Playing with Numbers Class 6 Notes Maths
Factors and Multiples
FactorsThe numbers which exactly divides the given number are called the Factors of that number.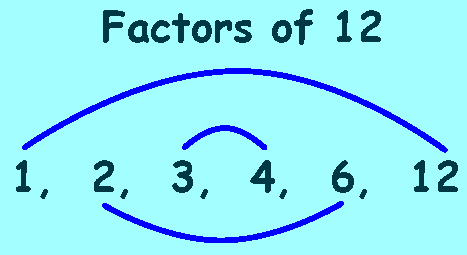 As we can see that we get the number 12 by
As we can see that we get the number 12 by
1 × 12, 2 × 6, 3 × 4, 4 × 3, 6 × 2 and 12 ×1
Hence,
1, 2, 3, 4, 6 and 12 are the factors of 12.
The factors are always less than or equal to the given number.
Multiples
If we say that 4 and 5 are the factors of 20 then 20 is the multiple of 4 and 5 both.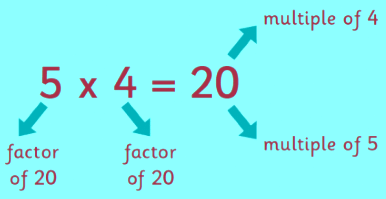
For Example:
List the multiples of 3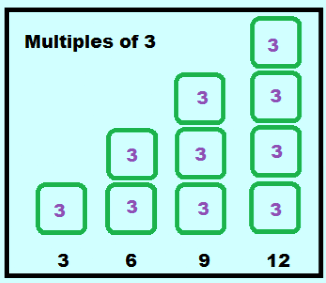
Multiples are always more than or equal to the given number.
Some facts about Factors and Multiples
- 1 is the only number which is the factor of every number.
- Every number is the factor of itself.
- All the factors of any number are the exact divisor of that number.
- All the factors are less than or equal to the given number.
- There are limited numbers of factors of any given number.
- All the multiples of any number are greater than or equal to the given number.
- There are unlimited multiples of any given numbers.
- Every number is a multiple of itself.
Perfect Number
If the sum of all the factors of any number is equal to the double of that number then that number is called a Perfect Number.
Perfect Number | Factors | Sum of all the factors |
6 | 1, 2, 3, 6 | 12 |
28 | 1, 2, 4, 7, 14, 28 | 56 |
496 | 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 31, 62, 124, 248, 496 | 992 |
Prime and Composite Numbers
Prime NumbersThe numbers whose only factors are 1 and the number itself are called the Prime Numbers.
Like 2, 3, 5, 7, 11 etc.
Composite Numbers
All the numbers with more than 2 factors are called composite numbers or you can say that the numbers which are not prime numbers are called Composite Numbers.
Like 4, 6, 8, 10, 12 etc.
Remark: 1 is neither a prime nor a composite number.
Even and Odd Numbers
All the multiples of 2 are even numbers. To check whether the number is even or not, we can check the number at one's place. If the number at ones place is 0,2,4,6 and 8 then the number is even number.
The numbers which are not even are called Odd Numbers.
Remark: 2 is the smallest even prime number. All the prime numbers except 2 are odd numbers.
Tests for Divisibility of Numbers
1. Divisibility by 2: If there are any of the even numbers i.e. 0, 2, 4, 6 and 8 at the end of the digit then it is divisible by 2.
Example: Check whether 63 is divisible by 2 or not.
Sol: The last digit of 63 is 3 i.e. odd number so 63 is not divisible by 2.
2. Divisibility by 3: A given number will only be divisible by 3 if the total of all the digits of that number is multiple of 3.
Example: Check whether 2400 is divisible by 3 or not.
Sol: The sum of the digits of 2400 i.e. 2 + 4 + 0 + 0 = 6, which is the multiple of 3 so 2400 is divisible by 3.
3. Divisibility by 4: We have to check whether the last two digits of the given number are divisible by 4 or not. If it is divisible by 4 then the whole number will be divisible by 4.
