Trigonometry: Solved Examples | Quantitative Aptitude (Quant) - CAT PDF Download
Question 1: 3sinx + 4cosx + r is always greater than or equal to 0. What is the smallest value ‘r’ can to take?
A. 5
B. -5
C. 4
D. 3
Answer : 5
Explanation-
3sinx + 4cosx ≥ -r

3/5 = cosA ⇒ sinA = 4/5
5(sinx cosA + sinA cosx) ≥ -r
5(sin(x + A)) ≥ -r
5sin (x + A) ≥ -r
-1 ≤ sin (angle) ≤ 1
5sin (x + A) ≥ -5
rmin = 5
The question is "What is the smallest value ‘r’ can to take?"
Hence, the answer is 5.
Choice A is the correct answer.
Question 2: Sin2014x + Cos2014x = 1, x in the range of [-5π, 5π], how many values can x take?
A. 0
B. 10
C. 21
D. 11
Answer: 21
Explanation-
We know that Sin2x + Cos2x = 1 for all values of x.
If Sin x or Cos x is equal to –1 or 1, then Sin2014x + Cos2014x will be equal to 1.
Sin x is equal to –1 or 1 when x = –4.5π or –3.5π or –2.5π or –1.5π or –0.5π or 0.5π or 1.5π or 2.5π or 3.5π or 4.5π.
Cosx is equal to –1 or 1 when x = –5π or –4π or –3π or –2π or –π or 0 or π or 2π or 3π or 4π or 5π.
For all other values of x, Sin2014 x will be strictly lesser than Sin2x.
For all other values of x, Cos2014 x will be strictly lesser than Cos2x.
We know that Sin2x + Cos2x is equal to 1. Hence, Sin2014x + Cos2014x will never be equal to 1 for all other values of x. Thus there are 21 values.
The question is "How many values the 'x' can take?"
Hence, the answer is 21.
Choice C is the correct answer.
Question 3: Consider a regular hexagon ABCDEF. There are towers placed at B and D. The angle of elevation from A to the tower at B is 30 degrees, and to the top of the tower at D is 45 degrees. What is the ratio of the heights of towers at B and D?
A. 1:√3
B. 1:2√3
C. 1:2
D. 3:4√3
Answer: 1:2√3
Explanation-
Let the hexagon ABCDEF be of side ‘a’. Line AD = 2a. Let towers at B and D be B’B and D’D respectively.
From the given data we know that ∠B´AB = 30° and ∠D´AD = 45°. Keep in mind that the Towers B’B and D´D are not in the same plane as the hexagon.

In Triangle B’AB,
tan ∠B´AB 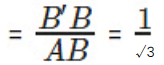
⇒ B’B = 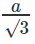
In Triangle D´AD, tan ∠D´AD 
⇒ D’D = 2a
Ratio of heights = 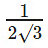
Answer choice (B)
The question is "What is the ratio of heights?"
Hence, the answer is 1:2√3
Choice B is the correct answer.
Question 4: Find the maximum and minimum value of 8 cos A + 15 sin A + 15
A. 11√2+15
B. 30; 8
C. 32; -2
D. 23; 8
Answer: 1:2√3
Explanation-
Always look out for Pythagorean triplets, we know that (8,15,17) is one
∴ The expression becomes: 
Let there be a angle B for which sin B = 8/17, cos B = 15/17
⇒ 17( sin B cos A + cos B sin A) + 15
17(sin(A+B)) + 15
We know that sin(A+B)max = 1
sin(A+B)min = -1
∴ Max value = 17 * 1 +15 = 32
Min value = 17 * -1 + 15 = -2
The question is "to find the maximum and minimum value "
Hence, the answer is 32; -2
Choice B is the correct answer.
Question 5: : If cos A + cos2 A = 1 and a sin12 A + b sin10 A + c sin8 A + d sin6 A - 1 = 0. Find the value of a+b/c+d
A. 4
B. 3
C. 6
D.1
Answer. 3
Explanation.
Given,
Cos A = 1 - Cos2A
⇒ Cos A = Sin2 A
⇒ Cos2A = Sin4A
⇒ 1 – Sin2 A = Sin4 A
⇒ 1 = Sin4 A + Sin2 A
⇒ 13 = (Sin4A + Sin2A)3
⇒ 1 = Sin12 A + Sin6A + 3Sin8 A + 3Sin10 A
⇒ Sin12 A + Sin6A + 3Sin8 A + 3Sin10 A – 1 = 0
On comparing,
a = 1, b = 3 , c = 3 , d = 1 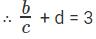
The question is "Find the value of a+b/c+d"
Hence, the answer is 3
Choice B is the correct answer.
Question 6: In the below figure, the sheet of width W is folded along PQ such that R overlaps S Length of PQ can be written as :-

