Nutrition, Digestion | Science & Technology for State PSC Exams - BPSC (Bihar) PDF Download
Food. It is a mixture of certain chemicals that removes hunger and gives a feeling of strength to work, to build tissue and to store energy.
The food has six components:
1. Carbohydrates
2. Protein
3. Fats
4. Water
5. Minerals
6. Vitamins
Sources of Carbohydrates
 Different sources of carbohydrates
Different sources of carbohydrates
- The carbohydrates are obtained from wheat, rice, potato, banana, sugar, gur, tapoica, honey and jaggery.
- Excess of carbohydrates are stored in the liver and in the muscles as glycogen.
- The energy is stored in the body in the form of Adenosine triphosphate (A.T.P.).
- The various sources of fats are in the form of ground nuts, cashew nut, butter, ghee, meat, egg and milk.
Categories of Carbohydrates:
Monosaccharides—glucose, fructose, galactose.
Disaccharides—maltoes, lactose, sucrose.
Polysaccharides—starch and glycogen.
Effects of abnormal intake of carbohydrates. If the food is deficient in carbohydrates, the body becomes weak and less active. The wrinkles appear on the outer surface and the development of internal tissues of the body gets also affected. The excess intake of carbohydrates causes diarrhoea, diabetes and obesity.
Proteins: Proteins are organic compounds of higher molecular weight formed of amino acids. Egg, meat, fish, pulses specially soyabean and milk are the sources of protein.
Malnutrition. The diet which does not meet the require-ments of an individual is called malnutrition.
Balanced diet. Proportions of proteins, fats, carbohydrates, salts, water and vitamins needed to meet the nutritional requirement of the organism.
Glycogenesis. It is the conversion of glucose into glycogen in the liver.
Glyconeogenesis. It is the conversion of excess amino acids into carbohydrates in the liver.
Basal metabolic rate. The minimum amount of energy required by the body for beating of the heart, circulation of blood, breathing and the regulation of body temperature is termed as basal metabolic rate or BMR.
Factors that affect of BMR
Body size and composition
Age and growth
State of nutrition
Climate
Different types of amino acids
The amino acids are of two types:
(i) Essential amino acids
(ii) Non-essential amino acids
The amino acids which are not synthesised by the body, though vital for the maintenance of the body are essential amino acids. These are present in milk, meat, egg and soyabean. The amino which are synthesised in the human body are called non-essential amino acids.
Different functions of fats Different sources of fat
Different sources of fat
These are important food storage compounds. The fat is stored in adipose tissues. Phospholipids form cell membrane and enzyme system in mitochondria. The oxidation of fats yields large amount of energy to body cell. The fats protect the body from the effects of cold. The animal fats are the sources of vitamin A and D.
Vitamins. The term vitamin was coined by Funk. They are required for normal growth and maintenance. Their presence in the food is very essential because many of them cannot be synthesized by the body.
Saturated Fats. The fats which do not have any double bonds between the carbons of the molecular chain are known as saturated fats. They are solid at room temperature e.g., palmitic, stearic acid and vanaspati ghee.
Unsaturated Fats. These are the fats containing one or more double bonds between the carbons of the chain. They have generally low melting point, e.g., groundnut oil, olive oil and mustard oil.
- The high saturated fats are solid at room temperature.
- They get deposited in the arteries walls and cause the obstruction of normal blood flow.
- This leads to high blood pressure and heart diseases like arteriosclerosis (blockage of artery), and coronory attack.
Roughage
The roughage is generally constituted by indigestible plant cellulose. Our food should have some roughage material because it helps in retaining water, adds bulk to the food and prevents constipation. Roughage are required to maintain proper digestive system.
 Food rich in roughage
Food rich in roughage
The important source of roughage in our food are salad, vegetables, fruits with stems, corn cob (bhutta), and half-broken wheat (dalia).
The diet of an individual depends on the special needs. For example, the pregnant women require extra quantity of amino acids, calcium, iron and sufficient vitamins to carry out healthy building processes for developing child in their womb. The amino acids are essential for tissue growth, calcium for bones and iron for blood.
A developing child upto the age of 12, requires more diet as compared to his body weight. He needs surplus supply of protein, calcium, iron, vitamin D and C to build healthy body. Mother’s milk contains sufficient amino acids and fatty acids for the tissue growth of the baby. Also it supplies the baby with active protective antibodies to fight against the diseases.
Factors which leads to loss of nutrient value
Deep frying or prolonged heating results in loss of nutrients and vitamins. Some water-soluble vitamins like vitamin C are lost when they are soaked in water for long period.
Vitamins C are oxidised when fruits and vegetables are left out for long time. Some grains lose their nutrients when they are washed. The husked pulses and cereals are more nutritious than dehusked ones. Faulty cooking method may also lead to loss of nutrients. Endemic nutritional deficiencies may occur due to biological factors or geographical factors.
