 − 1)2 = 6002 − 2(600)(1) + 12 = 360000 − 1200 + 1 = 358801
Question 7: Find the squares of the following numbers by visual method:
(i) 52
(ii) 95
(iii) 505
(iv) 702
(v) 99
Answer 7: (i) We have:
52 = 50 + 2
Let us draw a square having side 52 units. Let us split it into 50 units and 2 units.
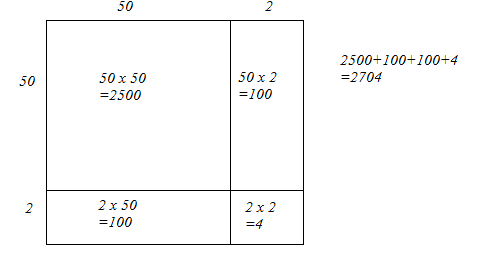
The sum of the areas of these four parts is the square of 52. Thus, the square of 52 is 2704.
(ii) We have:
95 = 90 + 5
Let us draw a square having side 95 units. Let us split it into 90 units and 5 units.
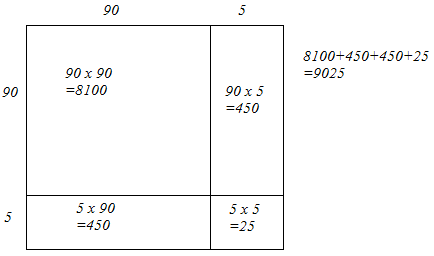
The sum of the areas of these four parts is the square of 95. Thus, the square of 95 is 9025.
(iii) We have:
505 = 500 + 5
Let us draw a square having side 505 units. Let us split it into 500 units and 5 units.
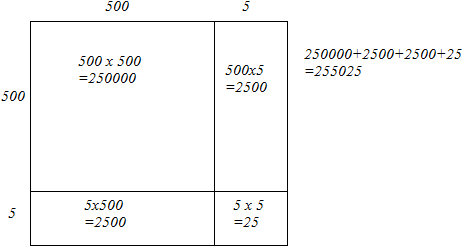
The sum of the areas of these four parts is the square of 505. Thus, the square of 505 is 255025.
(iv) We have:
702 = 700 + 2
Let us draw a square having side 702 units. Let us split it into 700 units and 2 units.
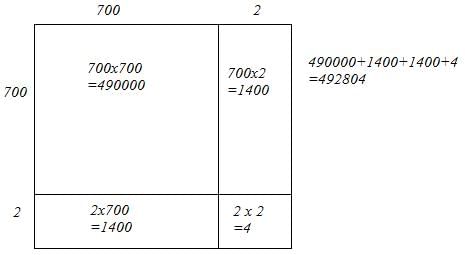
The sum of the areas of these four parts is the square of 702. Thus, the square of 702 is 492804.
(v) We have:
99 = 90 + 9
Let us draw a square having side 99 units. Let us split it into 90 units and 9 units.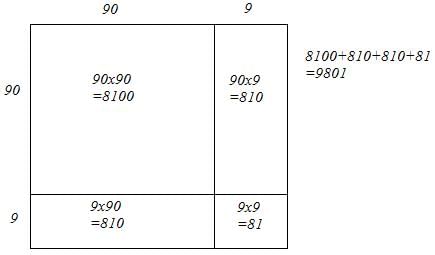
The sum of the areas of these four parts is the square of 99. Thus, the square of 99 is 9801.
FAQs on Chapter 3 - Squares and Square Roots (Ex-3.3) - Class 8 Math RD Sharma Solutions - RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Mathematics
| 1. What is the definition of a perfect square? |  |
| 2. How can I find the square root of a perfect square? |  |
| 3. Can a non-perfect square have a whole number square root? |  |
| 4. Is every positive integer a perfect square? |  |
| 5. How can I determine if a number is a perfect square without calculating its square root? |  |