Class 9 Science: Sample Question Paper- 1 (With Solutions) PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Class IX |

|
| Science |

|
| Section - A |

|
| Section - B |

|
| Section - C |

|
| Section - D |

|
Class IX
Science
Max. Marks : 80
Duration : 3 hrs.
General Instructions:
Read the following instructions very carefully and strictly follow them :
1. The question paper comprises four sections A, B, C and D. There are 36 questions in the question paper. All questions are compulsory.
2. Section–A – question no. 1 to 20 - all questions and parts thereof are of one mark each. These questions contain multiple choice questions (MCQs), very short answer questions and assertion - reason type questions. Answers to these questions should be given in one word or one sentence.
3. Section–B – question no. 21 to 26 are short answer type questions, carrying 2 marks each. Answers to these questions should be in the range of 30 to 50 words.
4. Section–C – question no. 27 to 33 are short answer type questions, carrying 3 marks each. Answers to these questions should be in the range of 50 to 80 words.
5. Section–D – question no. 34 to 36 are long answer type questions carrying 5 marks each. Answer to these questions should be in the range of 80 to 120 words.
6. There is no overall choice. However, internal choices have been provided in some questions. A student has to attempt only one of the alternatives in such questions.
7. Wherever necessary, neat and properly labelled diagrams should be drawn.
Section - A
Q.1. Name the anion and cation that constitute the molecule of magnesium oxide. (1 Mark)
OR
Define atomic number. (1 Mark)
Ans. Magnesium oxide → MgO, Cation → magnesium (Mg2+), Anion → oxide (O2–).
OR
It is the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom.
Q.2. Name a non-metal that is tetra-atomic. (1 Mark)
Ans. Phosphorus.
Q.3. Which of the following are true for an element?
(i) Atomic number = number of protons + number of electrons
(ii) Mass number = number of protons + number of neutrons
(iii) Atomic number = number of protons = number of neutrons
(iv) Atomic number = number of protons = number of electrons
(a) (i) and (ii)
(b) (i) and (iii)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
Ans. (d)
Solution. Atomic number = Number of protons = Number of electrons in neutral atom. Mass number = Number of protons + Number of neutrons.
Q.4. How can we obtain different gases from air? (1 Mark)
Ans. By fractional distillation.
Q.5. What is the primary cause of marasmus? (1 Mark)
Ans. Primary cause of marasmus is protein deficiency.
Q.6. What is the unit of gravitational constant? (1 Mark)
OR
Give reason for the statement, “The value of g is greater at the poles than at the equator.” (1 Mark)
Ans. The unit of gravitational constant is Nm2 kg–2.
OR
At poles the radius of the earth is lesser than that at the equator.
Q.7. What is filtration? (1 Mark)
Ans. When the insoluble component is separated by filtering the solution through a medium or membrane it is called filtration.
Q.8. Write the names of the elements present in common salt. (1 Mark)
Ans. Sodium and chlorine
Q.9. At what place on the earth’s surface is the weight of a body minimum? (1 Mark)
Ans. At the equator
OR
What is centre of gravity of a body? (1 Mark)
Ans. The centre of gravity of a body is a point at which the resultant of all the parallel forces experienced by various particles of the body, due to attraction of earth, passes irrespective of the orientation of the body.
Q.10. Why did Rutherford select a gold foil in his alpha-ray scattering experiment? (1 Mark)
Ans. He selected a gold foil because it has high malleability.
Q.11. For the separation of what kind of solutes is the process of chromatography used? (1 Mark)
Ans. Chromatography is used for the separation of those solutes that dissolve in the same solvent.
OR
How can we separate cream from milk? (1 Mark)
Ans. By the process of centrifugation.
Q.12. Give an example of a uniformly accelerated motion. (1 Mark)
Ans. Motion of a free falling body.
OR
A person standing at A goes to B by following any of the paths 1, 2, or 3. Which path can we measure to find the average velocity? (1 Mark)
Ans. Since the displacement between A and B is the shortest distance, or displacement, between the two points, the average velocity can be determined from path 1.
Q.13. If the heater works 60 joules in one minute, what is its power? (1 Mark)
Ans. r = Work Done / Time Taken
P = 60 / 60 = 1 J/s = 1 Watt
For question numbers 14, 15 and 16, two statements are given- one labelled Assertion (A) and the other labelled Reason (R). Select the correct answer to these questions from the codes (a), (b), (c) and (d) as given below:
Q.14. Assertion: A 40 kg girl is running along a circular path of radius 1 m with a uniform speed. The work done by the girl is zero.