Digestion:
Absorption
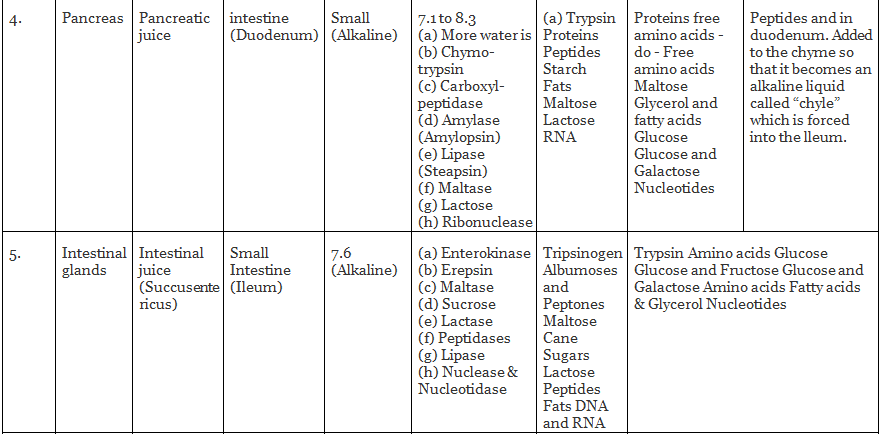
As a result of digestion, protein is broken down to its monomer amino acids; carbohydrates into monosaccharide glucose, fructose and galactose; and fats into fatty acids and glycerol. These end-products of digestion are finally absorbed in the wall of the small intestine.
Intestine has a vast surface for absorption owing to the presence of numerous finger-like folds of the intestinal wall called “villi”.Amino acids and monosaccharide sugars are easily absorbed and passed directly into the blood capillaries of the villi, and then to the hepatic portal circulation which carries them into the liver. Fatty acids and glycerols do not reach the blood stream, but pass into the lymph capillaries of the villi called “Lacteales”. In lacteales, fats are re-synthesised into small fat molecules called “Chylomicrons”. Lacteales finally pours it into the blood circulation.
Metabolism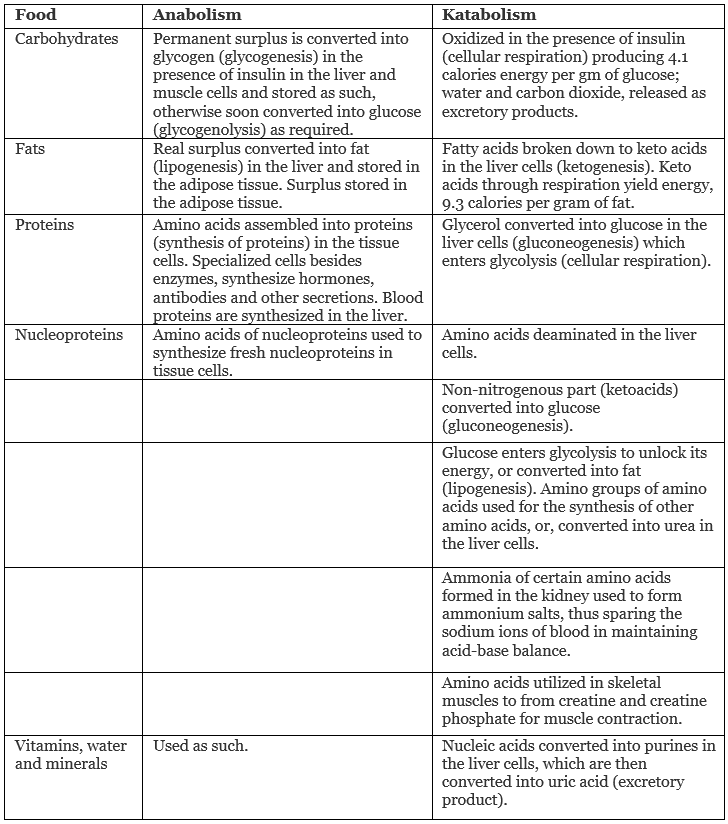
Physiology of Digestion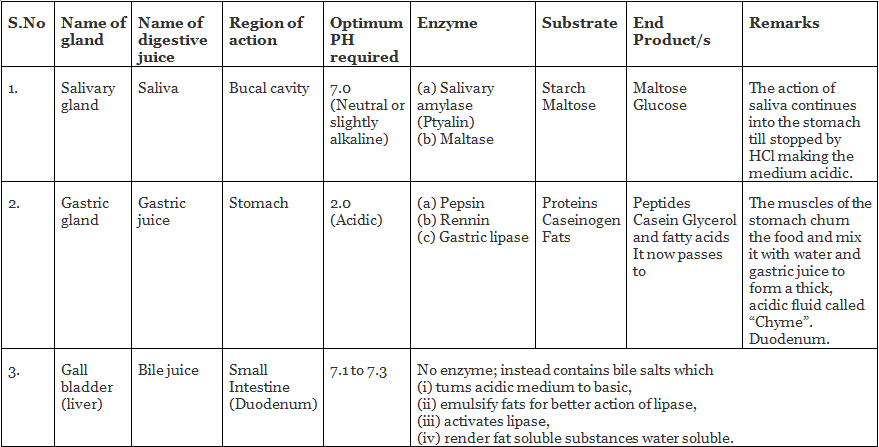
|
137 videos|475 docs|217 tests
|
FAQs on Nutrition, Digestion - Science & Technology for State PSC Exams - BPSC (Bihar)
| 1. What is the role of nutrition in digestion? |  |
| 2. How does the process of digestion work? |  |
| 3. What are the essential nutrients needed for digestion? |  |
| 4. How does poor nutrition affect digestion? |  |
| 5. What are some tips for maintaining good nutrition and digestion? |  |
|
137 videos|475 docs|217 tests
|

|
Explore Courses for BPSC (Bihar) exam
|

|


















