NCERT Exemplar Solutions: Chemical Effects of Electric Current | Science Class 8 PDF Download
Multiple Choice Questions
Q.1. An electric current can produce
(a) heating effect only.
(b) chemical effect only.
(c) magnetic effect only.
(d) chemical, heating, and magnetic effects.
Ans: d
Solution: Electric current causes a chemical reaction when it passes through a conducting solution. This is a chemical effect of electric current.
When an electric current passes through the bulb. Its filament gets heated and bulb starts glowing. This is the heating effect of electric current.
When an electric current is passed through a circuit it produces a magnetic field around it. This is the magnetic effect of electric current.
Q.2. Boojho and Paheli performed experiments taking similar bulbs and cells but two different solutions A and B as shown in Fig.14.1.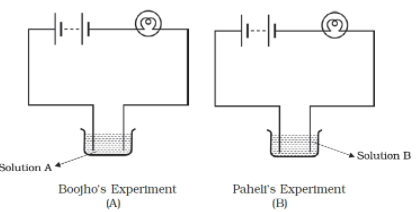
They found that the bulb in the setup A glows more brightly as compared to that of the setup B. You would conclude that
(a) higher current is flowing through the circuit in setup A.
(b) higher current is flowing through the circuit in setup B.
(c) equal current is flowing through both the circuits.
(d) the current flowing through the circuits in the two setups cannot be compared in this manner.
Ans: a
Solution: Higher current is flowing through the circuit in setup A because solution A is a good conductor of electricity compared to solution B.
Q.3. Boojho’s uncle has set up an electroplating factory near his village. He should dispose of the waste of the factory
(a) in the nearby river.
(b) in the nearby pond.
(c) in the nearby cornfield.
(d) according to the disposal guidelines of the local authority.
Ans: d
Solution: Waste disposal is a major concern in the electroplating industry as it causes water pollution and releases a hazardous chemical into water bodies. Hence it should be disposed of according to guidelines of the local authority.
Q.4. When an electric current is passed through a conducting solution, there is a change of colour of the solution. This indicates
(a) the chemical effect of current.
(b) the heating effect of current.
(c) the magnetic effect of current.
(d) the lightning effect of current.
Ans: a
Solution: Conducting a solution through electric current cause’s chemical reaction. This causes a change in colour and this is the chemical effect of electric current.
Q.5. Which one of the following solutions will not conduct electricity?
(a) lemon juice
(b) vinegar
(c) tap water
(d) vegetable oil
Ans: d
Solution: Vegetable oil does not contain ions hence it cannot conduct electricity.
Q.6. Which of the following metals is used in electroplating to make objects appear shining?
(a) iron
(b) copper
(c) chromium
(d) aluminium
Ans: c
Solution: Chromium metal is used in electroplating to make objects appear shining because chromium has shining property and is scratch resistant.
Q.7.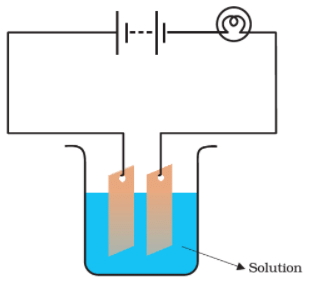
Which of the following solutions will not make the bulb in Fig 14.2 glow?
(a) sodium chlorides
(b) copper sulphate
(c) silver nitrate
(d) sugar solution in distilled water
Ans: d
Solution: The sugar solution is neither acidic nor basic and it cannot ionize to conduct electricity. Similarly, distilled water has no ions in it to conduct electricity. Hence the mixture of sugar solution and distilled water will not conduct electricity.
Very Short Answer Questions
Q.8. Fill in the blanks
(a) The object to be electroplated is taken as ______ electrode.
(b) One of the most common applications of chemical effect of electric current is ______ .
(c) Small amount of a mineral salt present naturally in water makes it a ______ of electricity.
(d) Electroplating of ______ is done on objects like water taps and cycle bell to give them a shiny appearance.
Ans: (a) Cathode
(b) Electroplating
(c) Conductor
(d) Chromium
Q.9. Why is a layer of zinc-coated over iron?
Ans: Iron readily reacts with atmospheric air to form rust. In order to prevent it from rusting zinc is coated over iron.
Q.10. Will the solution of sugar in distilled water conduct electricity?
Ans: No, the sugar solution is neither acidic nor basic and it cannot ionize to conduct electricity.