Reason: In this case, displacement is zero after one complete rotation.
(a) Both A and R are true, and R is correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) A is true, but R is false.
(d) A is false, but R is true.
Ans. (A)
Solution.
Since, displacement is zero after one complete rotation, so work done by the girl is zero.
Q.15. Assertion: Atomicity of ozone is three while that of oxygen is two.
Reason: Atomicity is the number of atoms constituting a molecule.
(a) Both A and R are true, and R is correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) A is true, but R is false.
(d) A is false, but R is true.
Ans. (a)
Solution. Atomicity is the number of atoms constituting a molecule. An oxygen molecule (written as O2) consists of 2 atoms of oxygen (O) and hence has an atomicity of 2. Similarly, an ozone molecule (O3) consists of 3 atoms of oxygen and has an atomicity of 3.
OR
Assertion: Relative atomic mass of the atom of element is the average masses of the atom as compared to 1/12th the mass of one carbon-12 atom.
Reason: Carbon-12 isotope is the standard reference for measuring atomic masses.
(a) Both A and R are true, and R is correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) A is true, but R is false.
(d) A is false, but R is true.
Ans. (b)
Solution. Carbon-12 is taken as standard reference because no other nuclides have exactly whole number.
Q.16. Assertion: Tuberculosis is an acute disease.
Reason: Disease that lasts for a short period is called acute disease.
(a) Both A and R are true, and R is correct explanation of the assertion.
(b) Both A and R are true, but R is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(c) A is true, but R is false.
(d) A is false, but R is true.
Ans. (d)
Solution. Tuberculosis is a chronic disease as it persists for a long time. Acute diseases, on the other hand, last for a short time and do not cause major health effects. e.g., common cold.
Q. No. 17 - 20 contain five sub-parts each. You are expected to answer any four sub parts in these questions.
Q.17. Read the following and answer any four questions from 17 (i) to 17 (v)
In order to overcome the objections raised against Rutherford’s model of the atom, Neil Bohr put forward the following postulates about the model of an atom. Only certain special orbits known as discrete orbits of electrons are allowed inside the atom. While revolving in discrete orbits the electrons do not radiate energy.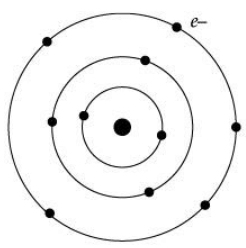 (i) Atoms are made up of _______ , _______ and _______.
(i) Atoms are made up of _______ , _______ and _______.
(a) electrons, protons, neutrons
(b) cations, anions, charges
(c) positive charges, negative charges, bonds
(d) ions, orbits, molecules
Ans. (d)
(ii) Who amended Rutherford’s shortcomings?
(a) Dalton
(b) Neil Bohr
(c) J.J. Thomson
(d) E. Goldstein
Ans. (b)
(iii) Name the number of electrons that K shell and L shell can accommodate.
(a) 8, 8 respectively.
(b) 2, 8 respectively.
(c) 1, 8 respectively.
(d) 5, 10 respectively
Ans. (c)
(iv) State True or False: Atomic mass of an element is the sum of the number of protons / electrons and neutrons.
(a) True
(b) False
Ans. (a)
(v) Where is the positive charge located inside the atom?
(a) Orbit
(b) Ion
(c) Nucleus
(d) Neutron
Ans. (c)
Q.18. Read the following and answer any four questions from 18 (i) to 18 (v).
Sanjana observed that when 3.0 gm of carbon is burnt in 8.0 gm of oxygen, 11.0 gm of carbon dioxide is produced. Based on the given information, answer the following questions.
(i) Explain the above result.
(a) It means carbon and oxygen are combined in the ratio of 3:8 to form carbon dioxide. Thus, when there is 3 gm carbon and 50 gm oxygen, then also only 8 gm of oxygen will be used and 11 gm of carbon dioxide will be formed. The remaining oxygen is not used.
(b) It means carbon and oxygen are combined in the ratio of 8:3 to form carbon dioxide. Thus, when there is 8 gm carbon and 50 gm oxygen, then also only 3 gm of oxygen will be used and 11 gm of carbon dioxide will be formed. The remaining oxygen is not used.
