Chapter 19 - Visualising Shapes (Part - 1), Class 8, Maths RD Sharma Solutions | RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Mathematics PDF Download
PAGE NO 19.9:
Question 1:
What is the least number of planes that can enclose a solid? What is the name of the solid?
ANSWER:
The least number of planes that can enclose a solid is 4.Tetrahedron is a solid with four planes (faces).
Question 2:
Can a polyhedron have for its faces:
(i) 3 triangles?
(ii) 4 triangles?
(iii) a square and four triangles?
ANSWER:
(i)No, because in order to complete a polyhedron, we need at least four triangular faces.
(ii)Yes, a polyhedron with 4 triangular faces is a tetrahedron.
(iii)Yes, with the help of a square bottom and four triangle faces, we can form a pyramid.
Question 3:
Is it possible to have a polyhedron with any given number of faces?
ANSWER:
Yes, it is possible to have a polyhedron with any number of faces.
The only condition is that there should be at least four faces.
This is because there is no possible polyhedron with 3 or less faces.
Question 4:
Is a square prism same as a cube?
ANSWER:
Yes, a square prism and a cube are the same.Both of them have 6 faces, 8 vertices and 12 edges.
The only difference is that a cube has 6 equal faces, while a square prism has a shape like a cuboid with two squarefaces, one at the top and the other at the bottom and with, possibly, 4 rectangular faces in between.
Question 5:
Can a polyhedron have 10 faces, 20 edges and 15 vertices?
ANSWER:
No, because every polyhedron satisfies Euler's formula, given below: F + V = E + 2
Here, number of faces F = 10
Number of edges E = 20
Number of vertices V = 15
So, by Euler's formula:
LHS: 10 + 15 = 25
RHS: 20 + 2 = 22,
which is not true because 25≠22
Hence, Eulers formula is not satisfied and no polyhedron may be formed.
Question 6:
Verify Euler's formula for each of the following polyhedrons: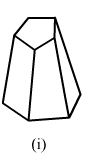
ANSWER:
(i)In the given polyhedron:Edges E = 15
Faces F = 7
Vertices V = 10
(i)In the given polyhedron:Edges E = 15
Faces F = 7
Vertices V = 10
Now, putting these values in Euler's formula:
LHS: F + V = 7 + 10 = 17
LHS: E + 2 = 15 + 2 = 17
LHS = RHS
Hence, the Euler's formula is satisfied.Now, putting these values in Euler's formula:
LHS: F + V = 7 + 10 = 17
LHS: E + 2 = 15 + 2 = 17
LHS = RHS
Hence, the Euler's formula is satisfied.
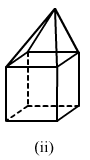
(ii)In the given polyhedron:Edges E = 16
Faces F = 9
Vertices V = 9
(ii)In the given polyhedron:Edges E = 16
Faces F = 9
Vertices V = 9
Now, putting these values in Euler's formula:
RHS: F + V = 9 + 9 = 18
LHS: E + 2 = 16 + 2 = 18
LHS = RHS
Hence, Euler's formula is satisfied.
Now, putting these values in Euler's formula:
RHS: F + V = 9 + 9 = 18
LHS: E + 2 = 16 + 2 = 18
LHS = RHS
Hence, Euler's formula is satisfied.
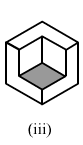
(iii)In the following polyhedron:Edges E = 21
Faces F = 9
Vertices V = 14
(iii)In the following polyhedron:Edges E = 21
Faces F = 9
Vertices V = 14
Now, putting these values in Euler's formula:
LHS: F + V = 9 + 14 = 23
RHS: E + 2 = 21 + 2 = 23
This is true.
Hence, Euler's formula is satisfied.Now, putting these values in Euler's formula:
LHS: F + V = 9 + 14 = 23
RHS: E + 2 = 21 + 2 = 23
This is true.
Hence,
Euler's formula is satisfied.
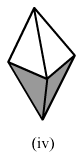
(iv)In the following polyhedron:Edges E = 8
Faces F = 5
Vertices V = 5
(iv)In the following polyhedron:Edges E = 8
Faces F = 5
Vertices V = 5
Now, putting these values in Euler's formula:
LHS: F + V = 5 + 5 = 10
RHS: E + 2 = 8 + 2 = 10
LHS = RHS
Hence, Euler's formula is satisfied.Now, putting these values in Euler's formula:
LHS: F + V = 5 + 5 = 10
RHS: E + 2 = 8 + 2 = 10
LHS = RHS
Hence, Euler's formula is satisfied.
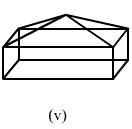
(v)In the following polyhedron:
Edges E = 16
Faces F = 9
Vertices V = 9(v)
In the following polyhedron:Edges E = 16
Faces F = 9
Vertices V = 9
Now, putting these values in Euler's formula:
LHS: F + V = 9 + 9 = 18
RHS: E + 2 = 16 + 2 = 18
LHS = RHS
Hence, Euler's formula is satisfied.
PAGE NO 19.10:
Question 7:
Using Euler's formula find the unknown:
| Faces | ? | 5 | 20 |
| Vertices | 6 | ? | 12 |
| Edges | 12 | 9 | ? |
ANSWER:
We know that the Euler's formula is: F + V = E + 2
(i) The number of vertices V is 6 and the number of edges E is 12.
Using Euler's formula:
F + 6 = 12 + 2
F + 6 = 14
F = 14 - 6
F = 8
So, the number of faces in this polyhedron is 8.
(ii)Faces, F = 5
Edges, E = 9.
We have to find the number of vertices.
Putting these values in Euler's formula:
5 + V = 9 + 25 + V = 11
V = 11 - 5
V = 6
So, the number of vertices in this polyhedron is 6.
(iii)Number of faces F = 20
Number of vertices V = 12
Using Euler's formula:
20 + 12 = E + 2
32 = E + 2
E + 2 = 32
E = 32 - 2
E = 30.
So, the number of edges in this polyhedron is 30.
FAQs on Chapter 19 - Visualising Shapes (Part - 1), Class 8, Maths RD Sharma Solutions - RD Sharma Solutions for Class 8 Mathematics
| 1. What are the different types of shapes that can be visualized in mathematics? |  |
| 2. How can visualizing shapes help in solving mathematical problems? |  |
| 3. What is the importance of visualizing shapes in real-life applications? |  |
| 4. How can one improve their ability to visualize shapes in mathematics? |  |
| 5. Are there any strategies or techniques to enhance visualization skills in mathematics? |  |





















