Concept & Functions - Human Resource Management | Human Resource Management - B Com PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| Introduction |

|
| Concept of HRM |

|
| Objectives of HRM |

|
| Human Resource Functions |

|
Introduction
Human resource management (HRM) involves managing people in an organization based on four key principles:
- Importance of Human Resources: Human resources are the most valuable assets of an organization, and their effective management is crucial for success.
- Alignment with Corporate Objectives: HR policies and procedures should be closely linked to and contribute significantly to the achievement of corporate objectives and strategic plans.
- Influence of Corporate Culture: Corporate culture, along with values, organizational climate, and managerial behavior, greatly impacts organizational excellence. Therefore, this culture needs to be managed, which may involve changing or reinforcing organizational values and ensuring their acceptance and adherence through continuous effort from the top management.
- Integration and Involvement: HRM focuses on integrating all members of the organization and fostering a sense of common purpose among them.
Concept of HRM
Human Resource Management (HRM) is a strategic approach to managing an organization’s most valuable asset – its people. It involves the acquisition, motivation, development, and management of human resources in a way that aligns with the organization’s goals and core values.
Proactive Approach
- HRM is proactive, meaning it anticipates future needs and challenges rather than just reacting to them. This involves planning for recruitment, training, and employee relations before issues arise.
Techniques and Functions
- HRM includes familiar functions like manpower planning, selection, performance appraisal, salary administration, training, and management development.
- Additionally, it involves special programs aimed at improving communication, employee involvement, commitment, and productivity within the organization.
Three Meanings of HRM
- Valuable Source. Employees are seen as a valuable resource that requires investment in their development.
- Human Resources. Recognizes that employees have unique characteristics and cannot be treated like material resources. This approach emphasizes humanizing organizational life and incorporating human values.
- Social Realities. Focuses on social units and processes within the organization, such as job roles, team dynamics, and inter-team processes.
Qualitative Improvement
- HRM is about enhancing the quality of human resources, who are considered the most valuable assets of an organization. People are the sources, resources, and end-users of all products and services.
Evolution from Personnel Management
- While HRM has evolved from personnel management and behavioral science, it is more comprehensive and multidisciplinary. It is a scientific process aimed at continuously improving employees’ competencies and capabilities to meet present and future organizational goals.
Production Model Approach
- HRM is seen as a production model that maximizes individual skills and motivation through consultation with the workforce. This approach aims to produce high levels of commitment to company strategic goals.
- HRM is not just about ‘people practices’ but involves managing work and people in the organization. It includes both individual and collective dimensions of management.
Traditional vs. Strategic HRM
- Traditional personnel management is non-strategic and reactive, focusing on low-level employees and unionized workers. In contrast, HRM is preventive and strategic, with an emphasis on developing people and their competencies.
- HRM integrates various subsystems like performance appraisal, training, organization development, and employee welfare in a meaningful way.
Assumptions of HRM
- HRM is based on the assumption that employees are reservoirs of untapped resources that can be developed.
- Development is seen as self-development rather than something imposed from outside.
The organization also evolves with the overall benefits along with the growth of its members.
The organization further fosters a culture that prioritizes harmonious superior-subordinate relationships, teamwork, collaboration among different groups, open communication, and, above all, the integration of organizational goals with employee needs.
Top management takes the initiative for HRM, formulates necessary plans and strategies, and creates an overall climate and support for its implementation.
The management of human resources is more of an art than a science. In practice, it is an “art” full of pitfalls, judgment calls, and learning from past mistakes.
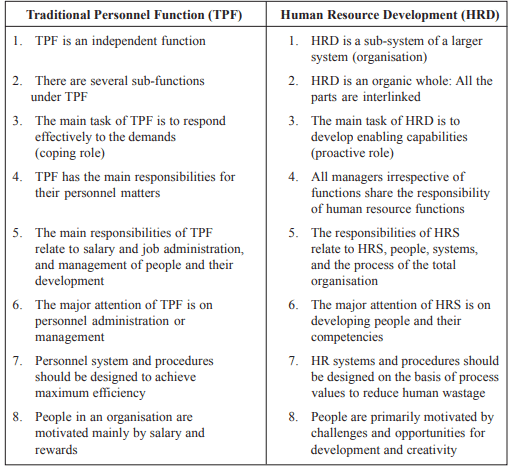
Some Basic Assumptions Underlying Traditional Personnel Function and Human Resources System
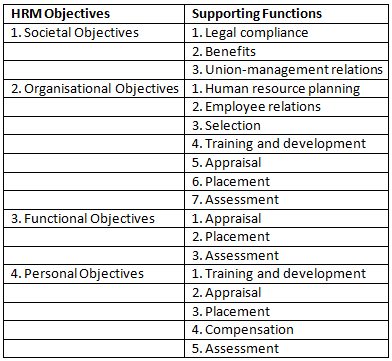
Objectives of HRM
The main goal of Human Resource Management (HRM) is to make sure that an organization has a skilled and willing workforce. However, there are other important objectives as well. HRM objectives can be categorized into four types: societal, organizational, functional, and personal.
