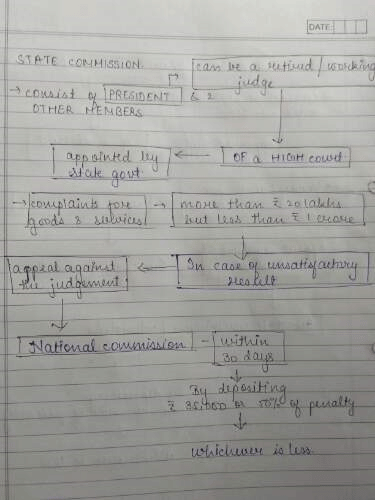
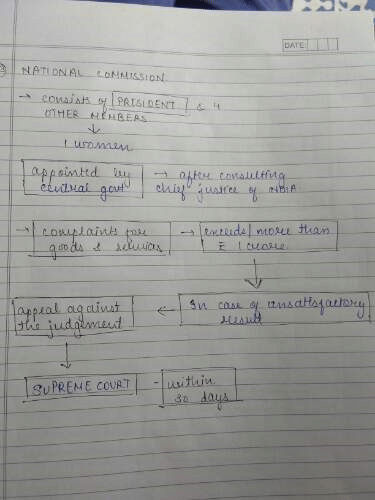
Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Notes > Consumer protection chapter notes business studies class 12 cbse
Consumer protection chapter notes business studies class 12 cbse PDF Download
FAQs on Consumer protection chapter notes business studies class 12 cbse
| 1. What is consumer protection and why is it important? |  |
Ans. Consumer protection refers to the measures taken to safeguard the rights and interests of consumers in the marketplace. It ensures that consumers are protected from unfair trade practices, misleading advertisements, and substandard goods or services. Consumer protection is important because it promotes fair competition, builds consumer trust, and ensures that consumers have access to safe and quality products or services.
| 2. What are the different types of consumer protection laws? |  |
Ans. There are several types of consumer protection laws, including:
- Product Liability Laws: These laws hold manufacturers, distributors, and sellers responsible for any harm caused by defective products.
- Consumer Contract Laws: These laws regulate the terms and conditions of consumer contracts, ensuring they are fair and transparent.
- Advertising Laws: These laws prohibit false or misleading advertisements, ensuring that consumers receive accurate information about products or services.
- Consumer Privacy Laws: These laws protect consumers' personal information from unauthorized use or disclosure.
- Consumer Complaint Laws: These laws establish procedures for consumers to file complaints against businesses and seek remedies for any harm suffered.
| 3. How can consumers protect themselves from fraudulent practices? |  |
Ans. Consumers can protect themselves from fraudulent practices by taking the following measures:
- Research and Compare: Before making a purchase, consumers should research the product or service, compare prices and quality, and read reviews from other consumers.
- Verify the Seller: Consumers should ensure that the seller or business is reputable, has a physical address and contact information, and is licensed if required.
- Read Contracts and Terms: Consumers should carefully read and understand contracts or terms before making a purchase, paying attention to hidden fees, cancellation policies, and warranties.
- Secure Online Transactions: When making online purchases, consumers should only use secure websites, verify the payment gateway's security measures, and avoid sharing sensitive information on unsecured platforms.
- Report Complaints: If consumers encounter fraudulent practices, they should report the incident to the appropriate consumer protection agencies or authorities.
| 4. What are the rights of consumers under consumer protection laws? |  |
Ans. Consumers have several rights under consumer protection laws, including:
- Right to Safety: Consumers have the right to be protected from hazardous products or services that could pose a risk to their health or safety.
- Right to Information: Consumers have the right to receive accurate and complete information about products or services, including their price, quality, ingredients, and potential risks or side effects.
- Right to Choice: Consumers have the right to choose from a variety of products or services at competitive prices, without being subjected to unfair or restrictive practices.
- Right to Redress: Consumers have the right to seek compensation, refunds, or repairs for faulty or substandard products or services.
- Right to Education: Consumers have the right to be educated about their rights and responsibilities, enabling them to make informed decisions in the marketplace.
| 5. How can consumers resolve disputes with businesses? |  |
Ans. Consumers can resolve disputes with businesses by following these steps:
- Contact the Business: Consumers should first contact the business directly to express their concerns and attempt to resolve the issue.
- File a Complaint: If the business does not provide a satisfactory resolution, consumers can file a complaint with the appropriate consumer protection agency or ombudsman.
- Seek Mediation or Arbitration: Consumers can opt for mediation or arbitration services, where an impartial third party helps facilitate a resolution between the consumer and the business.
- Take Legal Action: If all other methods fail, consumers can consider taking legal action by filing a lawsuit against the business in a civil court. It is advisable to consult with a lawyer before pursuing this option.
Related Searches