Example Check the number 23436 is divisible by 4 or not.
Sol: The last two digits of 23436 are 36 which are divisible by 4, so 23436 are divisible by 4.
4. Divisibility by 5: Any given number will be divisible by 5 if the last digit of that number is ‘0' or ‘5'.
Example: Check whether 6300 is divisible by 5 or not.
Sol: The last digit of 6300 is 0 so it is divisible by 5.
5. Divisibility by 6: Any given number will be divisible by 6 if it is divisible by 2 and 3 both. So we should do the divisibility test of 2 and 3 with the number and if it is divisible by both then it is divisible by 6 also.
Example: Check the number 342341 is divisible by 6 or not.
Sol: 342341 is not divisible by 2 as the digit at ones place is odd and is also not divisible by 3 as the sum of its digits i.e. 3 + 4 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 1 = 17 is also not divisible by 3.Hence 342341 is not divisible by 6.
6. Divisibility by 7: Any given number will be divisible by 7 if we double the last digit of the number and then subtract the result from the rest of the digits and check whether the remainder is divisible by 7 or not. If there is a large number of digits then we have to repeat the process until we get the number which could be checked for the divisibility of 7.
Example: Check the number 2030 is divisible by 7 or not.
Sol: Given number is 2030
- Double the last digit, 0 × 2 = 0
- Subtract 0 from the remaining number 203 i.e. 203 – 0 = 203
- Double the last digit, 3 × 2 = 6
- Subtract 6 from the remaining number 20 i.e. 20 - 6 = 14
- The remainder 14 is divisible by 7 hence the number 203 is divisible by 7.
7. Divisibility by 8: We have to check whether the last three digits of the given number are divisible by 8 or not. If it is divisible by 8 then the whole number will be divisible by 8.
Example: Check whether the number 74640 is divisible by 8 or not.
Sol: The last three digit of the number 74640 is 640. As the number 640 is divisible by 8 hence the number 74640 is also divisible by 8.
8. Divisibility by 9: Any given number will be divisible by 9 if the total of all the digits of that number is divisible by 9.
Example: Check whether 6390 is divisible by 9 or not.
Sol: The sum of the digits of 6390 is 6 + 3 + 9 + 0 = 18 which is divisible by 9 so 6390 is divisible by 9.
9. Divisibility by 10: Any given number will be divisible by 10 if the last digit of that number is zero.
Example: Check the number 123 and 2630 are divisible by 10 or not.
Sol:
- The ones place digit is 3 in 123 so it is not divisible by 10.
- The ones place digit is 0 in 2630 so it is divisible by 10.
Common Factors and Common Multiples
Example 1: What are the common factors of 25 and 55?
Sol: Factors of 25 are 1, 5.
Factors of 55 are 1, 5, 11.
Common factors of 25 and 55 are 1 and 5.
Example 2: Find the common multiples of 3 and 4.
Sol:
Common multiples of 3 and 4 are 0, 12, 24 and so on.
Co-prime Numbers
If 1 is the only common factor between two numbers then they are said to be Co-prime Numbers.
Example: Check whether 7 and 15 are co-prime numbers or not.
Sol: Factors of 7 are 1 and 7.
Factors of 15 are 1, 3, 5 and 15.
The common factor of 7 and 15 is 1 only. Hence they are the co-prime numbers.
Prime Factorisation
Prime Factorisation is the process of finding all the prime factors of a number.
There are two methods to find the prime factors of a number-
1. Prime factorisation using a factor tree
We can find the prime factors of 70 in two ways.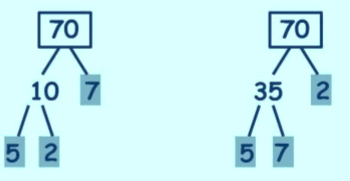
The prime factors of 70 are 2, 5 and 7 in both the cases.
2. Repeated Division Method
Find the prime factorisation of 64 and 80.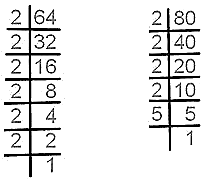
The prime factorisation of 64 is 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 2.
