Introduction: Analogy | Reasoning Aptitude for Competitive Examinations - Bank Exams PDF Download
| Table of contents |

|
| What is Analogy? |

|
| Analogy Types |

|
| Tips and Tricks to Solve Analogies |

|
| Solved Examples |

|
Analogy questions in competitive exams assess logical reasoning, problem-solving, and cognitive abilities. They demand the identification of patterns and relationships, promoting analytical thinking. These questions gauge both verbal and non-verbal reasoning skills, making the topic integral to competitive exam preparation. Mastering analogies not only aids in exam performance but also nurtures essential skills applicable in various professional scenarios.
What is Analogy?
An analogy is like a tool that helps explain how different things or ideas are similar or connected to each other.
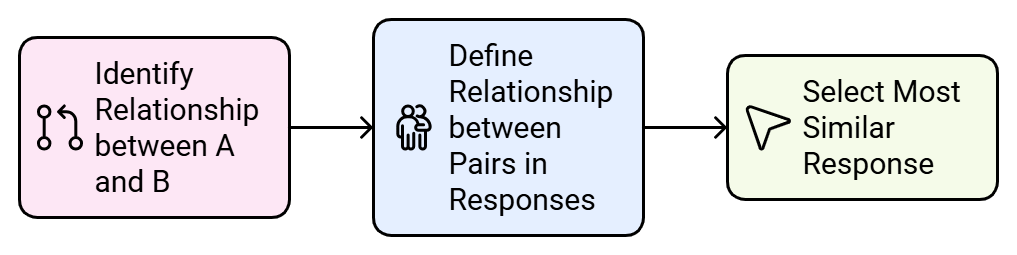
- Questions of this type examine your ability to precisely define a connection or relationship between two words and to recognize the similarity between two relationships.
- First, define the relationship between the two words in bold type. Then, define the relationship between the pairs of words in each of the possible responses and choose the response in which the relationship is most similar to the relationship between the two words in bold.
- In this type of question, two objects related in some way are given, and a third object is also given with four or five alternatives.
- You have to find out which one of the alternatives bears the same relation with the third object as the first and second objects are related.
Analogy Types
The analogy is an important topic of reasoning that comes under the logical reasoning section. It has many types and the questions will be formed in all such types. The types of analogy are mentioned below.
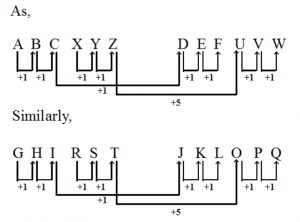
1. Letter/Word-Based Analogy
- In this type of analogy, a pair of letters or words are given and has certain fixed logical similarities between them.
- As per this pair relationship, another pair of letters or words is also formed in which one word or letter is given, and we need to find an unknown letter or word that comes there as per the logical relation following in the first pair.
- It contains questions based on the position of letters, opposite letters, synonyms and antonyms of words, etc.
- The candidates need to understand the logic followed in the first given pair and then find the next pair following the same logic.
- Example
D : F: : R:?
In D and F, there is a difference of two, then the unknown letter will be T. Now the series will be D : F: : R: T
2. Number-Based Analogy
- In this type of analogy, a pair of numbers is given which is related in a certain manner, and we need to find the unknown number following the same logic followed in the given pair.
- The questions will be formed in a number-based analogy based on the basic mathematical operations of numbers like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division.
- Apart from this, the questions are also formed based on squares and cubes of numbers, etc.
- Example:
5 : 25 : : 7 : ?
52 = 25 then 72 = 49
2 : 8 : : 6 : ?
23 = 8 then 63 = 216
3. Letters/Words and Number-Based Analogy (Mixed Analogy)
- In this type of analogy, the questions will be formed on both words/letters and numbers. It is also known as a mixed analogy.
- The candidate first needs to understand the relation of logic by which letters or words and numbers are related to each other and follow the same logic, the unknown number and letters or words need to be found.
- Example:
B2D5 : C4E25 : : F5H9 : ?
B+1 = C, 22 = 2, D+1 = E, 52 = 25
i.e. B2D5 = C4E25 then
F+1 = G, 52 = 25, H+1 = I, 92 = 81
Then, F5H9 = G25I81
4. Image-Based Analogy
- In this type of analogy figures and images are given and have certain similarities between them.
- The candidates need to mark the logic followed in the given pair of images and predict the new unknown image using this logic.
- The questions will be formed on mirror images, water images, and rotation of figures in clockwise and anti-clockwise directions. The candidates need to answer the resultant figure based on the relationship or logic followed in the given pair.
- Example:
Select a suitable figure from the Answer Figures that would replace the question mark (?).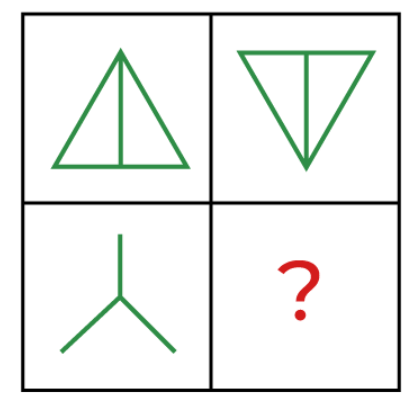
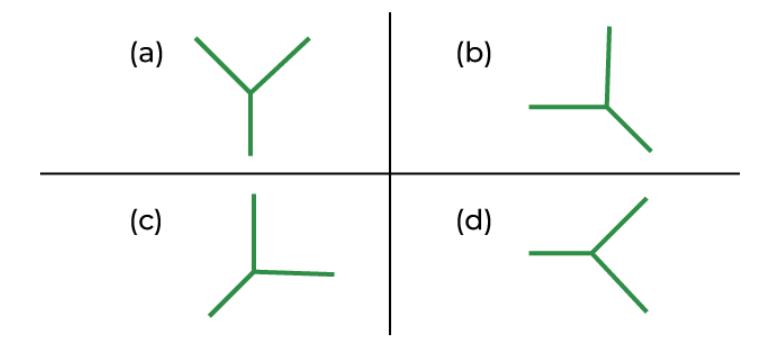
Answer: Option A
Solution: We can see that in the first row, the second image is vertically opposite of the first image. Hence, even in the second row, we will follow the same rule.
5. Miscellaneous Analogy
- In this type of analogy, the questions will be formed on any logic or relationship.
- In this type, the questions are asked from any subject or section like General Knowledge, General Awareness, Current Affairs, Science and Technology, Mathematics, etc.
The candidates must know all these sections well to answer these questions. It requires more and more practice. - Example:
Force : Newton : : Current : ___
SI unit of Force is Newton similarly SI unit of Current is Ampere
Tips and Tricks to Solve Analogies
- The study of analogy is simple. It falls into neat, distinguishable patterns. Thus, it can be learned. Try to decipher these patterns quickly.
- Gain familiarity with the patterns that analogies’ questions exhibit over and over again. This will help you identify the trap. Consequently, you will be able to increasingly develop your ability to solve analogy’ questions quickly.
- Remember that while solving an analogy question, you must look for the precise relationship that the pair of words share in the question.
- If you cannot find an exact match of the relationship in the pairs of words, then the relationship you have formed between the pair of words is inaccurate. That is because analogies involve an exactness and precision to their solving.
- It is also extremely important to substitute the pair of words into your sentence in the same order as they are given in. For instance, “artist creates a painting” is correct and “a painting created by an artist” is incorrect.
Solved Examples
Example 1: baker : eating -
(a) surgeon : anesthesia
(b) author : reading
(c) gardener : watering
(d) policeman : enforcement
Ans: (b)
Sol: The relationship between the words in bold type: eating is an activity involving the product of the baker's work. Response (b) has the same relationship: reading is an activity involving the product of the author's work. The other responses are incorrect: anesthesia is a stage that precedes a surgeon's work. Watering is one of the jobs of a gardener. Enforcement is the objective of the policeman's work.
Example 2: to shutter : is closed -
(a) to explain : is understood
(b) to estimate : is exact
(c) to believe : is correct
(d) to permit : is forbidden
Ans: (a)
Sol: The relationship between the words in bold type: to shutter something causes it to be closed. Response (a) contains the same relationship: to explain something causes it to be understood. The other responses are incorrect: to estimate is to make an approximate calculation of something's worth, not an exact one; to believe something is to think that it is correct; to permit something means to declare that it is not forbidden.
Example 3: deck : fleet -
(a) ruler : country
(b) roof : neighborhood
(c) clothespin : laundry
(d) player : team
Ans: (b)
Sol: The relationship between the words in bold type: a deck is the upper part of a ship, and a group of ships makes up a fleet. Response (b) contains the same relationship: a roof is the upper part of a house, and a group of houses makes up a neighborhood. The other responses are incorrect: a ruler is someone who rules over a country. A clothespin is a means for hanging laundry on a clothesline. A player may be part of a team.
Example 4: warn : wariness -
(a) distort : truth
(b) provoke : anger
(c) know : proficiency
(d) dissuade : action
Ans: (b)
Sol: The relationship between the words in bold type: to warn means to do something that produces wariness in someone else. Response (2) contains the same relationship: to provoke means to do something that produces anger in someone else. The other responses are incorrect: to distort means to twist the truth. To know means to have proficiency. To dissuade means to cause someone to refrain from a particular action.
Example 5: Curd : Milk :: Shoe : ?
(a) Leather
(b) Cloth
(c) Jute
(d) Silver
Ans: (a)
Sol: As curd is made from milk similarly shoe is made from leather.
Example 6: Calf : Piglet :: Shed : ?
(a) Prison
(b) Nest
(c) Pigsty
(d) Den
Ans: (c)
Sol: Calf is the young one of a cow, and piglet is the young of a pig.. Shed is the dwelling place of cow. Similarly Pigsty is the dwelling place of pig.
Example 7: Malaria : Mosquito :: ? : ?
(a) Poison : Death
(b) Cholera : Water
(c) Rat : Plague
(d) Medicine : Disease
Ans: (b)
Sol: As malaria is caused due to mosquito similarly cholera is caused due to water.
Example 8: ABC : ZYX :: CBA : ?
(a) XYZ
(b) BCA
(c) YZX
(d) ZXY
Ans: (a)
Sol: CBA is the reverse of ABC similarly XYZ is the reverse of ZYX.
Example 9: 4 : 18 :: 6 : ?
(a) 32
(b) 38
(c) 11
(d) 37
Ans: (b)
Sol: As, (4)2 + 2 =18
Similarly, (6)2 + 2 = 38.
Example 10: Chill : Freeze
(a) Slice : Cut
(b) Simmer : Boil
(c) Roast : Stew
(d) Cook : Fry
Ans: (b)
Sol: In this problem, the student is expected to spot the relationship that Chill is a lower degree than Freeze and Simmer and Boil are similarly related as Simmer is a lower degree than Boil. The answer thus is option (b).
|
72 videos|112 docs|113 tests
|
FAQs on Introduction: Analogy - Reasoning Aptitude for Competitive Examinations - Bank Exams
| 1. What is the definition of analogy? |  |
| 2. What are the different types of analogies? |  |
| 3. How can I approach solving analogies in exams? |  |
| 4. What tips and tricks can help me solve analogies more effectively? |  |
| 5. Can you provide an example of a solved analogy? |  |