RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Math Chapter 4 - Cubes and Cube Roots (Part-3) | RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Mathematics PDF Download
Question 1: Find the cube roots of the following numbers by successive subtraction of numbers:
1, 7, 19, 37, 61, 91, 127, 169, 217, 271, 331, 397, ...
(i) 64
(ii) 512
(iii) 1728
Answer 1:
(i) We have:
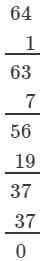
∵∵ Subtraction is performed 4 times.
(ii) We have:
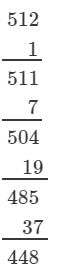
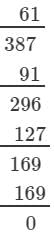
∵∵ Subtraction is performed 8 times.
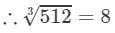
(iii) We have:
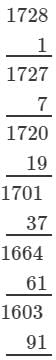
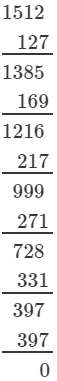
∵∵ Subtraction is performed 12 times.
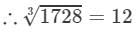
Question 2: Using the method of successive subtraction examine whether or not the following numbers are perfect cubes:
(i) 130
(ii) 345
(iii) 792
(iv) 1331
Answer 2: (i) We have:
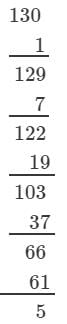
∵∵ The next number to be subtracted is 91, which is greater than 5.
∴∴ 130 is not a perfect cube.
(ii) We have:
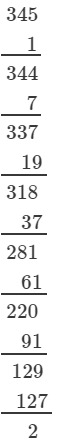
∵∵ The next number to be subtracted is 161, which is greater than 2.
∴∴ 345 is not a perfect cube.
(iii) We have:
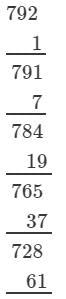

∵∵ The next number to be subtracted is 271, which is greater than 63.
∴∴ 792 is not a perfect cube.
(iv) We have:
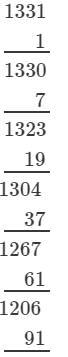
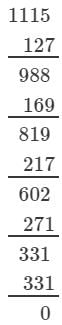
∵∵ The subtraction is performed 11 times.

Thus, 1331 is a perfect cube.
Question 3: Find the smallest number that must be subtracted from those of the numbers in question 2 which are not perfect cubes, to make them perfect cubes. What are the corresponding cube roots?
Answer 3: (i) We have:
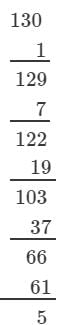
∵∵ The next number to be subtracted is 91, which is greater than 5.
∴∴ 130 is not a perfect cube.
However, if we subtract 5 from 130, we will get 0 on performing successive subtraction and the number will become a perfect cube.
If we subtract 5 from 130, we get 125. Now, find the cube root using successive subtraction.
We have:
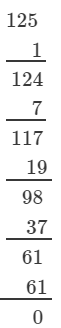
∵∵ The subtraction is performed 5 times.
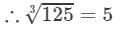
Thus, it is a perfect cube.
(ii) We have:
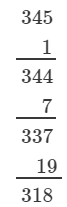
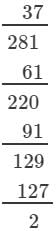
∵∵ The next number to be subtracted is 161, which is greater than 2.
∴∴ 345 is not a perfect cube.
However, if we subtract 2 from 345, we will get 0 on performing successive subtraction and the number will become a perfect cube.
If we subtract 2 from 345, we get 343. Now, find the cube root using successive subtraction.
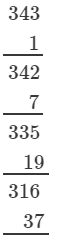
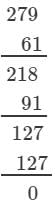
∵∵ The subtraction is performed 7 times.
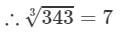
Thus, it is a perfect cube.
(iii) We have:
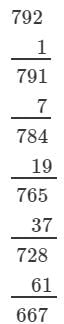
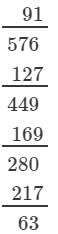
∵∵ The next number to be subtracted is 271, which is greater than 63.
