NCERT Exemplar Solutions: Fibre to Fabric | Advance Learner Course: Science Class 6 PDF Download
Multiple Choice Questions
Q.1. The rearing of silkworms for obtaining silk is called
(a) cocoon
(b) silk
(c) sericulture
(d) silviculture
Ans: c
Explanation:
Breeding and management of silkworms for obtaining silk are called sericulture.
Q.2. Which of the following is not a type of silk?
(a) Mulberry silk
(b) Tassar silk
(c) Mooga silk
(d) Moth silk
Ans: d
Explanation:
Mulberry silk, Tasar Silk and Mooga silk are the varieties of silk produced by different silkworms whereas Moth silk is not a variety of silk.
Q.3. Paheli wanted to buy a gift made of animal fibre obtained without killing the animal. Which of the following would be the right gift for her to buy?
(a) Woollen shawl
(b) Silk scarf
(c) Animal fur cap
(d) Leather jacket
Ans: a
Explanation:
Obtained from wool which does not require the killing of animals. Wool is obtained from hairs of sheep, yak, camel, goat, etc. Silk is obtained after killing silkworm, Animal fur cap is obtained from fur which requires the killing of an animal. A leather jacket is obtained from the skin of animals which needs killing of animals.
Q.4. The silk fibre is obtained from
(a) fleece of sheep
(b) cotton ball
(c) cocoon
(d) shiny jute stalk
Ans: c
Explanation:
Silk is a fibre obtained from the cocoons of silkworms.
Q.5. A wool fibre cannot be obtained from which of the following?
(a) Goat
(b) Llama
(c) Alpaca
(d) Moth
Ans: d
Explanation:
Wool can be obtained from animals like sheep, goat, camel, yak, rabbit, etc. A moth is a type of insect.
Q.6. Selective breeding is a process of
(a) selecting the offsprings with desired properties.
(b) selecting the parents with desired properties.
(c) selecting an area for breeding.
(d) selecting fine hair for good quality wool.
Ans: b
Explanation:
Selective breeding is the process of the crossing of two selected varieties having different traits to produce a hybrid having good traits of both, e.g., some breeds of sheep possess only soft under-hair.
Q.7. The general process that takes place at a sheep shearing shed is
(a) removal of fleece.
(b) separating the hair of different textures.
(c) washing of sheep fibre to remove grease.
(d) rolling of sheep fibre into yarn.
Ans: a
Explanation:
Removal of fleece from sheep is known as shearing. Shearing will be done manually by razors or by shearing machines.
Q.8. The term sericulture is used for
(a) culture of bacteria.
(b) rearing of the silkworm.
(c) making silk fabric from silk yarn.
(d) production of sarees.
Ans: b
Explanation:
Breeding and management of silkworms for obtaining silk are called sericulture.
Q.9. Reeling of silk is
(a) a process of making silk reels.
(b) the spinning of silk fibres.
(c) the weaving of silk cloth.
(d) the process of taking silk threads from the cocoon.
Ans: d
Q.10. Silkworms secrete fibre made of
(a) fat
(b) cellulose
(c) protein
(d) nylon
Ans: c
Explanation:
A salivary gland of silkworm releases a protein which is used as silk.
Very Short Answer Questions
Q.1. Fill in the blanks in the following statements.
(a) _________ and _________ fibres are obtained from animals.
(b) Silk fibres come from _________ of silk _________.
(c) Wool yielding animals bear _________ on their body.
(d) Hair trap a lot of _________, which is a poor _________ of heat.
Ans:
(a) Silk and Wool fibres are obtained from animals.
(b) Silk fibres come from cocoons of the silk moth.
(c) Wool yielding animals bear hair on their body.
(d) Hair trap a lot of air, which is a poor conductor of heat.
Q.2. State whether the following statements are True or False. If false, correct them.
(a) Silkworms are caterpillars of the silk moth.
(b) In India, camels and goats are generally reared for obtaining wool.
(c) The rearing of silkworms for obtaining silk is called silviculture.
(d) In the process of obtaining wool from fleece, sorting is done after scouring.
(e) Yak hair is not used to make woollen fabric.