(c) It means carbon and oxygen are combined in the ratio of 3:8 to form carbon dioxide. Thus, when there is 8 gm carbon and 50 gm oxygen, then also only 3 gm of oxygen will be used and 11 gm of carbon dioxide will be formed. The remaining oxygen is not used.
(d) It means carbon and hydrogen are combined in the ratio of 3:8 to form carbon dioxide. Thus, when there is 3 gm carbon and 50 gm oxygen, then also only 8 gm of oxygen will be used and 11 gm of carbon dioxide will be formed. The remaining oxygen is not used.
Ans. (a)
(ii) Name the law of chemical combination will govern your answer?
(a) Law of mass conservation
(b) Law of definite proportions.
(c) Law of conservation of energy
(d) Law of inertia
Ans. (b)
(iii) What does this law say?
(a) All pure samples of a compound do not contain the same elements combined together in the same proportion by mass.
(b) The elements are always present in definite proportion by density in a chemical substance.
(c) The elements are always present in definite proportion by mass in a chemical substance. All pure samples of a compound contain the same elements combined together in the same proportion by mass.
(d) The elements may be present in definite proportion by volume in a chemical substance. All pure samples of a compound contain the same elements combined together in the same proportion by mass.
Ans. (c)
(iv) Which postulate of Dalton’s atomic theory is the result of law of conservation of mass?
(a) Atoms combine in the ratio of small whole numbers to form compounds.
(b) The relative number and kinds of atoms are constant in a given compound.
(c) Atoms of different elements have different masses.
(d) Atoms can neither be sub divided, created nor destroyed.
Ans. (d)
(v) Name one more compound which can be formed by combining carbon and oxygen.
(a) Carbon disulphide
(b) Carbon monoxide
(c) Methane
(d) Ethane
Ans. (b)
Q.19. Read the following and answer any four questions from 19 (i) to 19 (v).
Study the given figure and answer the following questions.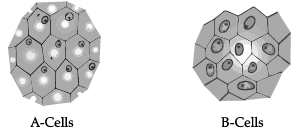 (i) Identify A and B cells.
(i) Identify A and B cells.
(a) A cells and B cells both are Turgid cells
(b) A cells and B cells both are Plasmolysed cells
(c) A cells –Plasmolysed cells, B cells – Turgid cells
(d) A cells – Turgid cells, B cells – Plasmolysed cells
Ans. (d)
(ii) What will happen if B cells are kept in hypotonic solution?
(a) B cells kept in hypotonic solution will remain as they are.
(b) B cells kept in hypotonic solution will become deplasmolysed if done so immediately after plasmolysis.
(c) B cells kept in hypotonic solution will get plasmolysed.
(d) B cells will not get turgid when kept in hypotonic solution
Ans. (b)
(iii) What will happen if A cells are kept in hypertonic solution?
(a) A cells kept in hypertonic solution will remain as they are.
(b) A cells kept in hypertonic solution will become turgid.
(c) A cells kept in hypertonic solution will become plasmolysed.
(d) A cells kept in hypertonic solution will become deplasmolysed.
Ans. (c)
(iv) What is isotonic solution?
(a) Isotonic solution: A solution that has less tonicity as another solution with which it is compared.
(b) Isotonic solution: A solution that has more tonicity as another solution with which it is compared.
(c) Isotonic solution: A solution that has zero tonicity as another solution with which it is compared.
(d) Isotonic solution: A solution that has the same tonicity as another solution with which it is compared.
Ans. (d)
(v) What is plasmolysis?
(a) Shrinkage of protoplast
(b) Swelling of protoplast
(c) Rupture of protoplast due to endosmosis
(d) Formation of protoplast due to endosmosis
Ans. (a)
Q.20. Read the following and answer any four questions from 20 (i) to 20 (v).
Study the given diagram and answer the following questions.
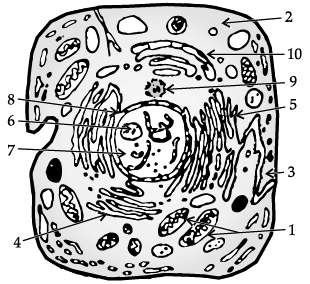
(i) Identify the given diagram
(a) Structure of animal cell
(b) Structure of plant cell
(c) Bacterial cell
(d) Prokaryotic cell
Ans. (a)
(ii) The function of part labelled as 1 is _________.
(a) Release of energy
(b) Protein synthesis
(c) Transmission of heredity characters
(d) Storage
Ans. (a)
(iii) Mention any two structures which are not found in above cell.