∴∴ 792 is not a perfect cube.
However, if we subtract 63 from 792, we will get 0 on performing successive subtraction and the number will become a perfect cube.
If we subtract 63 from 792, we get 729. Now, find the cube root using the successive subtraction.
We have:

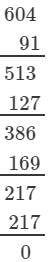
∵∵ The subtraction is performed 9 times.
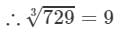
Thus, it is perfect cube.
Question 4: Find the cube root of each of the following natural numbers:
(i) 343
(ii) 2744
(iii) 4913
(iv) 1728
(v) 35937
(vi) 17576
(vii) 134217728
(viii) 48228544
(ix) 74088000
(x) 157464
(xi) 1157625
(xii) 33698267
Answer 4: (i) Cube root using units digit:
Let us consider 343.
The unit digit is 3; therefore, the unit digit in the cube root of 343 is 7.
There is no number left after striking out the units, tens and hundreds digits of the given number; therefore, the cube root of 343 is 7.
Hence, 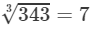
(ii) Cube root using units digit:
Let us consider 2744.
The unit digit is 4; therefore, the unit digit in the cube root of 2744 is 4.
After striking out the units, tens and hundreds digits of the given number, we are left with 2.
Now, 1 is the largest number whose cube is less than or equal to 2.
Therefore, the tens digit of the cube root of 2744 is 1.
Hence, 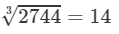
(iii) Cube root using units digit:
Let us consider 4913.
The unit digit is 3; therefore, the unit digit in the cube root of 4913 is 7.
After striking out the units, tens and hundreds digits of the given number, we are left with 4.
Now, 1 is the largest number whose cube is less than or equal to 4.
Therefore, the tens digit of the cube root of 4913 is 1.
Hence, 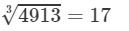
(iv) Cube root using units digit:
Let us consider 1728.
The unit digit is 8; therefore, the unit digit in the cube root of 1728 is 2.
After striking out the units, tens and hundreds digits of the given number, we are left with 1.
Now, 1 is the largest number whose cube is less than or equal to 1.
Therefore, the tens digit of the cube root of 1728 is 1.
Hence, 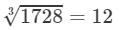
(v) Cube root using units digit:
Let us consider 35937.
The unit digit is 7; therefore, the unit digit in the cube root of 35937 is 3.
After striking out the units, tens and hundreds digits of the given number, we are left with 35.
Now, 3 is the largest number whose cube is less than or equal to 35 ( 33<35<4333<35<43).
Therefore, the tens digit of the cube root of 35937 is 3.
Hence, 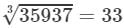
(vi) Cube root using units digit:
Let us consider the number 17576.
The unit digit is 6; therefore, the unit digit in the cube root of 17576 is 6.
After striking out the units, tens and hundreds digits of the given number, we are left with 17.
Now, 2 is the largest number whose cube is less than or equal to 17 (23<17<3323<17<33).
Therefore, the tens digit of the cube root of 17576 is 2.