A. 
B. 
C. 
D. Any two of the above
Answer: Any two of the above
Explanation-
If you are quick at observing , this question can be solved just by looking at the options as ,

∴ (d) Answer
Actually solving the question.
For R and S to overlap,
∆ PQR is congurent to ∆ PSQ
∴ ∠ QPR = ∝ ; ∠ SQP = ∠ PQR = 90 - ∝
⇒ ∠ RQT = 2∝ (180°-(180°-2∝))
We can draw the figure as :-

∴In ∆ QRT
QT = QR cos2∝
In ∆ PSQ,
SQ = PQ sin∝ = QR
∴ w = QT + SQ = PQ sin∝cos2∝ + PQ sin∝
= PQ sin∝ (1 + cos 2∝)
 (as shown earlier)
(as shown earlier)
The question is "Length of PQ can be written as "
Hence, the answer is Any two of the above
Choice D is the correct answer.
Question 7: Ram and Shyam are 10 km apart. They both see a hot air balloon passing in the sky making an angle of 60° and 30° respectively. What is the height at which the balloon could be flying?
A. 
B. 5√3
C. Both A and B
D. Can’t be determined
Answer: Both A and B
Explanation-
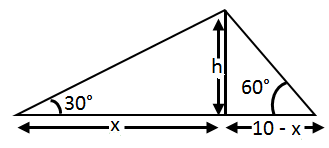
tan 30° = h/x

⇒ h = (10 – x) √3
⇒ 30 – 3x = x
⇒ 4x = 30
⇒ x = 30/4 = 15/2
⇒ 
Case 2 : 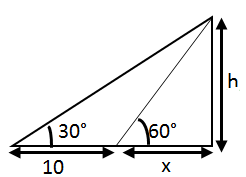

Also,
tan 30° = 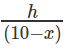
⇒
⇒ x = 5
H = 5√3
The question is "What is the height at which the balloon could be flying"
Hence, the answer is Both A and B
Choice C is the correct answer.
Question 8: A man standing on top of a tower sees a car coming towards the tower. If it takes 20 minutes for the angle of depression to change from 30° to 60°, what is the time remaining for the car to reach the tower?
A. 20√3 minutes
B. 10 minutes
C. 10√3 minutes
D. 5 minutes
Answer: 10 minutes
Explanation-
From the figure:-


