Important Questions for Class 8 Maths - Practical Geometry
Question 1: Draw a rectangle PQRS in which PQ = 7.2 cm and QR = 5.4 cm.
Solution: Steps of construction:
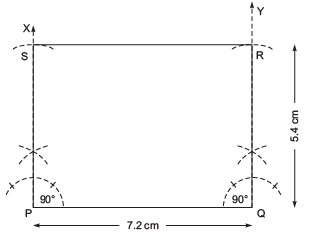
I. Draw a line segment PQ = 7.2 cm.
II. At P, draw such that ∠QPS = 90°.
such that ∠QPS = 90°.
III. From PX, cut off PS = 5.4 cm.
IV. At Q, draw such that ∠PQY = 90°.
such that ∠PQY = 90°.
V. From QY, cut off QR = 5.4 cm.
VI. Join R and S.
Thus, PQRS is the required rectangle.
Question 2: Draw a quadrilateral in which AB = 4.5 cm, BC = 5.1 cm, CD = 3.9 cm, ∠B = 90° and ∠C = 120°.

Solution: Steps of construction:
I. Draw a line segment AB = 4.5 cm.
II. At B, construct ∠ABX = 90°.
III. From cut off BC = 5.1 cm.
cut off BC = 5.1 cm.
IV. AT C, draw such that ∠BCY = 120°.
such that ∠BCY = 120°.
V. From , cut off CD = 3.9 cm.
, cut off CD = 3.9 cm.
VI. Join AD.
Thus, ABCD is the required quadrilateral
Question 3: Draw a square ABCD such that AB = 6.3 cm.
Solution: Steps of construction:
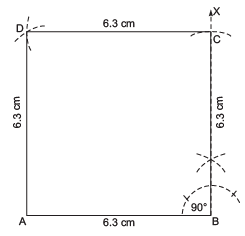
I. Draw  = 6.3 cm.
= 6.3 cm.
II. At B, draw  , such that ∠ABX = 90°.
, such that ∠ABX = 90°.
III. From  cut off BC = 6.3 cm.
cut off BC = 6.3 cm.
IV. With centre C and radius = 6.3 cm, draw an arc.
V. With centre A and radius = 6.3 cm, draw another arc to intersect the previous arc at D.
VI. Join DA and CD.
Thus, ABCD is the required square.
|
90 docs|16 tests
|
FAQs on Important Questions for Class 8 Maths - Practical Geometry
| 1. What is practical geometry? |  |
| 2. What are the basic tools used in practical geometry? |  |
| 3. How do you construct a perpendicular bisector? |  |
| 4. How do you construct an equilateral triangle? |  |
| 5. How do you measure the angles of a triangle using a protractor? |  |


















