The Northern Plains Class 4 Notes SST
What is a Plain?
A flat and level land is called a plain.
The plains of India include
- The Northern Plains and,
- The Coastal Plains
What are Northern Plains?
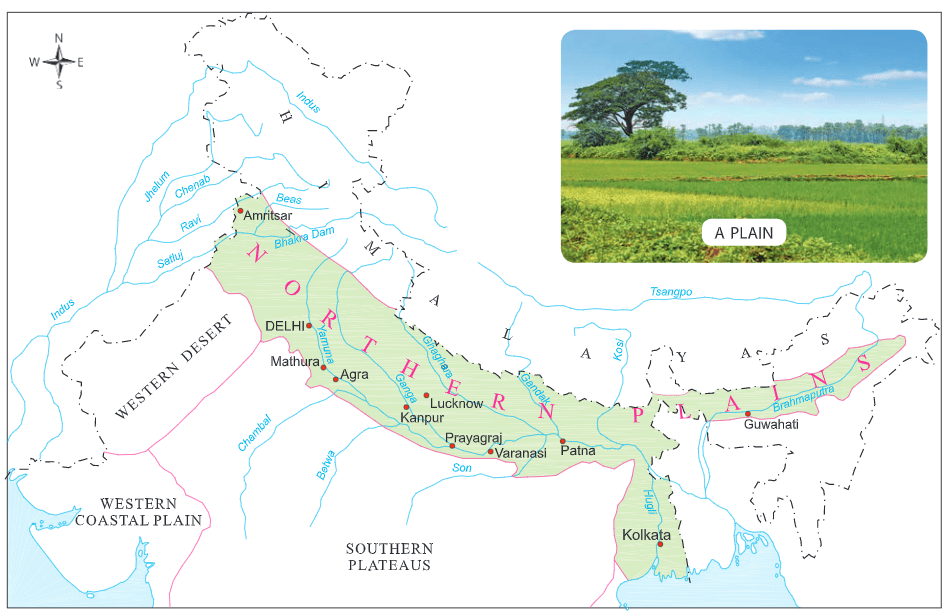
The Northern Plains are an important physical division of India. It is also known as Indo - Gangetic plains.
 Location of the Northern Plains
Location of the Northern Plains
- The Northern Plain is one of the largest and most fertile plains of India. It is one of the World’s most intensively farmed areas.
- They are located between the Himalayan rivers in the north and the Peninsular Plateau in the south.
How are The Northern Plains Formed?
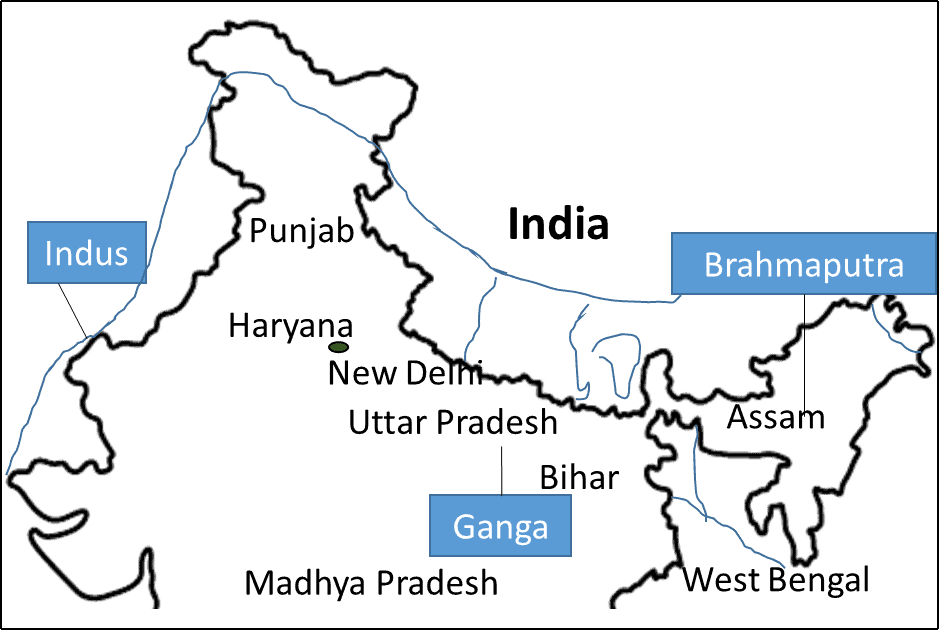
The Northern Plains are made up of two river basins.