(a) Cell wall and ribosomes
(b) Cell wall and golgi apparatus
(c) Cell membrane and Golgi apparatus
(d) Plastids and cell wall
Ans. (d)
(iv) The organelle responsible for intracellular transport is
(a) 1
(b) 2
(c) 3
(d) 4
Ans. (d)
(v) Chromosomes are present in ______.
(a) Cell membrane
(b) Golgi apparatus
(c) Endoplasmic reticulum
(d) Nucleus
Ans. (d)
Section - B
Q.21. Write any two differences between physical and chemical changes. (2 Mark)
Ans.
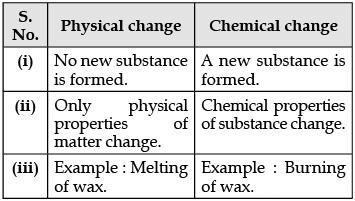 OR
OR
Calculate the number of aluminium ions present in 0.051 g of aluminium oxide [Atomic Mass of Al = 27 u] (2 Mark)
Ans.
Step I:
Gram molecular mass of Al2O3 = 2 × 27 + 3 × 16
= 102 g
∴ 102 g of Al2O3 = 1 mol
∴ 0.051 g of Al2O3 = 1 / 102 × 0.051 mol
= 0.0005 mol
Step II:
1 mol. of Al2O3 contain Al atom
= 2 × Avogadro No.
0.0005 mol of Al2O3 contain Al atoms
= 2 × 0.0005 × 6.022 × 1023
= 6.022 × 1020 atoms.
The number of Al ions (Al+3) present is the same as the number of Al atoms.
No. of Al3+ ions = 6.022 × 1020 ions.
Q.22. Draw a flowchart showing the separation of components of air. (2 Mark)
Ans. Air is a homogeneous mixture and can be separated into its components by the process of fractional distillation.
The flow diagram shows the steps of the process: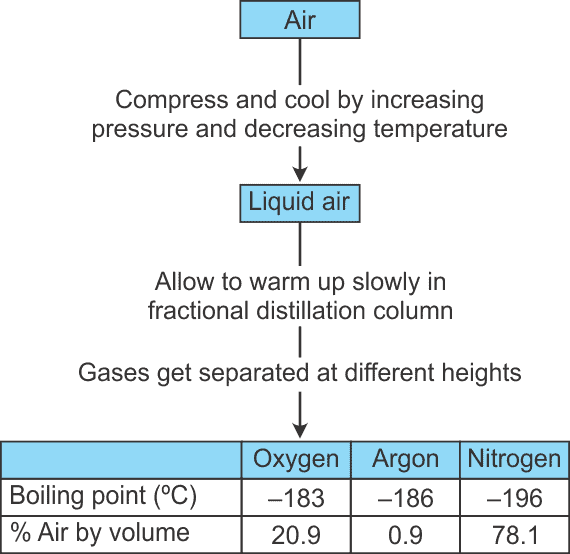
Q.23. Classify the following as pure substance or a mixture. If mixture, indicate whether homogeneous or heterogeneous .
(i) 24-carat gold
(ii) Air (2 Mark)
Ans.
(i) 24-carat gold is a pure substance.
(ii) Air is a homogeneous mixture in which the constituents are uniformly distributed throughout without any clear boundary of separation.
OR
Give two reasons to support the statement that CO2 is a compound and not a mixture. (2 Mark)
Ans.
(i) As compounds contain two or more elements combined in a fixed proportion, carbon and oxygen are present in a fixed ratio of 3:8 by mass in carbon dioxide.
(ii) As compounds can be broken down into simpler substances by chemical or electrochemical methods, the constituents of carbon dioxide cannot be separated by simple physical methods.
Q.24. A gun of mass 500 g fires a bullet of mass 10 g with a speed of 100 m/s. Find:(i) Initial momentum of ‘gun + bullet’.
(ii) Momentum gained by the bullet after firing. (2 Mark)
Ans. (i) Zero (both are at rest ).
(ii) Momentum gained by bullet.
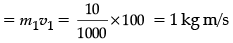
Q.25. Name three types of plastids found in plant cells and give one function of each. (2 Mark).
Ans. Chloroplast: Involved in the photosynthesis in plants.
Chromoplast: Impart attractive colours to flowers and fruits.
