Class 8 Exam > Class 8 Notes > Social Studies (SST) Class 8 > Short Notes - Resources
Class 8 Geography Chapter 1 Notes - Resources
| Table of contents |

|
| Resource |

|
| Types Of Resources |

|
| Conservation Of Resources |

|
| Flow Learning |

|
| Words that Matter |

|
Resource
Any substance, living being or service that has utility (i.e. can help us in any possible way) is said to be a resource.
- A resource has some value. The value can be associated with money (i.e. you have to pay money to get it), or just mental satisfaction (e.g. when you look at a beautiful painting or scenery, it feels pleasant, so the painting or scenery has utility).
- Examples of resources include books, stationery material, clothes, utensils, furniture, your teacher, school, rivers, water, electricity, and so on.
- The economic value of a resource may change with time.
- A substance may or may not be a resource depending on our knowledge. If we do not know how to write with a pen, then certainly the pen has no utility for us. So in this case the pen is not a resource. However, for those who know how to use a pen, it is a resource. So technology, ideas, knowledge, inventions, discoveries, etc. make a substance a resource.
- Time may also be a factor involved in making a substance a resource. Water has always been there, but its utility to manufacture electricity was not always known. When people realised that water can be used to produce electricity, water became a resource in a new way.
 Resources
Resources
Types Of Resources
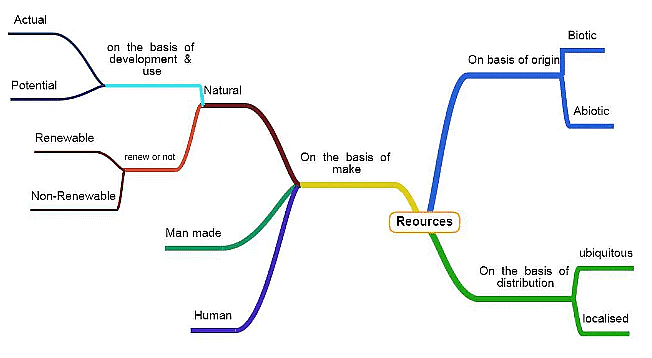
Resources may be natural, human, or human-made.
Natural Resources
- Natural resources are those that are taken from nature. They are used without modifying them, i.e. in the same form as they exist in. Rivers, lakes, air, soils, minerals, trees, mountains, etc. are natural resources.
 Natural Resources
Natural Resources - On the basis of level of development of resource, a natural resource can be actual or potential.
- An actual resource is one which is used currently. We know their quantity. Examples are: coal deposits.
- A potential resource is one whose utility is not known at present or is not used despite having utility; instead it may be useful at some time in future. It means that it has the potential to have utility, although it does not have any today. Examples include uranium deposits in Ladakh.
- On the basis of origin, a resource can be abiotic or biotic.
- A biotic resource is one that has life. Examples: plants and animals.
- An abiotic resource is non-living. Examples: light, air, furniture, books.
 Biotic and Abiotic Resources
Biotic and Abiotic Resources
- Natural resources may also be classified as renewable and non-renewable.
- A renewable resource can be used without any risk of its ending up. They exist in unlimited quantity, for example, solar energy and wind energy. On the other hand, use of non-renewable resources need to be controlled since once they end up, they cannot be renewed. Examples: coal, petroleum.
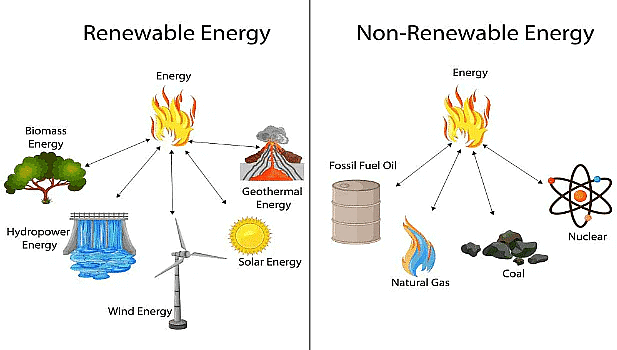 Renewable and Non-renewable Resources
Renewable and Non-renewable Resources
- On the basis of distribution, a resource can be ubiquitous or localised. A ubiquitous resource is found everywhere, like air.
- A localised resource is, however, found in certain parts of the world only, like we cannot find coal everywhere.
Human-made Resources
- Human-made resources have not been provided to us by nature.
- Human beings have used their intelligence to manufacture them for their own use. Examples include vehicles, buildings, roads, telephone, etc.
Human Resources
- Human resources include people who serve us in any way. Your teacher, doctor, carpenter, cobbler, etc. are human resources.
- Human resource development refers to the improvement of people’s skills so that they become more useful than before and are a better resource.
Conservation Of Resources
- Resource conservation is the concept of using resources carefully so that they do not end up quickly. The future generations also need the resources, but if we keep using them at a fast pace, they may end up, thus posing problems for the future.
- We should use resources in such a balanced way that we satisfy our needs as well as conserve them for the future. This concept is called sustainable development.
- We can contribute to sustainable development by switching off lights when not needed, by recycling things and using them again, and in many more ways.