tan 60° = h/b
equating the value of h from above two equation
⇒ a + b = 3b
⇒ 2b = a
⇒ b = a/2
Now since the car takes 20 minutes to travel a distance
Time taken to travel b = a/2 distance = 20/2 = 10 minutes
The question is "What is the time remaining for the car to reach the tower?"
Hence, the answer is 10 minutes
Choice B is the correct answer.
Question 9: A right angled triangle has a height ‘p’, base ‘b’ and hypotenuse ‘h’. Which of the following value can h2 not take, given that p and b are positive integers?
A. 74
B. 52
C. 13
D. 23
Answer: 23
Explanation-
We know that,
h2 = p2 + b2 Given, p and b are positive integer, so h2 will be sum of two perfect squares.
We see
a) 72 + 52 = 74
b) 62 + 42 = 52
c) 32 + 22 = 13
d) Can’t be expressed as a sum of two perfect squares
The question is "Which of the following value can h2 not take, given that p and b are positive integers? "
Hence, the answer is 23
Choice D is the correct answer.
Question 10: tan ∅ + sin ∅ = m, tan ∅ - sin ∅ = n, Find the value of m2- n2
A. 2√mn
B. 4√mn
C. m – n
D. 2mn
Answer: 4√mn
Explanation-
Adding the two equations,
tan ∅ =
Subtracting the same,
sin ∅ =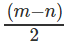
Since, there are no available direct formula for relation between sin∅ ∅tan∅ but we know that
cosec2 ∅ – cos2 ∅ = 1 
⇒ 
⇒((m2-n2))2 = 4(4mn)
⇒ m2 - n2 = 4√mn
The question is "To find the value of m2 - n2"
Hence, the answer is 4√mn
Choice B is the correct answer.
Question 11: A student is standing with a banner at the top of a 100 m high college building. From a point on the ground, the angle of elevation of the top of the student is 60° and from the same point, the angle of elevation of the top of the tower is 45°. Find the height of the student.
A. 35 m
B. 73.2 m
C. 50 m
D. 75 m
Answer: 73.2 m
Explanation-
Let BC be the height of the tower and DC be the height of the student.
In ∆ ABC
AB = BC cot 45°
AB = 100 x1
AB = 100 m ……………(i)
In rt. ∆ ABD
AB = BD cot 60°
AB = (BC + CD) cot 60°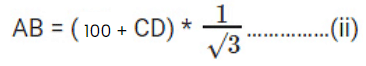
Equating (i) and (ii)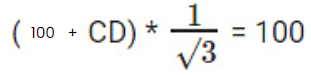
(100 + CD)= 100√3
CD = 100√3 – 100
= 10(1.732 – 1) = 100 * 0.732 = 73.2 m
The question is "To find the height of the student"
Hence, the answer is 73.2 m
Choice B is the correct answer.
Question 12: If Cos x – Sin x = √2 Sin x, find the value of Cos x + Sin x:
A. √2 Cos x
B. √2 Cosec x
C. √2 Sec x
D. √2 Sin x Cos x
Answer: √2 Cos x
Explanation-
Cos x – Sin x = √2 Sin x
⇒ Cos x = Sin x + √2 Sin x
⇒ Cos x = Sin x + √2 Sin x
⇒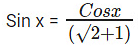
⇒ 
⇒ 
⇒ Sin x = (√2 - 1) Cos x
⇒ Sin x = √2 Cos x – Cos x
⇒ Sin x + Cos x = √2 Cos x
The question is "To find the value of Cos x + Sin x"
Hence, the answer is √2 Cos x
Choice A is the correct answer.
Question 13: 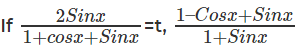 can be written as:
can be written as:
A. 1/t
B. t
C. √t Sec x
D. 
Answer. t
Explanation.

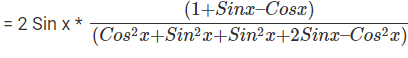
(Since, 1 = Cos2x + Sin 2x) 
The question is 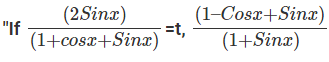 can be written as"
can be written as"
Hence, the answer is t
Choice B is the correct answer.
Question 14: A tall tree AB and a building CD are standing opposite to each other. A portion of the tree breaks off and falls on top of the building making an angle of 30°. After a while it falls again to the ground in front of the building, 4 m away from foot of the tree, making an angle of 45°. The height of the building is 6 m. Find the total height of the tree in meters before it broke.
A. 27√3 + 39
B. 12√3 + 10
C. 15√3 + 21
D. Insufficient Data
Answer: 15√3 + 21
Explanation-

Let the broken portion of tree AA’ be x. Hence A’C = A’G = x
From the figure, total height of the tree = x + y + 6
Consider triangle A’BG, tan 45° = 
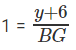
Or BG = y + 6
Consider triangle A’C’C, tan 30° = 

y√3 = y + 10 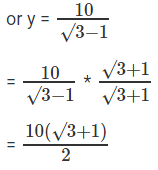
Therefore y = 5(√3 + 1)
Take sin 30° to find x
sin 30° = 
1/2 = y/x
or x = 2y
Height of the tree = x + y + 6
= 2 * 5(√3 + 1) + 5(√3 + 1) + 6
= 10√3 + 10 + 5√3 + 5 + 6
= 15√3 + 21 meters
Hence, the answer is 15√3 + 21
Choice C is the correct answer.
|
184 videos|131 docs|110 tests
|
FAQs on Trigonometry: Solved Examples - Quantitative Aptitude (Quant) - CAT
| 1. How do you find the sine of an angle in trigonometry? |  |
| 2. What is the cosine function used for in trigonometry? |  |
| 3. How do you calculate the tangent of an angle in trigonometry? |  |
| 4. What are the primary trigonometric functions? |  |
| 5. How is trigonometry used in real life applications? |  |

|
Explore Courses for CAT exam
|

|


















