Class 9 Exam > Class 9 Notes > Science Class 9 > Short Notes - Force and Laws of Motion
Force and Laws of Motion Class 9 Notes Science Chapter 8
- Force: It is a push or pull on an object that produces acceleration in the body on which it acts. S.I. unit of force is Newton.
- A force can do three things on a body.
(a)It can change the speed of a body.
(b)It can change the direction of motion of a body.
(c)It can change the shape and size of a body. - Balanced forces: Forces are said to be balanced forces if they nullify one another and their resultant force is zero.
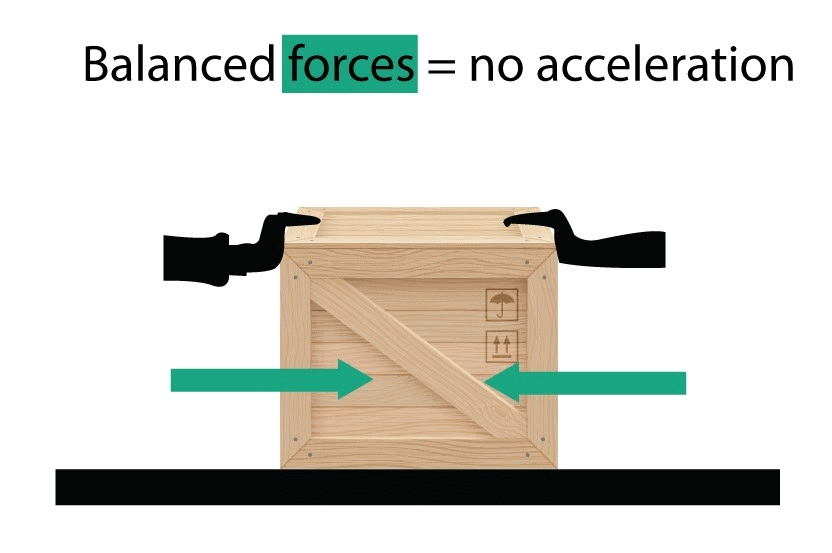
- Unbalanced forces: When two opposite forces acting on a body, move a body in the direction of the greater force or forces which brings motion in a body are called as unbalanced forces.
- First law of motion: An object remains in a state of rest or of uniform motion in a straight line unless acted upon by an external unbalanced force.
Question for Short Notes - Force and Laws of MotionTry yourself: Which of the following is NOT a possible effect of a force acting on an object?View Solution
- Inertia: The natural tendency of an object to resist a change in its state of rest or of uniform motion is called inertia.
The mass of an object is a measure of its inertia.
Its S.I. unit is kg.
A body with greater mass has greater inertia. - Frictional force: The force that always opposes the motion of objects is called force of friction.
- Second law of motion: The rate of change of momentum of an object is proportional to the applied unbalanced force in the direction of the force.
Mathematically, - Momentum: The momentum of an object is the product of its mass and velocity and has the same direction as that of the velocity. Its S.I. unit is kg m/s.
(p = mv )
1 Newton: A force of one Newton produces an acceleration of 1 m/s2 on an object of mass 1kg.
1N = 1 kg m/s2
(F = ma) - Third law of motion: To every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction and they act on two different bodies.
The document Force and Laws of Motion Class 9 Notes Science Chapter 8 is a part of the Class 9 Course Science Class 9.
All you need of Class 9 at this link: Class 9
|
84 videos|478 docs|60 tests
|
FAQs on Force and Laws of Motion Class 9 Notes Science Chapter 8
| 1. What is Newton's First Law of Motion? |  |
Ans. Newton's First Law of Motion states that an object at rest will remain at rest, and an object in motion will continue to move in a straight line at constant speed unless acted upon by an unbalanced external force. This law is often referred to as the law of inertia.
| 2. How do forces act in pairs according to Newton's Third Law of Motion? |  |
Ans. According to Newton's Third Law of Motion, for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. This means that when one object exerts a force on another object, the second object exerts a force of equal magnitude but in the opposite direction on the first object.
| 3. What is the formula for calculating force, and what does each term represent? |  |
Ans. The formula for calculating force is F = m × a, where F represents force measured in Newtons (N), m represents mass measured in kilograms (kg), and a represents acceleration measured in meters per second squared (m/s²). This formula shows that force is the product of mass and acceleration.
| 4. What is the significance of the concept of inertia in everyday life? |  |
Ans. The concept of inertia explains why objects tend to resist changes in their state of motion. For example, when a car suddenly stops, passengers lurch forward due to inertia. This principle is crucial for understanding safety measures in vehicles, such as seat belts, which help to counteract the effects of inertia during sudden stops.
| 5. How do balanced and unbalanced forces affect motion? |  |
Ans. Balanced forces do not change the motion of an object; they result in a net force of zero, meaning the object remains at rest or moves at a constant speed. Unbalanced forces, on the other hand, result in a net force that causes an object to accelerate, changing its speed or direction of motion.
Related Searches

