- The basin in the west is watered by Indus and its tributaries. The eastern basin is watered by the river Ganga and its tributaries, and the Brahmaputra.
 Rivers of Northern Plain
Rivers of Northern Plain
- The plain is the result of the deposit of soil carried by the rivers Indus, Ganga, Brahmaputra, and their tributaries.
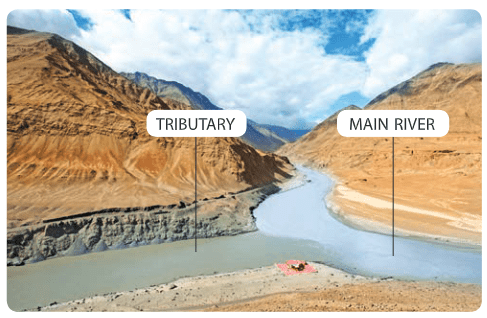 A smaller river that flows into a bigger river is the tributary of the bigger river.
A smaller river that flows into a bigger river is the tributary of the bigger river.
Importance of Northern Plains
The Northern Plains region is one of the most fertile regions of our country.
- This region supplies food grains to many of the central and southern states.
- The fertility of the soil in the basins differs due to many factors.
 In Northern Plains, most farmers use tractors to plow their fields.
In Northern Plains, most farmers use tractors to plow their fields.
- Some of the factors are the distance from the rivers, rainfall during monsoons, and the height from the sea.
- Generally, the Great Northern Plains are fertile, densely populated, and are the basins of Sutlej, Beas, Ravi, Ganga, Yamuna, Brahmaputra, and their tributaries. Indus, Ganga, Yamuna and Brahmaputra originate in the Himalayas.
- Some of the well-known ancient cities are situated on the bank of these rivers especially on the bank of the river Ganga.

Rishikesh, Haridwar, Prayag, Allahabad, Varanasi, Pataliputra, and Kolkata are some prominent out of them.
Parts of the Great Northern Plains
It is interesting to note that the Great Northern Plain can be broadly studied in four parts.
These areLocation of Northern Plains on Indian Map
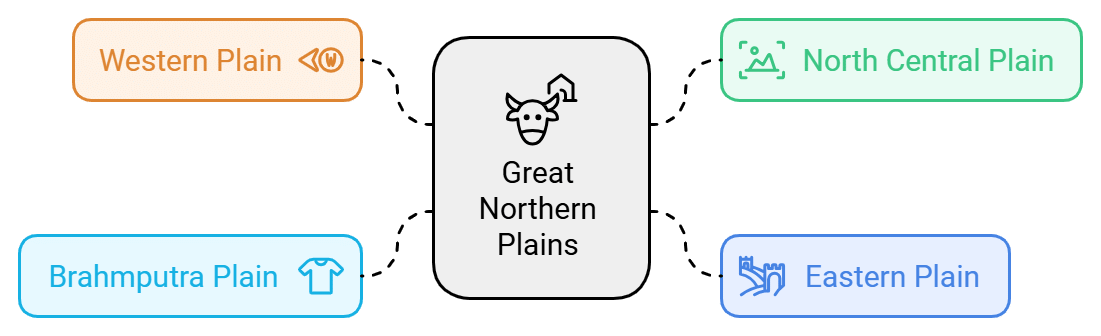 Parts of the Great Northern Plains
Parts of the Great Northern Plains
Western Plain: Rajasthan
- The Western Plain encompasses regions like Rajasthan and parts of Punjab.
- Historically, it was watered by ancient rivers such as Saraswati and Drishadvati, although these rivers are now mostly invisible or dried up.
- Despite the arid climate in some areas, fertile regions like Bikaner are found within this plain.
- Bikaner is known for its agriculture, particularly for crops like wheat, mustard, and cotton.
 Wheat, Mustard, and Cotton Crops
Wheat, Mustard, and Cotton Crops - The soil here is rich in nutrients, making it suitable for cultivation.