Ans:
- True
- False- In India, sheep are reared for obtaining wool.
- False- The rearing of silkworms for obtaining silk is called sericulture
- True
- False- Yak hair is used to make woollen fabric.
Q.3. How does the hair of certain animals help in keeping their bodies warm?
Ans: Hair are bad conductors of heat, hence they will not allow the escape of heat from the body, which ensures their bodies are kept warm.
Short Answer Questions
Q.1. Match the items of Column I with the items given in Column II.
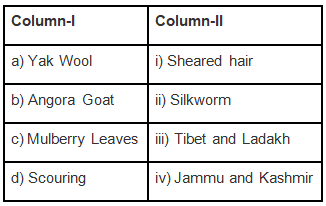
Ans:
Q.2. Various steps involved to obtain wool from fleece are given here.
(i) Picking out the burrs
(ii) Dyeing in various colours
(iii) Shearing
(iv) Scouring
(v) Sorting
Write the above steps in the correct sequence in which they are carried out.
Ans:
(iii) Shearing
(iv) Scouring
(v) Sorting
(i) Picking out the burrs
(ii) Dyeing in various colours
Q.2. Some words related to silk are jumbled up. Write them in their correct form.
(a) TURECULRISE
(b) WILSMORK
(c) BELMURRY
(d) RINGLEE
Ans:
(a) sericulture
(b) silkworm
(c) mulberry
(d) reeling
Q.3.Figure shows three rings of circles with letters in them. Some of these letters in each ring can form the name of one wool yielding animal. Find the names of these animals.
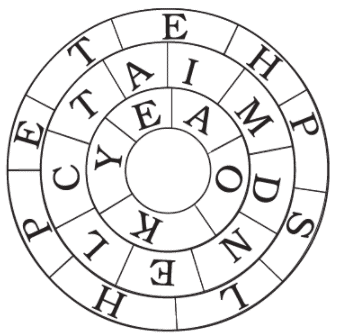
Ans:
Yak, Camel, Sheep
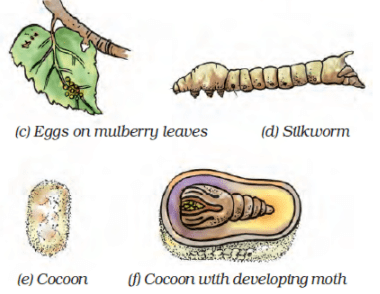
18. Write a caption for each of the figures given as Figure (a–d).
(a)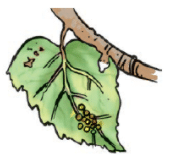
(b)
(c)
(d)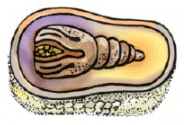
Ans:
a) Eggs of silk moth on mulberry leaves
b) Silkworm
c) Cocoon
d) Cocoon with developing moth
Q.3. Steps for the production of silk are given below in a jumbled order. Arrange them in their proper sequence.
(a) Eggs are warmed to a suitable temperature for the larvae to hatch from eggs.
(b) Fibers are taken out from the cocoon.
(c) After 25 to 30 days, the caterpillars stop eating and start spinning cocoons.
(d) The larvae/caterpillars or silkworms are kept in clean trays along with freshly chopped mulberry leaves.
(e) Female silk moths lay eggs.
(f) Cocoons are kept under the sun or boiled in water.
Ans:
(e) Female silk moths lay eggs.
(a) Eggs are warmed to a suitable temperature for the larvae to hatch from eggs.
(d) The larvae/caterpillars or silkworms are kept in clean trays along with freshly chopped mulberry leaves.
(c) After 25 to 30 days, the caterpillars stop eating and start spinning cocoons.
(f) Cocoons are kept under the sun or boiled in water.
(b) Fibers are taken out from the cocoon.
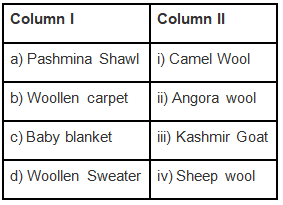
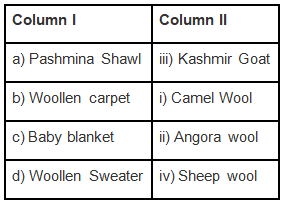
Q.4. A wholesale woollen fibre dealer gets the woollen fibre of different textures sorted for various purposes. Match the items in Column I with the woollen fibre in Column II.