Hence, 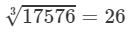
(vii) Cube root by factors:
On factorising 134217728 into prime factors, we get:
134217728=2×2×2×2×2×2×2×2×2×2×2×2×2×2×2×2×2×2×2×2×2×2×2×2×2×2×2
On grouping the factors in triples of equal factors, we get:
134217728={2×2×2}×{2×2×2}×{2×2×2}×{2×2×2}×{2×2×2}×{2×2×2}×{2×2×2}×{2×2×2}×{2×2×2}
Now, taking one factor from each triple, we get:
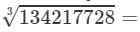 2×2×2×2×2×2×2×2×2=5121342177283=2×2×2×2×2×2×2×2×2=512
2×2×2×2×2×2×2×2×2=5121342177283=2×2×2×2×2×2×2×2×2=512
(viii) Cube root by factors:
On factorising 48228544 into prime factors, we get:
48228544=2×2×2×2×2×2×7×7×7×13×13×1348228544=2×2×2×2×2×2×7×7×7×13×13×13
On grouping the factors in triples of equal factors, we get:
48228544={2×2×2}×{2×2×2}×{7×7×7}×{13×13×13}48228544=2×2×2×2×2×2×7×7×7×13×13×13
Now, taking one factor from each triple, we get:
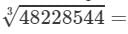 2×2×7×13=364
2×2×7×13=364
(ix) Cube root by factors:
On factorising 74088000 into prime factors, we get:
74088000=2×2×2×2×2×2×3×3×3×5×5×5×7×7×774088000=2×2×2×2×2×2×3×3×3×5×5×5×7×7×7
On grouping the factors in triples of equal factors, we get:
74088000={2×2×2}×{2×2×2}×{3×3×3}×{5×5×5}×{7×7×7}74088000=2×2×2×2×2×2×3×3×3×5×5×5×7×7×7
Now, taking one factor from each triple, we get:
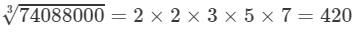
(x) Cube root using units digit:
Let is consider 157464.
The unit digit is 4; therefore, the unit digit in the cube root of 157464 is 4.
After striking out the units, tens and hundreds digits of the given number, we are left with 157.
Now, 5 is the largest number whose cube is less than or equal to 157 (53<157<6353<157<63).
Therefore, the tens digit of the cube root 157464 is 5.
Hence, 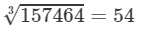
(xi) Cube root by factors:
On factorising 1157625 into prime factors, we get:
1157625=3×3×3×5×5×5×7×7×71157625=3×3×3×5×5×5×7×7×7
On grouping the factors in triples of equal factors, we get:
1157625={3×3×3}×{5×5×5}×{7×7×7}1157625=3×3×3×5×5×5×7×7×7
Now, taking one factor from each triple, we get:
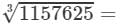 3×5×7=10511576253=3×5×7=105
3×5×7=10511576253=3×5×7=105
(xii) Cube root by factors:
On factorising 33698267 into prime factors, we get:
33698267=17×17×17×19×19×1933698267=17×17×17×19×19×19
On grouping the factors in triples of equal factors, we get:
33698267={17×17×17}×{19×19×19}33698267=17×17×17×19×19×19
Now, taking one factor from each triple, we get:
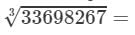 17×19=323336982673=17×19=323
17×19=323336982673=17×19=323
Question 5: Find the smallest number which when multiplied with 3600 will make the product a perfect cube. Further, find the cube root of the product.
Answer 5: On factorising 3600 into prime factors, we get:
3600=2×2×2×2×3×3×5×53600=2×2×2×2×3×3×5×5
On grouping the factors in triples of equal factors, we get:
3600={2×2×2}×2×3×3×5×53600=2×2×2×2×3×3×5×5
It is evident that the prime factors of 3600 cannot be grouped into triples of equal factors such that no factor is left over.
Therefore, 3600 is not a perfect cube.
However, if the number is multiplied by (2×2×3×5=602×2×3×5=60), the factors can be grouped into triples of equal factors such that no factor is left over.
Hence, the number 3600 should be multiplied by 60 to make it a perfect cube.
Also, the product is given as:
3600×60={2×2×2}×2×3×3×5×5×60⇒216000={2×2×2}×2×3×3×5×5×(2×2×3×5)⇒216000={2×2×2}×{2×2×2}×{3×3×3}×{5×5×5}3600×60=2×2×2×2×3×3×5×5×60⇒216000=2×2×2×2×3×3×5×5×2×2×3×5⇒216000=2×2×2×2×2×2×3×3×3×5×5×5
To get the cube root of the produce 216000, take one factor from each triple.
Cube root = 2×2×3×5=602×2×3×5=60
Hence, the required numbers are 60 and 60.
Question 6: Multiply 210125 by the smallest number so that the product is a perfect cube. Also, find out the cube root of the product.