Societal Objectives
- Societal objectives focus on being socially and ethically responsible to the needs and challenges of society.
- HRM aims to minimize the negative impact of societal demands on the organization while addressing these needs.
- Organizations that fail to use their resources for society's benefit in ethical ways may face restrictions, such as laws enforcing reservation in hiring and addressing discrimination and safety concerns.
Organizational Objectives
- Organizational objectives acknowledge the role of HRM in enhancing organizational effectiveness.
- HRM is not an end in itself but a means to help the organization achieve its primary goals.
- The human resource department exists to serve the rest of the organization and contribute to its success.
Functional Objectives
- Functional objectives aim to maintain the HR department's contribution at a level suitable for the organization's needs.
- HRM practices should be adjusted to meet the specific demands of the organization.
- The level of service provided by the HR department must be tailored to fit the organization it serves.
Personal Objectives
- Personal objectives focus on helping employees achieve their personal goals, as long as these goals enhance their contribution to the organization.
- Meeting employees' personal objectives is crucial for their retention, motivation, and performance.
- If personal objectives are not met, employee satisfaction may decline, leading to higher turnover rates.
HRM Objectives and Functions
Human Resource Functions
Human resource management plays a crucial role in planning, developing, and implementing policies and programs to effectively utilize an organization’s human resources. It focuses on the people at work and their relationships within the organization. The objectives of human resource management are to ensure the effective use of human resources, foster positive working relationships among all members, and promote maximum individual development.
The major functional areas in human resource management include:
Planning: This involves determining the number and type of employees needed to achieve organizational goals. Research is essential for forecasting human resource supplies and predicting future needs. The basic strategy is staffing and employee development.
Staffing: This area focuses on recruiting and selecting human resources for the organization. It includes attracting qualified applicants and selecting the most suitable candidates for positions.
Employee Development: This function provides employees with the necessary skills and knowledge to perform their jobs effectively. It includes training programs for new and experienced employees, as well as development programs for higher-level responsibilities.
Employee Maintenance: This involves ensuring employee satisfaction and retention through various programs and policies.
Human Resource Planning
- Human Resource Planning involves determining the number and type of employees needed to achieve organizational goals. This function requires research to collect and analyze information for forecasting human resource supplies and predicting future needs. The basic strategy includes staffing and employee development.
Job Analysis
- Job Analysis is the process of describing the nature of a job and specifying the human requirements, such as skills and experience needed to perform it. The outcome of job analysis is a job description, which outlines work duties and activities. Job descriptions are crucial for personnel programs and practices as job content significantly influences them.
Staffing
- Staffing focuses on recruiting and selecting human resources for an organization. It involves attracting qualified applicants and selecting the most suitable candidates for positions. Human resource planning and recruiting precede the selection process.
Orientation
- Orientation is the initial step in helping a new employee adjust to their job and the organization. It familiarizes new employees with aspects such as pay and benefit programs, working hours, and company rules and expectations.
Training and Development
- Training and Development provide employees with the skills and knowledge necessary to perform their jobs effectively. Organizations often offer training programs for experienced employees whose jobs are undergoing changes. Development programs prepare employees for higher-level responsibilities within the organization.
Performance Appraisal
- Performance Appraisal monitors employee performance to ensure it meets acceptable levels. Human resource professionals develop and administer performance appraisal systems, while supervisors and managers are responsible for the actual appraisal. Performance appraisal information is crucial for pay, promotion, and disciplinary actions, as well as for employee development through feedback.
Career Planning
- Career Planning involves assessing an individual employee’s potential for growth and advancement within the organization. It has emerged from employees’ desire to grow in their jobs and advance in their careers.
Compensation
- The human resource personnel determine how much employees should be paid for performing certain jobs. Pay is obviously related to the maintenance of human resources.
- Since compensation is a major cost to many organisations, it is a major consideration in human resource planning. Compensation affects staffing in that people are generally attracted to organisations offering a higher level of pay in exchange for the work performed.
Benefits
- Benefits are another form of compensation to employees other than direct pay for work performed.
- The human resource function of administering employee benefits shares many characteristics of the compensation function.
- Benefits include both the legally required items and those offered at the employer’s discretion.
- The cost of benefits has risen to such a point that they have become a major consideration in human resources planning.
- However, benefits are primarily related to the maintenance area, since they provide for many basic employee needs.
Labour Relations
- Labour relations refer to interaction with employees who are represented by a trade union.
- Unions are organisations of employees who join together to obtain more voice in decisions affecting wages, benefits, working conditions, and other aspects of employment.