Q.26. Write the chemical formulae of: (2 Mark)
(i) Silver nitrate
(ii) Magnesium sulphate
(iii) Potassium carbonate
(iv) Barium chloride
Ans. (i) AgNO3
(ii) MgSO4
(iii) K2CO3
(iv) BaCl2
Section - C
Q.27. You are provided with mixture of camphor, common salt and soil. Using various techniques how will you separate the components of this mixture? Write the various steps involved. (3 Mark)
Ans. (i) First, heat the mixture. As camphor is sublimable, it will vapourize and so it can be separated through sublimation.
(ii) To separate mixture of common salt and soil, we will dissolve them in water. As salt is soluble in water, and soil is not soluble in water, soil can be separated through filtration.(iii) At the end, we get salt solution. Salt can be separated from water by evaporation.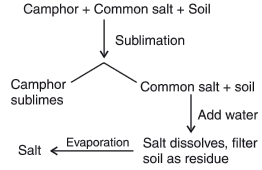
OR
Describe an activity with labelled diagram to obtain dye from blue ink. Name the component which gets evaporated. (3 Mark)
Ans.
- Fill half a beaker with water. Put a watch-glass on the top of the beaker. Add a few drops of blue ink on the watch-glass (as shown in the figure).
- Now, heat the beaker till a solid mass is obtained. You will observe that a solid residue of the dye is obtained in the watch-glass.
- Ink is a colloidal solution. It is a heterogeneous mixture of dye and water. Heating leads to the evaporation of water. This leaves behind the dye in the watch-glass.
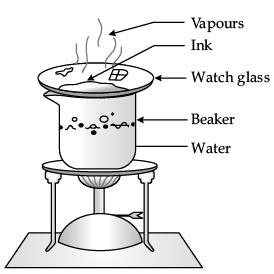 Q.28. What are the three limitations that hinder the approach to deal with infectious diseases? (3 Mark)
Q.28. What are the three limitations that hinder the approach to deal with infectious diseases? (3 Mark)
Ans.
The limitations are:
- Once a person has an infectious disease, his / her body functions are damaged and may never recover completely.
- This treatment will take time, so someone suffering from a disease is likely to be bedridden for some time.
- Person suffering from an infectious disease may spread this infection to other people acting as the source.
Q.29.
(i) You are given a mixture of mustard oil and water. Name the process that can be used to obtain mustard oil from the above mixture.
(ii) Draw a well labelled diagram of the above process. (3 Mark)
Ans.
(i) Process: Using separating funnel.
(ii) 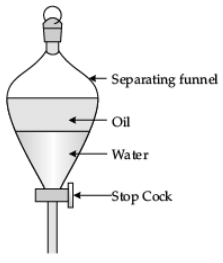 Q.30. Same drug does not work against the microbes belonging to different groups. Why? State the mechanism of antibiotics in killing bacteria. (3 Mark)
Q.30. Same drug does not work against the microbes belonging to different groups. Why? State the mechanism of antibiotics in killing bacteria. (3 Mark)
Ans. Every micro-organism has its own biochemical cycle. So one type of antibiotic can stop or block biochemical cycle of one type of microorganism only, but not all types of microorganisms. Antibiotic, destroy the cell wall during the asexual reproduction cycle; hence, the bacteria can be easily killed.
Q.31. Four persons jointly lift a 250 kg box to a height of 1 m and hold it.
(i) Calculate the work done by the persons in lifting the box.
(ii) How much work is done for just holding the box?
(iii) Why do they get tired while holding it ? (g = 10 ms–2) (3 Mark)
Ans. (i) F = 250 × 10 = 2500 N
s = 1 m
W = F × s = 2500 × 1
= 2500 J
(ii) Zero, as there is no displacement.
(iii) To hold the box, men are applying a force which is opposite and equal to the gravitational force acting on the box. While applying the force muscular effort is involved, and so they feel tired.
Q.32. A cyclist goes around a circular track of diameter 105 metres in 5 minutes. Calculate his speed. (3 Mark)
Ans. Here, diameter = 105 m, radius (r) = 105/2
Time taken t = 5 × 60 = 300 s
Speed, v = 2πr/t =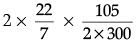 = 1.10 m/s
= 1.10 m/s
Q.33. Complete the given table : (3 Mark)
Ans. (a) Virus
(b) Female mosquito
(c) Cholera
(d) AIDS
(e) Sexual contact / Sharing of needles / blood transfusion / mother to infant.
(f) Air.
