NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 - Triangles (Exercise 7.3)
Q1. ∆ ABC and ∆ DBC are two isosceles triangles on the same base BC and vertices A and D are on the same side of BC (see Fig). If AD is extended to intersect BC at P, show that
(i) ΔABD ≅ ΔACD
(ii) ΔABP ≅ ΔACP
(iii) AP bisects ∠A as well as ∠D.
(iv) AP is the perpendicular bisector of BC.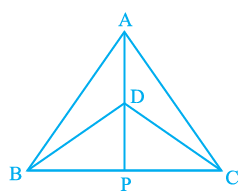
Ans: In the above question, it is given that ΔABC and ΔDBC are two isosceles triangles.
(i) ΔABD and ΔACD are similar by SSS congruency because:
AD = AD (It is the common arm)
AB = AC (Since ΔABC is isosceles)
BD = CD (Since ΔDBC is isosceles)
∴ ΔABD ≅ ΔACD.
(ii) ΔABP and ΔACP are similar as:
AP = AP (It is the common side)
∠PAB = ∠PAC (by CPCT since ΔABD ≅ ΔACD)
AB = AC (Since ΔABC is isosceles)
So, ΔABP ≅ ΔACP by SAS congruency condition.
(iii) ∠PAB = ∠PAC by CPCT as ΔABD ≅ ΔACD.
AP bisects ∠A. — (i)
Also, ΔBPD and ΔCPD are similar by SSS congruency as
PD = PD (It is the common side)
BD = CD (Since ΔDBC is isosceles.)
BP = CP (by CPCT as ΔABP ≅ ΔACP)
So, ΔBPD ≅ ΔCPD.
Thus, ∠BDP = ∠CDP by CPCT. — (ii)
Now by comparing (i) and (ii) it can be said that AP bisects ∠A as well as ∠D.
(iv) ∠BPD = ∠CPD (by CPCT as ΔBPD ΔCPD)
and BP = CP — (i)
also,
∠BPD +∠CPD = 180° (Since BC is a straight line.)
⇒ 2∠BPD = 180°
⇒ ∠BPD = 90° —(ii)
Now, from equations (i) and (ii), it can be said that
AP is the perpendicular bisector of BC.
Q2. AD is an altitude of an isosceles triangle ABC in which AB = AC. Show that
(i) AD bisects BC
(ii) AD bisects ∠ A.
Ans: It is given that AD is an altitude and AB = AC. The diagram is as follows: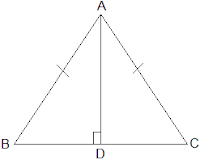
(i) In ΔABD and ΔACD,
∠ADB = ∠ADC = 90°
AB = AC (It is given in the question)
AD = AD (Common arm)
∴ ΔABD ≅ ΔACD by RHS congruence condition.
Now, by the rule of CPCT,
BD = CD.
So, AD bisects BC
(ii) Again, by the rule of CPCT, ∠BAD = ∠CAD
Hence, AD bisects ∠A.
Q3. Two sides AB and BC and median AM of one triangle ABC are respectively equal to sides PQ and QR and median PN of ΔPQR (see Fig). Show that:
(i) ΔABM ≅ ΔPQN
(ii) ΔABC ≅ ΔPQR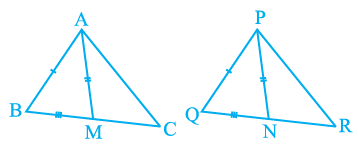
Ans: Given parameters are:
AB = PQ,
BC = QR and
AM = PN
(i) ½ BC = BM and ½ QR = QN (Since AM and PN are medians)
Also, BC = QR
So, ½ BC = ½ QR
⇒ BM = QN
In ΔABM and ΔPQN,
AM = PN and AB = PQ (As given in the question)
BM = QN (Already proved)
∴ ΔABM ≅ ΔPQN by SSS congruency.
(ii) In ΔABC and ΔPQR,
AB = PQ and BC = QR (As given in the question)
∠ABC = ∠PQR (by CPCT)
So, ΔABC ≅ ΔPQR by SAS congruency.
Q4. BE and CF are two equal altitudes of a triangle ABC. Using RHS congruence rule, prove that the triangle ABC is isosceles.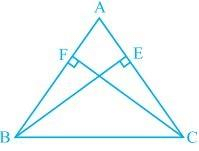
Ans: It is known that BE and CF are two equal altitudes.
Now, in ΔBEC and ΔCFB,
∠BEC = ∠CFB = 90° (Same Altitudes)
BC = CB (Common side)
BE = CF (Common side)
So, ΔBEC ≅ ΔCFB by RHS congruence criterion.
Also, ∠C = ∠B (by CPCT)
Therefore, AB = AC as sides opposite to the equal angles is always equal.
Q5. ABC is an isosceles triangle with AB = AC. Draw AP ⊥ BC to show that ∠ B = ∠ C.
Ans: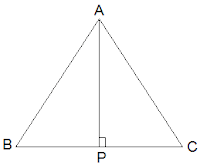
Now, ΔABP and ΔACP are similar by RHS congruency as
∠APB = ∠APC = 90° (AP is altitude)
AB = AC (Given in the question)
AP = AP (Common side)
So, ΔABP ≅ ΔACP.
∴ ∠B = ∠C (by CPCT)
|
276 docs|155 tests
|
FAQs on NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 7 - Triangles (Exercise 7.3)
| 1. What are the properties of a triangle? |  |
| 2. How do you classify triangles based on their angles? |  |
| 3. What is the Pythagorean theorem and how is it used in triangles? |  |
| 4. Can a triangle have two right angles? |  |
| 5. How can we determine if two triangles are similar? |  |






