Ans:
Long Answer Questions
Q.1. Complete the paragraph related to the life history of silk moth by filling in the blanks. The ____(a)___ silk moth lays ___(b)___, from which hatch ____(c)___ called ___(d)____ or ___(e)____. They grow in size and when the caterpillar is ready to enter the next stage of its life history called ___(f)____, it first weaves a covering to hold itself, which is known as ___(g)____.
Ans:
The a) female silk moth lays b) eggs, from which hatch c) larvae called d) caterpillars or e) silkworms. They grow in size and when the caterpillar is ready to enter the next stage of its life history called f) pupa, it first weaves a covering to hold itself, which is known as g) cocoon.
Q.2. Paheli went to the market to buy sarees for her mother. She took out a thread from the edge of the two sarees shown by the shopkeeper and burnt them. One thread burnt with a smell of burning hair and the other burnt with the smell of burning paper. Which thread is from a pure cotton saree and which one from a pure silk saree? Give a reason for your answer.
Ans: A thread which burns with the smell of burning paper is of cotton because both paper and cotton are cellulose which is carbohydrate and hence they burn with similar odour. Similarly, the thread which is burnt with the smell of burning hair is silk because silk, as well as hair, are proteins hence they burn with a similar characteristic smell.
Q.3. Explain the phrase – “Unity is Strength” on the basis of the making of fabric from the fibre.
Ans: Fabric is made of a thin hair-like strand called fibres. It is easy to break a fibre thread as it is fragile and easy to break as well. On the other hand, fabric is the accumulation of many fibre threads which are hard to break and needs an enormous amount of energy to break the fabric. Hence, based on making of fabric from fibre it is said that unity is strength.
Q.4. Write various steps for processing fibres into wool.
Ans:
Step I: The fleece of the sheep along with a thin layer of skin is removed from its body [Figure (a)]. This process is called shearing. Machines similar to those used by barbers are used to shave off hair. Usually, hair is removed during the hot weather. This enables sheep to survive without their protective coat of hair. The hair provides woollen fibres. Woollen fibres are then processed to obtain woollen yarn. Shearing does not hurt the sheep just as it does not hurt when you get a hair cut or your father shaves his beard. Do you know why? The uppermost layer of the skin is dead. Also, the hair of sheep grows again just as your hair does.
Step II: The sheared skin with hair is thoroughly washed in tanks to remove grease, dust and dirt. This is called scouring. Nowadays scouring is done by machines [Fig. (b) and (c)].
Step III: After scouring, sorting is done. The hairy skin is sent to a factory where the hair of different textures is separated or sorted.
Step IV: The small fluffy fibres, called burrs, are picked out from the hair. These are the same burrs which sometimes appear on your sweaters. The fibres are scoured again and dried. This is the wool ready to be drawn into fibres.
Step V: The fibres can be dyed in various colours, as the natural fleece of sheep and goats is black, brown or white.
Step VI: The fibres are straightened, combed and rolled into yarn. The longer fibres are made into wool for sweaters and the shorter fibres are spun and woven into woollen cloth.
Q.5. Describe the life history of silk moth with the help of figures of various stages.
Ans:
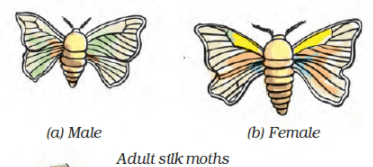
|
26 videos|32 docs|9 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Exemplar Solutions: Fibre to Fabric - Advance Learner Course: Science Class 6
| 1. What is the process of converting fibres into fabric called? |  |
| 2. What are natural fibres? |  |
| 3. How are synthetic fibres different from natural fibres? |  |
| 4. What are the advantages of using synthetic fibres? |  |
| 5. What are the different methods of obtaining fibres from plants? |  |
|
26 videos|32 docs|9 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for Class 6 exam
|

|

