The prime factorisation of 80 is 2 × 2 × 2 × 2 × 5.
Highest Common Factor (HCF)
The highest common factor (HCF) of two or more given numbers is the greatest of their common factors. Its other name is (GCD) Greatest Common Divisor.
Method to find HCF
To find the HCF of given numbers, we have to find the prime factorisation of each number and then find the HCF.
Example: Find the HCF of 60 and 72.
Sol: First, we have to find the prime factorisation of 60 and 72.
Then encircle the common factors.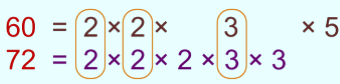 HCF of 60 and 72 is 2 × 2 × 3 = 12.
HCF of 60 and 72 is 2 × 2 × 3 = 12.
Lowest Common Multiple (LCM)
The lowest common multiple of two or more given number is the smallest of their common multiples.
Methods to find LCM
1. Prime Factorisation Method: To find the LCM we have to find the prime factorisation of all the given numbers and then multiply all the prime factors which have occurred a maximum number of times.
Example: Find the LCM of 60 and 72.
Sol: First, we have to find the prime factorisation of 60 and 72.
Then encircle the common factors.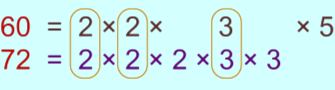
To find the LCM, we will count the common factors one time and multiply them with the other remaining factors.
LCM of 60 and 72 is 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 3 × 5 = 360
2. Repeated Division Method: If we have to find the LCM of so many numbers then we use this method.
Example: Find the LCM of 105, 216 and 314.
Sol: Use the repeated division method on all the numbers together and divide until we get 1 in the last row.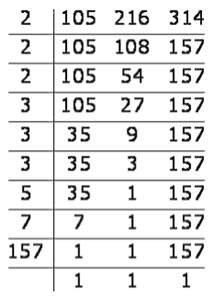 LCM of 105,216 and 314 is 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 3 × 3 × 5 × 7 × 157 = 1186920
LCM of 105,216 and 314 is 2 × 2 × 2 × 3 × 3 × 3 × 5 × 7 × 157 = 1186920
Solved Examples
Example 1: There are two containers having 240 litres and 1024 litres of petrol respectively. Calculate the maximum capacity of a container which can measure the petrol of both the containers when used an exact number of times.
Sol: As we have to find the capacity of the container which is the exact divisor of the capacities of both the containers, i. e. maximum capacity, so we need to calculate the HCF.
The common factors of 240 and 1024 are 2 × 2 × 2 × 2.
Thus, the HCF of 240 and 1024 is 16.
Therefore, the maximum capacity of the required container is 16 litres.
Example 2: What could be the least number which when we divide by 20, 25 and 30 leaves a remainder of 6 in every case?
Sol: As we have to find the least number so we will calculate the LCM first.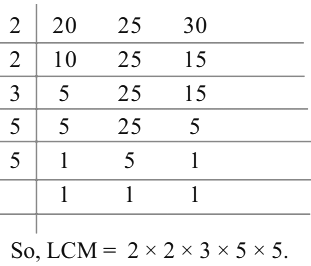
LCM of 20, 25 and 30 is 2 × 2 × 3 × 5 × 5 = 300.
Here 300 is the least number which when divided by 20, 25 and 30 then they will leave remainder 0 in each case. But we have to find the least number which leaves remainder 6 in all cases.
Hence, the required number is 6 more than 300.
The required least number = 300 + 6 = 306.
|
151 videos|223 docs|60 tests
|
FAQs on Playing with Numbers Class 6 Notes Maths
| 1. What are prime and composite numbers? |  |
| 2. How do you find the Highest Common Factor (HCF) of two numbers? |  |
| 3. What is the Lowest Common Multiple (LCM) and how do you calculate it? |  |
| 4. What are the tests for divisibility of numbers? |  |
| 5. How can prime factorization be used to find HCF and LCM? |  |

