Answer 6: On factorising 210125 into prime factors, we get:
210125=5×5×5×41×41210125=5×5×5×41×41
On grouping the factors in triples of equal factors, we get:
210125={5×5×5}×41×41210125=5×5×5×41×41
It is evident that the prime factors of 210125 cannot be grouped into triples of equal factors such that no factor is left over. Therefore, 210125 is not a perfect cube. However, if the number is multiplied by 41, the factors can be grouped into triples of equal factors such that no factor is left over.
Hence, the number 210125 should be multiplied by 41 to make it a perfect cube.
Also, the product is given as:
210125×41={5×5×5}×{41×41×41}⇒8615125={5×5×5}×{41×41×41}210125×41=5×5×5×41×41×41⇒8615125=5×5×5×41×41×41
To get the cube root of the produce 8615125, take one factor from each triple. The cube root is 5×41=2055×41=205.
Hence, the required numbers are 41 and 205.
Question 7: What is the smallest number by which 8192 must be divided so that quotient is a perfect cube? Also, find the cube root of the quotient so obtained.
Answer 7: On factorising 8192 into prime factors, we get:
8192=2×2×2×2×2×2×2×2×2×2×2×2×28192=2×2×2×2×2×2×2×2×2×2×2×2×2
On grouping the factors in triples of equal factors, we get:
8192={2×2×2}×{2×2×2}×{2×2×2}×{2×2×2}×28192=2×2×2×2×2×2×2×2×2×2×2×2×2
It is evident that the prime factors of 8192 cannot be grouped into triples of equal factors such that no factor is left over. Therefore, 8192 is not a perfect cube. However, if the number is divided by 2, the factors can be grouped into triples of equal factors such that no factor is left over.
Hence, the number 8192 should be divided by 2 to make it a perfect cube.
Also, the quotient is given as:
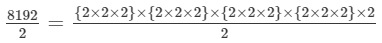
⇒4096={2×2×2}×{2×2×2}×{2×2×2}×{2×2×2}
To get the cube root of the quotient 4096, take one factor from each triple. We get:
Cube root = 2×2×2×2=162×2×2×2=16
Hence, the required numbers are 2 and 16.
Question 8: Three numbers are in the ratio 1 : 2 : 3. The sum of their cubes is 98784. Find the numbers.
Answer 8: Let the numbers be x, 2x and 3x.
Therefore
x3+(2x)3+(3x)3=98784⇒x3+8x3+273=98784⇒36x3=98784 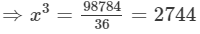
⇒x3=2744
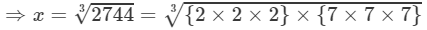 =2×7=14
=2×7=14
Hence, the numbers are 14, (2×14=282×14=28) and (3×14=423×14=42).
Question 9: The volume of a cube is 9261000 m3. Find the side of the cube.
Answer 9: Volume of a cube is given by:
V=s3V=s3, where s = Side of the cube
It is given that the volume of the cube is 9261000 m3; therefore, we have:
s3=9261000s3=9261000
Let us find the cube root of 9261000 using prime factorisation:
9261000=2×2×2×3×3×3×5×5×5×7×7×7={2×2×2}×{3×3×3}×{5×5×5}×{7×7×7}
9261000 could be written as a triples of equal factors; therefore, we get:
Cube root = 2×3×5×7=2102×3×5×7=210
Therefore
s3=9261000⇒s= 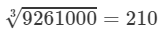
Hence, the length of the side of cube is 210 m.
FAQs on RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Math Chapter 4 - Cubes and Cube Roots (Part-3) - RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Mathematics
| 1. What is the formula to find the volume of a cube? |  |
| 2. How can I find the cube root of a number without using a calculator? |  |
| 3. How can I determine if a number is a perfect cube? |  |
| 4. How can I calculate the surface area of a cube? |  |
| 5. Can a cube root be negative? |  |





