- With regard to labour relations, the personnel responsibility primarily involves negotiating with the unions regarding wages, service conditions, and resolving disputes and grievances.
Record-keeping
A key part of human resource management is keeping employee records. This means collecting, storing, and finding different types of information about employees for various reasons.
Essential documents include:
- Application forms
- Health and medical history
- Job history (such as roles held, promotions, transfers, and layoffs)
- Seniority lists
- Earnings
- Hours worked
- Attendance
- Turnover rates
- Tardiness
- Other relevant information
Importance of Current Records: Keeping detailed and updated employee records is vital for many HR activities.
Employee Interest: Nowadays, employees want to know about their records. They often ask what information is included, why certain details are mentioned, and why some records are not up to date.
Key Functions of Personnel Records:These records serve several important purposes:
- They keep precise and current information about employees.
- They help in making decisions about employees, especially in comparison to others.
- They support recruitment by showing salary ranges for similar positions.
- They act as a historical log of actions taken regarding employees.
- They provide data for statistics that inform HR policies.
- They help fulfill legal and regulatory obligations.
Personnel Research:
- Research is an important part of human resource management.
- The aim of HR research is to collect facts and information to create and maintain effective programs.
- Running a successful HR program requires careful planning at the start and regular reviews afterwards.
- Research is necessary in different HR areas, such as:
- Recruitment
- Employee turnover
- Terminations
- Training
- Employee views on topics like wages, promotions, working conditions, and job security can be gathered through surveys.
- Even though it is very important, HR research is often ignored because HR workers are busy with urgent tasks.
- However, research should not just focus on solving immediate issues; it is also about preventing future problems.
- The HR department is in charge of research, but it should also include input from management at all levels, including supervisors.
- Help from trade unions and other organizations can be useful if used appropriately.
- Today's HR professionals also have to handle:
- Organizational change
- New technologies
- Innovation
- Diversity
- HR is now affected by ideas from many different organizations, not just one.
- Regular social audits of HR practices are becoming very important.
- The role of HR professionals is broad and requires a deep understanding of how the organization operates.
- A main goal for HR is to build a strong connection between employees and the organization since employee commitment is vital.
- One key responsibility of HR is to inform employees about changes and challenges in the organization and in the wider world.
- Employees should be kept updated on important business news, such as:
- Financial performance
- Growth plans
- Organizational restructuring
- HR professionals should share this information through different methods, including:
- Booklets
- Video materials
- Talks
Primary Responsibilities of an HR Manager:
- Gain a thorough understanding of the corporate culture, plans, and policies.
- Act as an internal consultant and change agent.
- Facilitate change and contribute to company strategy.
- Ensure open communication within the HR function and with individuals and groups both inside and outside the organization.
- Develop HR strategies that align with business goals.
- Foster team development and cooperation across the organization.
- Align human resources and work to achieve organizational objectives.
- Diagnose HR-related issues and implement appropriate solutions.
- Coordinate and support HR programs and services.
- Assess the impact of HR interventions on individual and organizational performance.
Pat McLegan’s Nine New Roles of HR Practitioners:
- Highlight issues related to internal and external workforce trends, and recommend strategies for long-term organizational excellence.
- Design HR systems and actions that maximize organizational performance.
- Facilitate the development of strategies that align with the organization's values and vision.
- Ensure smooth delivery of products and services to customers by effectively using resources and fostering commitment among employees, both within and outside the organization.
- Identify learning needs and create programs that accelerate individual and group learning.
- Help individuals adapt to new situations and support the transition to participative leadership models.
- Assist individuals in assessing their competencies, values, and goals to implement personal development plans.
- Enable individuals to add value in the workplace through interventions and skills that promote and sustain change.
- Assess the effectiveness of HR programs and communicate results to accelerate change and development within the organization.
Dave Ulrich’s Four Roles of HR:
- Strategic partner – transforming strategy into results by building value-creating organizations.
- Change agent – facilitating rapid change and innovation.
- Employee champion – managing talent and intellectual capital.
- Administrative expert – improving processes to enhance efficiency and reduce costs.
Human Resource Management has evolved significantly, and its role has expanded in modern organizations. Moving from traditional personnel management to HRM, many organizations have begun to focus on the totality of the company. HRM aims not only to improve productivity but also to enhance the quality of life for employees. It focuses on maximizing human resource development while contributing to broader socio-economic growth.
|
69 docs|25 tests
|
FAQs on Concept & Functions - Human Resource Management - Human Resource Management - B Com
| 1. What is Human Resource Management? |  |
| 2. What are the functions of Human Resource Management? |  |
| 3. What are the benefits of Human Resource Management? |  |
| 4. What skills are required for Human Resource Management? |  |
| 5. What are the different types of Human Resource Management? |  |
