Q.11. Name the effect of current responsible for the glow of the bulb in an electric circuit.
Ans: Heating effect of electric current.
Short Answer Questions
Q.12. Boojho made the circuit given in Fig. 14.3 and observed that the bulb did not glow. On Paheli’s suggestion, he added one more cell in the circuit. The bulb now glows. Explain.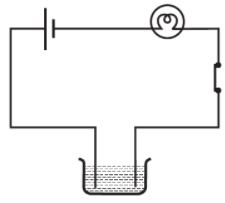
Ans: On adding another cell current flows through bulb sufficiently to make it glow.
Q.13. Paheli set up an experiment using liquid A in the beaker as shown in Fig. 14.4. She observed that the bulb glows. Then she replaced the liquid A by another liquid B. This time the bulb did not glow. Boojho suggested replacing the bulb by an LED. They observed that the LED glows. Explain.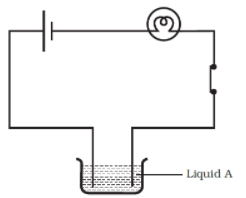
Ans: Current flowing through liquid B may be weak to make the bulb glow whereas it was strong enough to make the LED glow.
Q.14. Paheli wants to deposit silver on an iron spoon. She took a silver nitrate (AgNO3) solution in a beaker and set up a simple circuit for electroplating. Which terminal of the battery should the spoon be connected to? What material should the other electrode be made of?
Ans: The spoon should be connected to the negative terminal of the battery. The other electrode should be made of silver.
Q.15. Why is tin electroplated on iron to make cans used for storing food?
Ans: Tin is less reactive than iron. In order to prevent iron from reacting with food, tin is coated over iron for storing food.
Q.16. Observe Fig. 14.5.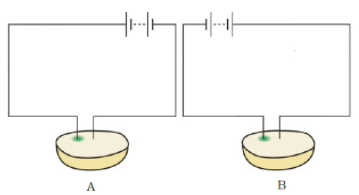
Which of these two circuits A or B shows the correct observation?
Ans: Diagram A shows the correct observation
Q.17. Observe the following circuits carefully. In which circuit will the bulb glow. Write ‘Yes’ or ‘No’ in the blank space provided along each of the circuit given in Fig. 14.6.
Ans: No
Yes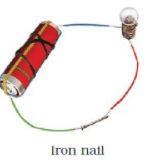
No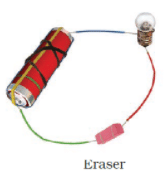
Yes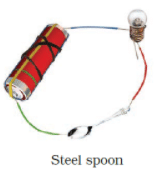
Long Answer Questions
Q.18. An electric current is passed through a conducting solution. List any three possible observations.
Ans: Three possible observations are
- Bubbles of gas may be formed on the electrodes.
- Deposits of metal may be seen on electrodes.
- Change in the colour of the solution may take place
- The solution may get heated.
Q.19. In the circuit given as Fig. 14.7, Boojho observed that copper is deposited on the electrode connected to the negative terminal of the battery. Paheli tried to repeat the same experiment. But she could find only one copper plate. Therefore she took a carbon rod as a negative electrode. Will copper be still deposited on the carbon rod? Explain your answer.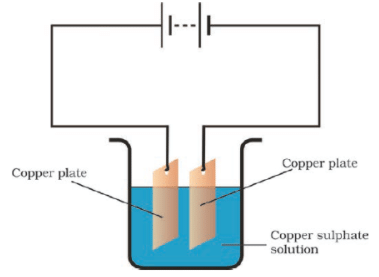
Ans: Copper from the copper sulphate solution will be deposited on the carbon rod. Copper sulphate dissociates into copper and sulphate when the electric current is passed through the copper sulphate solution. The free copper gets drawn to the electrode connected to the negative terminal of the battery, i.e. carbon rod and gets deposited on it. Thus, Paheli will obtain a coating of copper on carbon rod.
Q.20. Observe the circuit given in Fig. 14.8.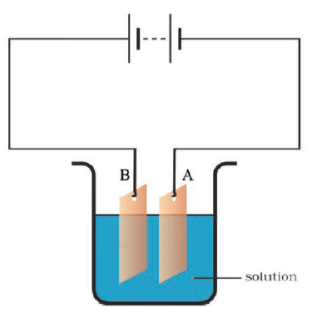
Boojho set up this circuit for purification of copper. What will be the nature of – (i) plate A (ii) plate B (iii) the solution? Explain the process of purification.