Section - D
Q.34. (i) Define kinetic energy. Derive an expression for the kinetic energy of an object.
(ii) The power of a motor pump is 5 kW. How much water per minute the pump can raise to height of 20 m? Take g = 10 ms–2. (5 Mark)
Ans.
(i) Energy possessed by a body by virtue of motion.
F = ma
W = F.s = energy
But v2 – u2 = 2 as or, as = 1/2 (v2 – u2)
Therefore, W = energy or, s = v2/2a
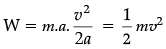
(ii) Energy = power × time = 5 kw × 1 min = 3 × 105 J
Therefore, mass of water drawn in 1 min,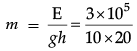
= 1.5 × 103 kg
Therefore, Volume of water = Mass / Density = 1.5 x 103 / 103
= 1.5 m3
Detailed Answer
(i) Let us take an equation of motion.
v2 – u2 = 2as
v2 – 0 = 2as
(As body starts from rest, u = 0)
a = v2/2s
F = ma =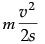
Work done = Kinetic energy
= F × s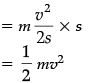
OR
(i) Define the work done by a constant force. Write its SI unit and define this unit.
(ii) A 3000 kg truck moving at a speed of 90 m/s stops after covering some distance. The force applied by brakes is 27000 N. Compute the distance covered and work done by this force. (5 Mark)
Ans. (i) Work is said to be done when a force acts on an object and the object covers some distance. Its SI unit is Joule.
One Joule: When a force of 1 N moves a body through a distance of 1 meter in its own direction.
(ii) u = 90 m/s; v = 0; F = – 27000 N; m = 3000 kg
F = ma
a = F / m
= – 27000 / 3000
= – 9 m/s2
Also v2 – u2 = 2as,
02 – (90)2 = 2(–9)s
s = 450 m
W = F × s
= – 27000 × 450
= – 12150000 J
= – 12150 kJ
– ve sign shows retarding force.
Q.35. (a) State Newton’s first law of motion.
(b) Look at the diagrams given below and state in which case will the block move and in which direction? Give reasons to support your answer. (5 Mark)
Ans. (a) A body continues to be in a state of rest or in state of uniform motion along a straight line unless an external force is applied on it to change the state.
(b) Case (ii) Right to left due to unbalanced force.
Q.36. What is meant by ‘inertia’? What are different types of inertia? Give two examples in each case. (5 Mark)
OR
Give statement for Newton’s second law of motion. Deduce a mathematical formulation for it. Using above derived expression, calculate the force exerted by a nail on the hammer of mass 500 g moving at 5.0 m/s striking it. Consider that the nail stops the hammer in a short time of 0.01 s. (5 Mark)
Ans. Inability of the body to change by itself its state of rest or state of uniform motion is called inertia.
Types: Inertia of rest : e.g. :
(i) When a card is flicked with a finger the coin placed over it falls in the tumbler.
(ii) Only the carom coin at the bottom of a pile is removed when a fast-moving carom striker hits it.
Inertia of motion : e.g. :
(i) When a moving bus stops suddenly, the luggage might slide towards the front side of the bus and fall.
(ii) We tend to fall forward when a bus suddenly stops.
OR
(i) Newton’s 2nd law of motion states that the force acting on a body is directly proportional to the product of its mass and acceleration produced by it in the body.
(ii) The rate of change of momentum of a body is directly proportional to the force applied on it and the change takes place in the direction of applied force.
Mathematical derivation : If the force ‘F’ changes its velocity from u to v in time t, then rate of change of momentum can be written as =
(mv - mu) / t = m(v - u) / t
This is equal to the force applied on the body by second law = m(v - u) / t
Hence, F = ma
m = 500, g = 0.5 kg, u = 5 m/s,
v = 0, t = 0.01 s
Acceleration of hammer = (0 - 5) / 0.01
a = – 500 m/s2
Force applied by the nail on hammer
f = ma = 0.5 × (– 500)
= – 250 N.
FAQs on Class 9 Science: Sample Question Paper- 1 (With Solutions)
| 1. What is the format of Class 9 Science Sample Question Paper- 1? |  |
| 2. How many sections are there in the Class 9 Science exam? |  |
| 3. What is the recommended class for this question paper? |  |
| 4. Are there any solutions provided for the sample question paper? |  |
| 5. How many meaningful Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) are provided in this article? |  |




