North Central Plain: Punjab, Haryana & UP
- The North Central Plain includes states like Punjab, Haryana, and parts of Uttar Pradesh.
- This region owes its fertility to the presence of rivers like the Sutlej, Beas, Ravi, Ganga, and Yamuna, which originate from the Himalayas.
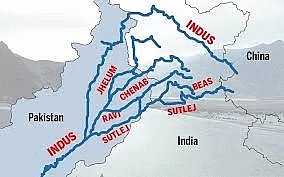 Rivers of Punjab
Rivers of Punjab - Agriculture is the primary occupation in this plain, with crops such as rice, wheat, sugarcane, and cotton being cultivated extensively.
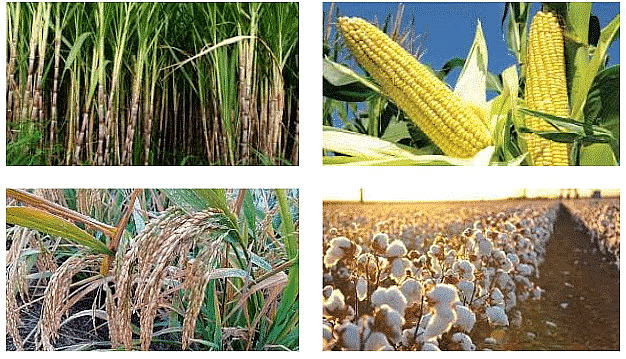 Crops grown in North Central Plain
Crops grown in North Central Plain - The population density in this area is high due to the availability of fertile land and water resources.
Eastern Plain: Bihar & West Bengal
- The Eastern Plain covers parts of Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, and West Bengal. It owes its fertility to the Ganga and its tributaries, which bring nutrient-rich sediment from the Himalayas.
- This region is an agricultural hub, producing crops like rice, jute, sugarcane, and pulses.
 Crops grown in Eastern Plain
Crops grown in Eastern Plain - However, the Eastern Plain faces frequent floods, especially in West Bengal, where heavy rainfall is common.
- These floods replenish the soil with nutrients but also cause damage to crops and infrastructure.
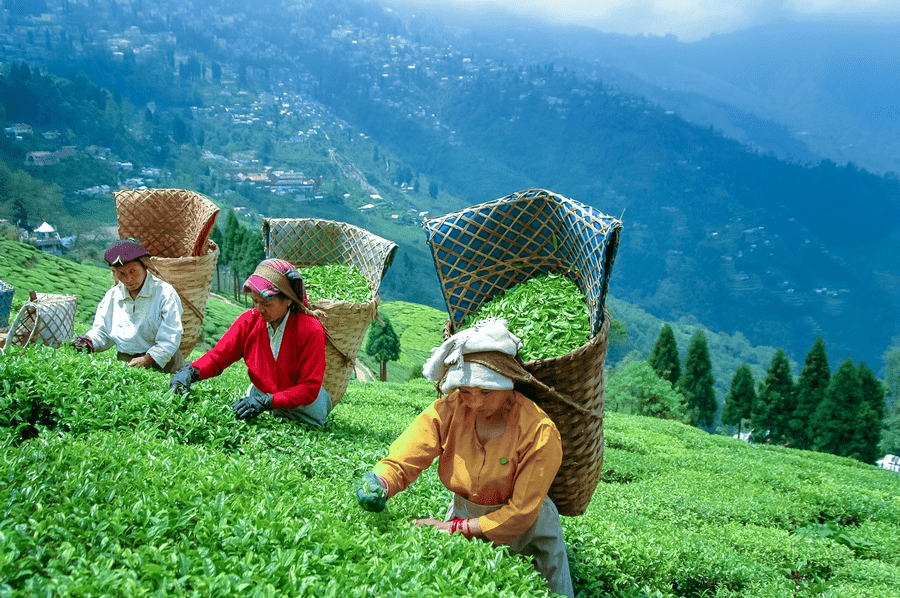 Tea Gardens in Darjeeling, West Bengal
Tea Gardens in Darjeeling, West Bengal
Brahmaputra Plain: Bangladesh
- The Brahmaputra Plain is primarily located in Bangladesh, although it extends into parts of northeastern India.