Flow Learning
Words that Matter
- Utility- A substance has utility if it can be used in any possible way to satisfy our needs.
- Value- Worth of a substance assessed on the basis of utility.
- Patent- It applies to the exclusive right over any idea or invention.
- Resource- Any substance having utility in any way is a resource.
- Technology- The application of the latest knowledge and skills in doing or making things is called technology.
- Natural Resource- Natural resources are those that are taken from nature.
- Actual Resource- An actual resource is one which is used currently and whose quantity is known.
- Potential Resource- A potential resource is one whose utility is not known at present or is not used despite having utility; instead it may be useful at some time in future.
- Abiotic Resource- An abiotic resource is a non-living resource
- Biotic Resource- A biotic resource is a living resource.
- Renewable Resource- A renewable resource can be used without any risk of its ending up because they exist in unlimited quantity.
- Non-renewable Resource- A non-renewable resource is one which is present in limited quantity.
- Ubiquitous Resource- A ubiquitous resource is one that is found everywhere.
- Localised Resource- A resource that is found only in certain parts of the world and not everywhere.
- Human-made Resource- Resources invented by human beings by using their intelligence are called human made resources.
- Human Resources- A human being who can contribute to his family, society, or economy is called a human resource.
- Human Resource Development- Human resource development refers to the improvement of people’s skills so that they become more useful than before and are a better resource.
- Stock of Resource- The amount of resource available for use is called its stock.
- Resource Conservation- Resource conservation is the concept of using resources carefully so that they do not end up quickly.
- Sustainable Development- It is the concept of using resources in a balanced way so that our purpose is solved, as well as they are also conserved for the future.
The document Class 8 Geography Chapter 1 Notes - Resources is a part of the Class 8 Course Social Studies (SST) Class 8.
All you need of Class 8 at this link: Class 8
|
65 videos|424 docs|46 tests
|
FAQs on Class 8 Geography Chapter 1 Notes - Resources
| 1. What are the different types of resources? |  |
Ans. There are four types of resources: natural resources, human resources, capital resources, and entrepreneurship resources. Natural resources include air, water, soil, minerals, plants, and animals. Human resources refer to the people who contribute their skills and labor. Capital resources are man-made tools and equipment used in production, such as machinery and buildings. Entrepreneurship resources involve the skills and creativity of individuals who start and manage businesses.
| 2. What is conservation of resources? |  |
Ans. Conservation of resources refers to the responsible use and management of natural resources to ensure their sustainability for future generations. It involves reducing waste, practicing recycling, using renewable energy sources, and adopting sustainable practices. Conservation efforts aim to protect and preserve the environment, prevent resource depletion, and promote a more sustainable way of living.
| 3. What is flow learning? |  |
Ans. Flow learning is an educational approach that emphasizes experiential and hands-on learning. It involves immersing students in real-life experiences and actively engaging them in the learning process. Flow learning encourages students to explore, experiment, and discover knowledge through direct experiences. It aims to promote deep understanding, critical thinking, and a lifelong love for learning.
| 4. What are words that matter in the context of resources? |  |
Ans. In the context of resources, "words that matter" refer to key concepts, terms, or ideas that are essential for understanding and discussing the topic. These words help to convey important information, facilitate effective communication, and enable individuals to grasp the significance of resources. Examples of words that matter in the context of resources include conservation, sustainability, renewable, depletion, and management.
| 5. How can we conserve resources in our daily lives? |  |
Ans. There are several ways to conserve resources in our daily lives. We can reduce energy consumption by turning off lights and appliances when not in use, using energy-efficient lighting and appliances, and insulating our homes. Conserving water can be achieved by fixing leaks, taking shorter showers, and using water-saving devices. Recycling and composting can help reduce waste and conserve natural resources. Finally, practicing mindful consumption, such as buying only what is necessary and opting for sustainable products, can also contribute to resource conservation.

|
Explore Courses for Class 8 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
Related Searches



