Ans: (i) In plate A- Pure copper
(ii) In plate B- Impure copper
(iii) The solution – Copper sulphate solution
Process of purification here is Electroplating.
Take copper sulphate and two copper plates of size around 10 cm × 4 cm. Take 250 mL of distilled water in a clean and dry beaker. Dissolve two teaspoonfuls of copper sulphate in it. Add a few drops of dilute sulphuric acid to copper sulphate solution to make it more conducting. Clean copper plates with sandpaper. Now rinse them with water and dry them. Connect the copper plates to the terminals of a battery and immerse them in copper sulphate solution.
When an electric current is passed through the copper sulphate solution, copper sulphate dissociates into copper and sulphate. The free copper gets drawn to the electrode connected to the negative terminal of the battery and gets deposited on it.
Q.21. Observe the following circuit given in Fig. 14.9.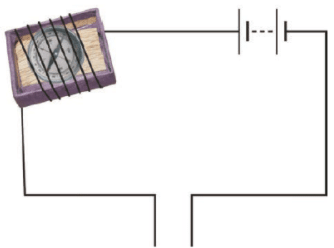
Current does not flow in the circuit if there is a gap between the two wires. Does it indicate that air is a poor conductor of electricity? Does air never conduct electricity? Explain.
Ans: Generally, air is a bad conductor of electricity. But in certain conditions like lightening air conducts electricity.
Q.22. Boojho made the circuit shown in Fig. 14.10. He wanted to observe what happens when an electric current is passed through water. But he forgot to add a few drops of lemon juice to water. Will it make any difference to his observations? Explain.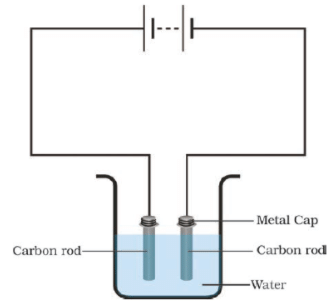
Ans: If the water is distilled water then without lemon juice it cannot conduct electricity and current will not pass through the circuit. If the water is salty then a feeble current will pass through circuits and bubbles will be observed on the negative electrode.
Q.23. Observing that the bulb does not glow in the circuit shown in Fig. 14.11 A, Boojho changed the circuit as shown in Fig 14.11 B. He observed deflection in the magnetic compass.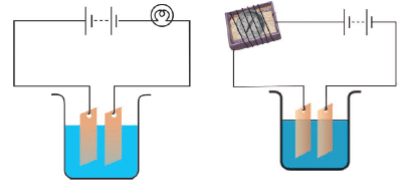
(i) What does the deflection in the magnetic compass indicate?
(ii) Why did the bulb not glow in Fig14.11 A?
(iii) What would be the effect of an increase in the number of turns in the coil wound around the magnetic compass in Fig. 14.11B?
(iv) What will be observed if the number of cells is increased in the circuit shown in Fig. 14.11B?
Ans: (i) It indicates the presence of current in the circuit.
(ii) The bulb did not glow because the current was not sufficient to make it glow.
(iii) Deflection in the magnetic compass will increase.
(iv) Deflection in the compass will increase further.
Q.24. You are provided with a magnetic compass, an empty matchbox, a battery of two cells and connecting wires. Using these objects how will you make a tester for testing an electric circuit? Draw the necessary circuit diagram and explain.
Ans: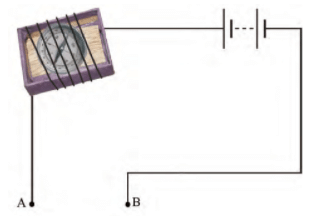 Magnetic compass needle shows deflection when current flows through the circuit. This is due to the magnetic effect of current.
Magnetic compass needle shows deflection when current flows through the circuit. This is due to the magnetic effect of current.
|
90 videos|273 docs|44 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar Solutions: Chemical Effects of Electric Current - Science Class 8
| 1. What are the chemical effects of electric current? |  |
| 2. How does an electric current cause chemical changes? |  |
| 3. What is electrolysis? |  |
| 4. How is electrolysis used in real-life applications? |  |
| 5. What is the role of electrodes in the chemical effects of electric current? |  |


