- It is formed by sediment deposited by the Brahmaputra river and its tributaries, making it exceptionally fertile.
- Agriculture is the mainstay of the economy in this region, with crops like rice, tea, jute, and mustard being cultivated.
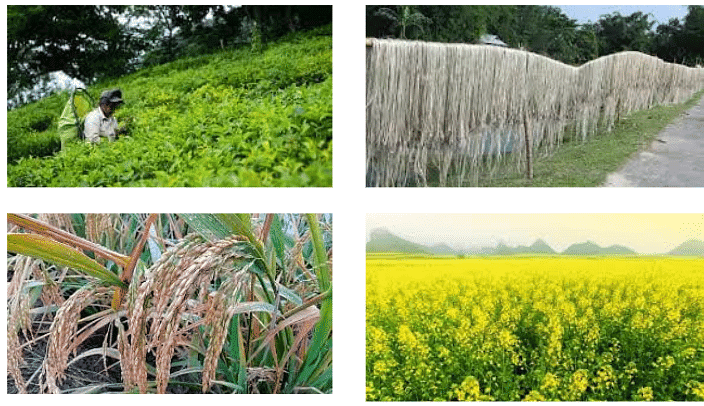 Crops grown in Brahmaputra Plain
Crops grown in Brahmaputra Plain - However, the Brahmaputra Plain is prone to frequent floods, which can cause devastation to crops, homes, and infrastructure.
- These floods also contribute to the dynamic nature of the landscape, with river channels constantly shifting and forming new islands.
- Despite the challenges posed by floods, the Brahmaputra Plain remains vital for agriculture and supports a dense population.
Ganga Brahmaputra Delta
- By the time a river reaches its end, it has lots of sediment. This sediment settles down and makes the river split into many channels or distributaries.
- In between these distributaries, triangular-shaped islands are formed.
- These are called Delta because they resemble a triangle(Δ).
- The Ganga- Brahmaputra delta is called as Sunderban.

Characteristics of Northern Plains
- Fertility: The fertility of the northern plains is unparalleled due to the continuous deposition of nutrient-rich soil by the rivers, making it ideal for agriculture.
- Population Density: These plains are densely populated regions, particularly the North Central and Eastern Plains, owing to the abundance of fertile land and water resources.
- River Origins: The major rivers of the northern plains, including the Indus, Ganga, Yamuna, and Brahmaputra, originate from the Himalayan mountain ranges, ensuring a steady supply of water and sediment.
 Haridwar
Haridwar - Ancient Cities: Several historically significant cities, such as Rishikesh, Haridwar, Varanasi, and Kolkata, are located along the banks of these rivers, showcasing the cultural and historical importance of the region.
Formation of Deltas
- Deposition Process: As rivers approach their mouths or deltas, they deposit sediment carried from upstream areas.
- Delta Formation: The deposited sediment leads to the formation of distributaries and triangular-shaped islands.
