Types of Combustion - Class 8 PDF Download
Combustion and Flame:
Types of Combustion: -
Combustion can be divided into three types – rapid combustion, spontaneous combustion and explosion.
 Fig: Types of combustion.Rapid Combustion:
Fig: Types of combustion.Rapid Combustion:
Combustion in which a substance burns rapidly and produces heat and flame is known as rapid combustion, such as combustion of natural gas, LPG, petrol etc. This is usually attained by introducing external heat. Substances which undergo rapid combustion have lower ignition temperature.
Spontaneous Combustion:
When a substance suddenly starts burning into a flame; without the supply of any external cause (such as heating; the combustion is called spontaneous combustion. Substances; which have relatively low temperature of ignition generally burn by spontaneous combustion.
Examples:
- Phosphorous and sulphur start burning instantaneously; at room temperature.
- Haystacks, linseed oil, coal, pyrite, etc. sometimes start burning suddenly with flame because of increase in temperature.
- In coal mines, fire breaks out many a times because of combustion of coal dust.
- Fire often breaks out suddenly because of increase in temperature due to sun or friction.
 Fig: Explosion.
Fig: Explosion.
Explosion: -
When combustion is accompanied by sudden production of heat, sound and large amount of gas, it is called explosion. Firecrackers and bombs are substances which show explosion.
Flame
All substances do not give flame while burning. Substances which vapourise while burning give flame and those which do not vapourise while burning do not give flame.
Fuels which burnt with flame are used to produce light.
 Fig: Flame.
Fig: Flame.
Example –
Kerosene, wax, wood, etc. burn with flame as they vapourise during burning.
Coal and coke do not vaporize while burning and hence do not produce flame.
Structure of flame
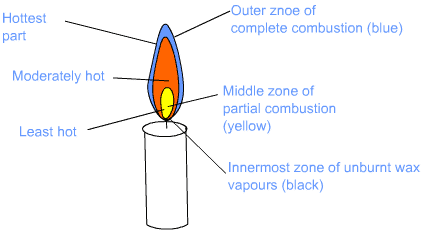
Flame can be divided into three zones – innermost zone, middle zone and outer zone
Innermost zone: Zone near the wick of a candle is called the innermost zone of the flame. The innermost zone is the zone of unburnt wax and is generally of black colour. It is the least hot zone.
Middle zone: Zone in the middle of the flame is called the middle zone. Middle zone of flame is moderately hot and of yellowish colour. In this zone, fuel burns partially. Middle zone is the luminous zone, because partial combustion of carbon produces glow.
Middle zone produces black deposits of unburnt carbon particles.
Outer zone: Outer zone of flame is of bluish colour and the hottest part of the flame. In this zone, fuel is completely burnt. Because of complete combustion, it gives bluish colour.
Fuel
All combustible materials are not considered as fuel. Charcoal, wood, LPG, cowdung cake, natural gas, petrol, diesel, kerosene etc. are known as fuel.
Criteria for ideal fuel:
- Easily and readily available
- Cheap
- Burns easily in air at moderate rate
- Produces large amount of heat
- Burns completely and does not leave any undesirable substance after burning.
- Substances which meet above criteria are known as ideal fuel. But ideal fuel is not available in practical life.
- Fuels which meet most of the criteria are considered as good fuel.
Fuel efficiency:
- Efficiency of a fuel is measured by its calorific value.
- Calorific value is the amount of heat produced by the complete burning of 1 kg of fuel. And hence calorific value of fuel is expressed in kilo joule per kg (k J/kg).
- A fuel with higher calorific value is considered as an efficient fuel.

Burning of Fuel Produces Harmful Products
Since, no fuel is considered as an ideal fuel, thus they do not undergo complete combustion and produce unwanted substances. These substances have harmful effect on the humans and the environment. Some of the harmful effects of burning of fuel are as follows:
(a) Fuels; like, wood, petrol, diesel, coal, etc. release unburnt carbon particles. These unburnt carbon particles create pollution by mixing in air. They lead to diseases of respiratory system and many other related diseases.
 Fig: Wood Fuel.
Fig: Wood Fuel.
(b) Incomplete combustion of carbon fuels produces carbon monoxide. Carbon monoxide is a poisonous gas which may kill a person.
(c) Most of the fuels release carbon dioxide gas. Excess carbon dioxide gas in the atmosphere leads to global warming.
(d) Burning of coal and diesel produce sulphur dioxide. Burning of petrol gives oxide of nitrogen. When these gases mix with rainwater, acids are formed. These acids fall along with rainwater and this is called acid rain. Acid rain is harmful for animals and plants. Acid rain is also harmful for buildings and monuments. The famous Taj Mahal has lost much of its sheen because of acid rain.
CNG is considered as a cleaner fuel. It releases harmful products in very small amount. Now-a-days CNG is being used to run vehicles in many towns, such as Delhi, Ahmadabad and Mumbai. This has helped in reducing the level of pollution.
FAQs on Types of Combustion - Class 8
| 1. What are the types of combustion? |  |
| 2. What is rapid combustion? |  |
| 3. What is spontaneous combustion? |  |
| 4. What is explosive combustion? |  |
| 5. What is the importance of understanding types of combustion? |  |

|
Explore Courses for Class 8 exam
|

|


















