Ex-19.2, (Part -2), Surface Area And Volume Of Right Circular Cylinder, Class 9 RD Sharma Solutions | RD Sharma Solutions for Class 9 Mathematics PDF Download
Q12. The curved surface area of a cylinder is 1320cm2 and its base had diameter 21 cm. Find the height and volume of the cylinder.
Solution:
Let, r be the radius of the cylinder
h be the height of the cylinder
⇒ 2r = 21cm
⇒ r = 21/2
= 10.5cm
Given, Curved surface area(CSA) = 1320cm2
⇒ 2Πrh = 1320
⇒ 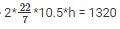
⇒ h = 1320/66
⇒ h = 20 cm
Volume of cylinder = πr2*h
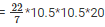
= 22 * 1.5 * 10.5 * 20
= 6930cm2
Q13. The ratio between the radius of the base and the height of a cylinder is 2:3.Find the total surface area of the cylinder, if its volume is 1617cm2.
Solution:
Let, r be the radius of the cylinder
h be the height of the cylinder
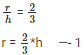
Volume of cylinder = πr2*h
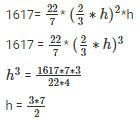
h = 10.5 cm
from, eq 1
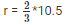
= 7 cm
Total surface area of cylinder = 2πr(h+r)
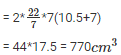
Q14. A rectangular sheet of paper, 44 cm*20 cm, is rolled along its length of form cylinder. Find the volume of the cylinder so formed.
Solution:
Given, the dimensions of the sheet are 44cm*20cm
Here, length = 44 cm
Height = 20 cm
2πr = 44
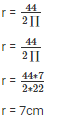
Volume of cylinder = r2*h
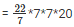
= 154*20 = 3080cm3
Q15. The curved surface area of cylindrical pillar is 264m2 and its volume is 924m3. Find the diameter and the height of the pillar.
Solution:
Let, r be the radius of the cylindrical pillar
h be the height of the cylindrical pillar
CSA = 264m2
2πrh = 264m2 ——– 1
⇒ Volume of the cylinder = 924m2
Π*r2*h = 924
Πrh(r) = 924
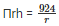
Substitute πrh in eq 1
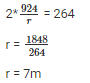
substitute r value in eq 1
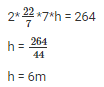
so, the diameter = 2r = 2(7) = 14 m and height = 6 m
Q16. Two circular cylinders of equal volumes have their heights in the ratio 1:2. Find the ratio of two radii.
Solution:
Let, r1,r2 be the radii of the cylinder
h1,h2 be the height of the cylinder
v1,v2 be the volume of the cylinder
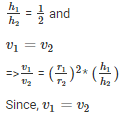
⇒ 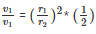
⇒ 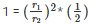
⇒ 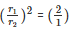
⇒ 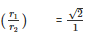
Hence, the ratio of the radii are 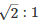
Q17. The height of a right circular cylinder is 10.5 m. Three times the sum of the areas of its two circular faces is twice the area of the curved surface. Find the volume of the cylinder.
Solution:
Let, r be the radius of the right circular cylinder
h be the height of the right circular cylinder
h = 10.5 cm
⇒ 3(2πr2) = 2(2πrh)
⇒ 3r = 2h
⇒ 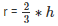
⇒ 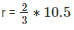
⇒ r = 7cm
Volume of the cylinder = r2*h
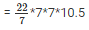
= 154*10.5
= 1617cm3
Q18. How many cubic meters of earth must be dug out to sink a well 21m deep and 6 m diameter? Find the cost of plastering the inner surface as well at Rs.9.50 perm2.
Solution:
Let, r be the radius
h be the height
here, h = 21m
2r = 6
⇒ r = 6/2
= 3 m
Volume of the cylinder = r2*h
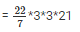
= 66*9
= 594cm3
Cost of plastering = 9.5 per m3
Cost of plastering inner surface = Rs.(594*9.50) = Rs. 5643
Q19. The trunk of a tree is cylindrical and its circumference is 176 cm. If the length of the tree is 3 m. Find the volume of the timber that can be obtained from the trunk.