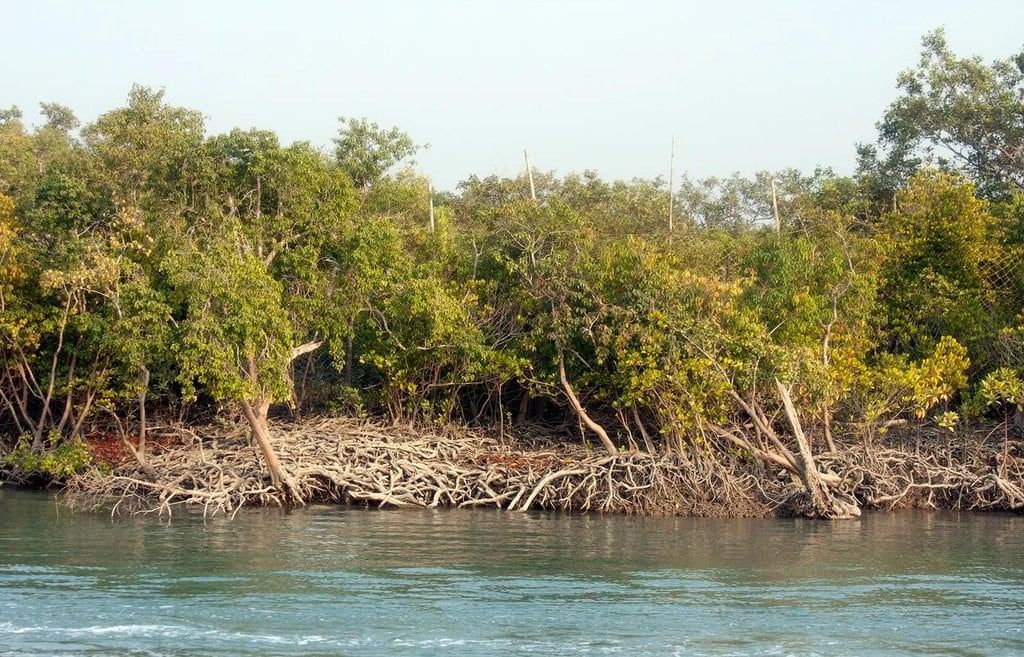 Sunderban Delta
Sunderban Delta - Sunderban Delta: The delta formed by the confluence of the Ganga and Brahmaputra rivers is known as the Sunderban delta, characterized by its rich biodiversity and mangrove forests.
Life in the Region
In the northern plains of India, there are several states and territories where people mostly work as farmers. They grow crops like rice, wheat, and sugarcane.
Punjab
- In Punjab, farmers use modern machines like tractors and harvesters to grow crops.
- People there enjoy eating dishes like makke ki roti, sarson ka saag, and lassi.
- They celebrate festivals like Baisakhi and Lohri and dance to folk music like Bhangra and Gidda.
- The Golden Temple in Amritsar attracts many tourists.
Haryana
- Similar to Punjab, farmers in Haryana also use modern farming equipment.
- Many people there rear cattle and farm for dairy products.
- Cities like Faridabad and Gurugram have industries like information technology and automobiles.
Delhi
- Delhi is the capital territory where many people work in offices or have their own businesses.
- It's known for its famous monuments like the Red Fort, Qutb Minar, and India Gate, which attract tourists from around the world.
Uttar Pradesh
- This state is famous for fruits like guavas and mangoes.
- It has industries like sugar, textiles, and chemicals.
- Traditional crafts like chikankari embroidery and silk sarees are famous here.
- The Kumbh Mela, a big religious festival, happens every 12 years in Prayagraj.
Bihar
- Bihar is known for its lychees and silk weaving in places like Bhagalpur.
- People there enjoy dishes like litti-chokha and sattu parantha.
- Important festivals include Chhath. Patna, Gaya, and Rajgir are popular tourist destinations.
West Bengal
- In West Bengal, rice, jute, and tea are the main crops.
- Darjeeling is famous for its tea gardens.
- The state has jute mills along the Hugli river.
- Fishing is significant in coastal areas.
- The main festival is Durga Puja.
Assam
- Assam is known for its tea and silk production.
- It also has petroleum and natural gas reserves in places like Digboi.
- Traditional clothing like mekhela-chador is common among women.
- The main festival celebrated there is Bihu.
Word Meaning
Alluvium – Fine soil brought down by the rivers and spread along the banks.
Tributaries – Rivers joining another big river. [Yamuna is a tributary of Ganga]
Basin – Region watered by a river.
Delta – Triangular shaped region formed between the channels of a river near its mouth.
Sediment – Solid material at the water bed.
Keep in Mind!
The northern plains extend from Punjab in the west to West Bengal in the east.
The plains are irrigated by Ganga and its tributaries and Brahmaputra rivers.
The plains have been the cradle of ancient Indian civilization.
The plains are the most populous and fertile regions.
Ganga is the holy river of the Hindus. But it is now polluted by waste flowing into it
from big cities and industrial towns.
|
50 videos|246 docs|46 tests
|
FAQs on The Northern Plains Class 4 Notes SST
| 1. What is a Plain? |  |
| 2. What are Northern Plains? |  |
| 3. How are The Northern Plains Formed? |  |
| 4. Importance of Northern Plains |  |
| 5. Parts of the Great Northern Plain |  |

















