Electricity Class 10 Worksheet Science Chapter 11
Q1: Multiple Choice Questions (MCQs)
(i) What is the positive terminal of an electric cell?
(a) Metal disc at the bottom
(b) Metal cap on the top
(c) Tungsten filament
(d) Thick wires
Ans: (b)
The positive terminal of an electric cell is represented by the metal cap on the top.
(ii) What is the purpose of a resistor in an electric circuit with an LED?
(a) Increases current flow
(b) Prevents excess current
(c) Enhances light production
(d) Acts as a switch
Ans: (b)
A resistor in an electric circuit with an LED controls the flow of current, preventing excess current that could damage the LED.
(iii) What is the primary purpose of argon gas in an electric bulb?
(a) Produces light
(b) Prevents heat
(c) Shields the filament
(d) Increases energy efficiency
Ans: (c)
Argon gas in an electric bulb protects the tungsten filament from heat, preventing it from breaking.
(iv) Which materials are good conductors of electricity?
(a) Plastics and fiberglass
(b) Copper and silver
(c) Mica and ceramics
(d) Argon gas and tungsten
Ans: (b)
Copper and silver are examples of good conductors of electricity.
(v) What is the function of a switch in an electric circuit?
(a) Increases current flow
(b) Completes or breaks the circuit
(c) Prevents electricity transmission
(d) Produces light in the circuit
Ans: (b)
A switch in an electric circuit completes or breaks the circuit, controlling the flow of electric current.
Q2: Fill in the Blanks
(i) An electric cell converts ____________ energy into electrical energy.
Ans: chemical
An electric cell converts chemical energy into electrical energy.
(ii) The filament of an electric bulb is made of ____________ metal.
Ans: tungsten
The filament of an electric bulb is made of tungsten metal.
(iii) LEDs consume ____________ electricity compared to ordinary bulbs.
Ans: less
LEDs consume less electricity compared to ordinary bulbs.
(iv) ____________ is used as an electric insulator.
Ans: Ceramics
Ceramics are used as electric insulators.
(v) ____________ is a good conductor of electricity commonly used in electric wires.
Ans: Copper
Copper is a good conductor of electricity and is commonly used in electric wires.
Q3: Match the Column (In a Table)
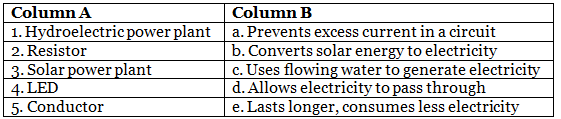
Ans:
Q4: True/False
(i) An electric bulb fuses when its filament breaks.
Ans: True
An electric bulb fuses when its filament breaks, and it cannot produce light.
(ii) Plastics and fiberglass are good conductors of electricity.
Ans: False
Plastics and fiberglass are insulators and do not conduct electricity.
(iii) The positive terminal of an LED must be connected to the negative terminal of an electric cell.
Ans: False
The positive terminal (longer wire) of an LED must be connected to the positive terminal of an electric cell.
(iv) Power plants use turbines to generate electricity.
Ans: True
Power plants use turbines to generate electricity by various means such as burning coal, flowing water, or nuclear energy.
(v) A switch in the 'OFF' position completes the electric circuit.
Ans: False
In the 'OFF' position, a switch breaks the electric circuit, preventing the flow of current.
|
22 videos|80 docs|16 tests
|
FAQs on Electricity Class 10 Worksheet Science Chapter 11
| 1. What is electricity? |  |
| 2. How is electricity generated? |  |
| 3. What are conductors and insulators in electricity? |  |
| 4. What are the dangers of electricity? |  |
| 5. How can we conserve electricity? |  |
|
22 videos|80 docs|16 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for Class 6 exam
|

|