Solution:
We know that, circumference = 2πr
⇒176 = 2πr
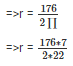
⇒ r = 28 cm
Here, height(h) = 3m = 300cm
Volume of timber = r2*h
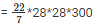
= 44*8400 = 739200cm3 (or) 0.7392m3
Q20. A well with 14 m diameter is dug 8 m deep. The earth taken out of it has been evenly spread all around it to a width of 21 m to form an embankment. Find the height of the embankment.
Solution:
Let, r be the radius of well
h be the height of well
here, h = 8m
2r = 14
⇒ r = 14/2
= 7m
Volume of well = r2*h
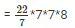
= 22*56
= 1232m3
Let, re be the radius of embankment
he be the height of embankment
Volume of well = Volume of embankment
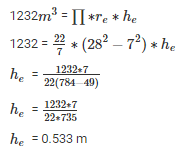
Q21. The difference between inside and outside surfaces of a cylindrical tube is 14 cm long is 88 sq.cm. If the volume of the tube is 176 cubic cm, Find the inner and outer radii of the tube.
Solution:
Let, R be the outer radius
R be the inner radius
Here, h = 14cm
2πRh – 2πrh = 88
⇒ 2πh(R – r) = 88
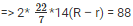
⇒ (R – r) = 1cm ——— 1
Volume of tube = π*R2*h – π*r2*h
176 = πh(R2 – r2)
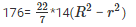
⇒ (R2 – r2) = 4
⇒ (R + r)(R – r) = 4
Here, (R – r) = 1
⇒ (R + r)(1) = 4
⇒ (R + r) = 4 cm
⇒ R = 4 – r ———— 2
Here , R – r = 1
⇒ R = 1 + r
Substitute R value in eq 2
⇒ 1 + r = 4 – r
⇒ 2r = 3
⇒ r = 32
= 1.5 cm
Substitute ‘r’ value in eq 1
⇒ R – 1.5 = 1
⇒ R = 1 + 1.5
⇒ R = 2.5 cm
Hence, the value of inner radii is 1.5 cm and radius of outer radii is 2.5 cm
Q.22. Water flows out through a circular pipe whose internal diameter is 2 cm, at the rate of 6 meters per second into a cylindrical tank. The water is collected in a cylindrical vessel radius of whose base is 60 cm. Find the rise in the level of water in 30 minutes?
Solution:
Given data is as follows :
Internal diameter of the pipe = 2 cm
Water flow rate through the pipe = 6 m/sec
Radius of the tank = 60 cm
Time = 30 minutes
The volume of water that flows for 1 sec through the pipe at the rate of 6 m/sec is nothing but the volume of the cylinder with n = 6
Also, given is the diameter which is 2 cm. Therefore ,
R = 1 cm
Since the speed with which water flows through the pipe is in meters/second, let us convert the radius of the pipe from centimeters to meters . Therefore ,
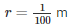
Volume of water collected in the tank after 30 minutes = Volume of water that flows through the pipe for 30 minutes
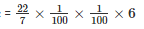
Now , we have to find the volume of water that flows for 30 minutes .
Since , speed of water is in metres/second , let us convert 30 minutes into seconds . It will be 30×60
Volume of water that flows for 30 minutes 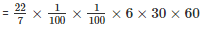
Now , considering the tank , we have been given the radius of tank in centimeters . Let us first convert it into metres . Let radius of tank be ‘R’ .
R = 60 cm
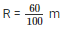
Volume of water collected in the tank after 30 minutes = Volume of water that flows through the pipe for 30 minutes
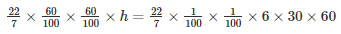
h = 3 m
Therefore , the height of the tank is 3 metres
FAQs on Ex-19.2, (Part -2), Surface Area And Volume Of Right Circular Cylinder, Class 9 RD Sharma Solutions - RD Sharma Solutions for Class 9 Mathematics
| 1. How do you find the surface area of a right circular cylinder? |  |
| 2. How do you find the volume of a right circular cylinder? |  |
| 3. Can you explain the concept of a right circular cylinder? |  |
| 4. What is the difference between the curved surface and the total surface area of a cylinder? |  |
| 5. How can the surface area and volume of a cylinder be used in real-life situations? |  |
















