Numerical Problems (Solved): Force and Newton's Law of Motion | Science Class 9 PDF Download
Q1: A cricket ball of mass 70 g moving with a velocity of 0.5 m s-1 is stopped by player in 0.5 s. What is the force applied by player to stop the ball?
Sol. Here m = 70 g = 0.070 kg; u = 0.5 m s-1; v = 0; t = 0.5 s 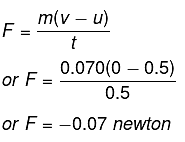
Q2: What will be acceleration of a body of mass 5 kg if a force of 200 N is applied to it?
Sol. Here m = 5 kg; F = 200 N
F = ma or a = F/m 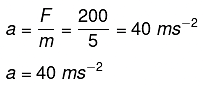
Q3: A bullet of mass 10 g is fired from a rifle. The bullet takes 0.003 s to move through its barrel and leaves with a velocity of 300 ms-1. What is the force exerted on the bullet by the rifle?
Sol. Here m = 10 g = 0.010 kg ; u = a ; v = 300 m s-1
t = 0.003 s, F = ?
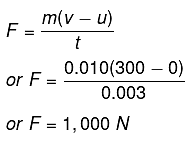
Q4: What force would be needed to produce an acceleration of 1 ms-2 on a ball of mass 1 kg?
Sol. Here m = 1 kg; a = 1 ms-2 ; F = ?
Now F = m a = 1 × 1
or F = 1 newton.
Q5: What is the acceleration produced by a force of 5 N exerted on an object of mass 10 kg?
Sol. Here F = 5 N; m = 10 kg; a = ?
Now F = ma o
a = 0.5 ms-2
Q6: How long should a force of 100 N act on a body of 20 kg so that it acquires a velocity of 100 ms-1?
Sol. Here v _ u = 100 m s-1, m = 20 kg; F = 100 N ;t = ?
We know
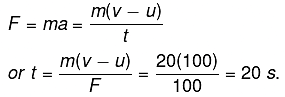
Q7: Which would require greater force: accelerating a 10 g mass at 5 m s_2 or 20 g mass at 2 m s-2?
Sol. In first case m1 = 10 g = kg = 0.010 kg;
Now a1 = 5 ms-2 ; F1 = ?
F1 = m1a1 = 0.010 × 5
F1 = 0.050 newton
In second case, m2 = 20 g =0.020 kg
or m2 = 0.020 kg
a2 = 2 m s-2 ; F2 = ?
Now F2 = m2a2 = 0.020 × 2
or F2 = 0.04 newton
We find that F1 > F2, hence more force is required to accelerate 10 g at 5 m s-2 than accelerating 20 g at 2 ms-2.
Q8: A force of 5 N gives a mass m1, an acceleration of 8 ms-2 and a mass m2, an acceleration of 24 m s-2. What acceleration would it give if both the masses are tied together?
Sol. Let us first find mass m1 and m2.
F = m1 a1
5 =m1 (8) or m1 = 5/8 kg
F = m2 a2
5 = m2 (24) or m2 = 5/24 kg
Total mass M = m1 + m2
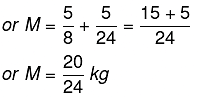
Let A be the acceleration produced in mass M.
F = MA
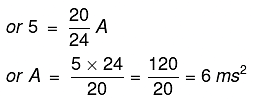
Hence the acceleration of the combination is 6 ms-2.
Q9: If 1000 N force is required to accelerate an object to the rate of 5m/s2, what will be the weight of the object?
Sol: According to question
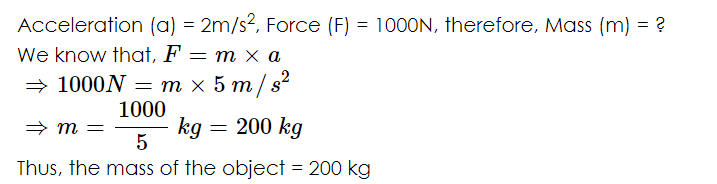
Q10: After applying a force of 1000 N an object of mass 2000 kg will achieve what acceleration?
Sol:
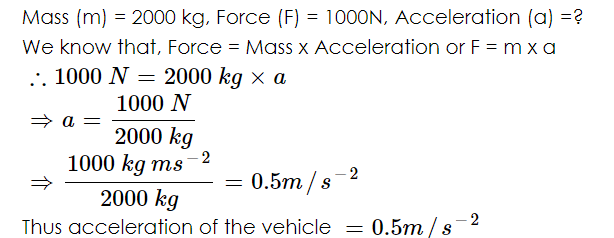
|
88 videos|369 docs|67 tests
|
FAQs on Numerical Problems (Solved): Force and Newton's Law of Motion - Science Class 9
| 1. What is the relationship between force and Newton's Law of Motion? |  |
| 2. How can you calculate the force acting on an object? |  |
| 3. What are the different types of forces that can act on an object? |  |
| 4. How does Newton's third law of motion relate to force? |  |
| 5. Can a force act on an object without causing it to accelerate? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|


















